14, May 2024
A Comprehensive Guide To The Map Of Africa: Understanding The Continent’s Diverse Landscape
A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Africa: Understanding the Continent’s Diverse Landscape
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Africa: Understanding the Continent’s Diverse Landscape
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Africa: Understanding the Continent’s Diverse Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Africa: Understanding the Continent’s Diverse Landscape

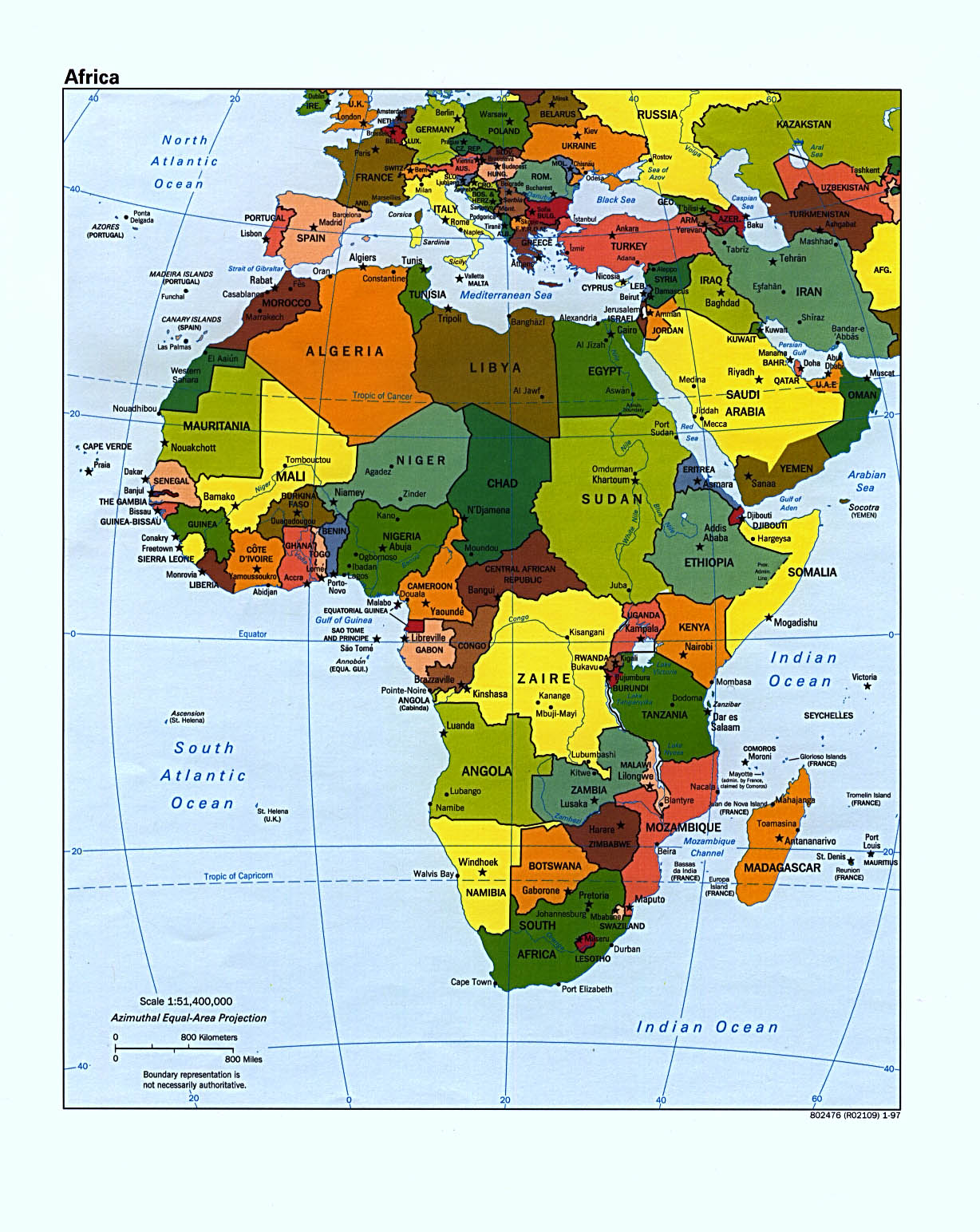
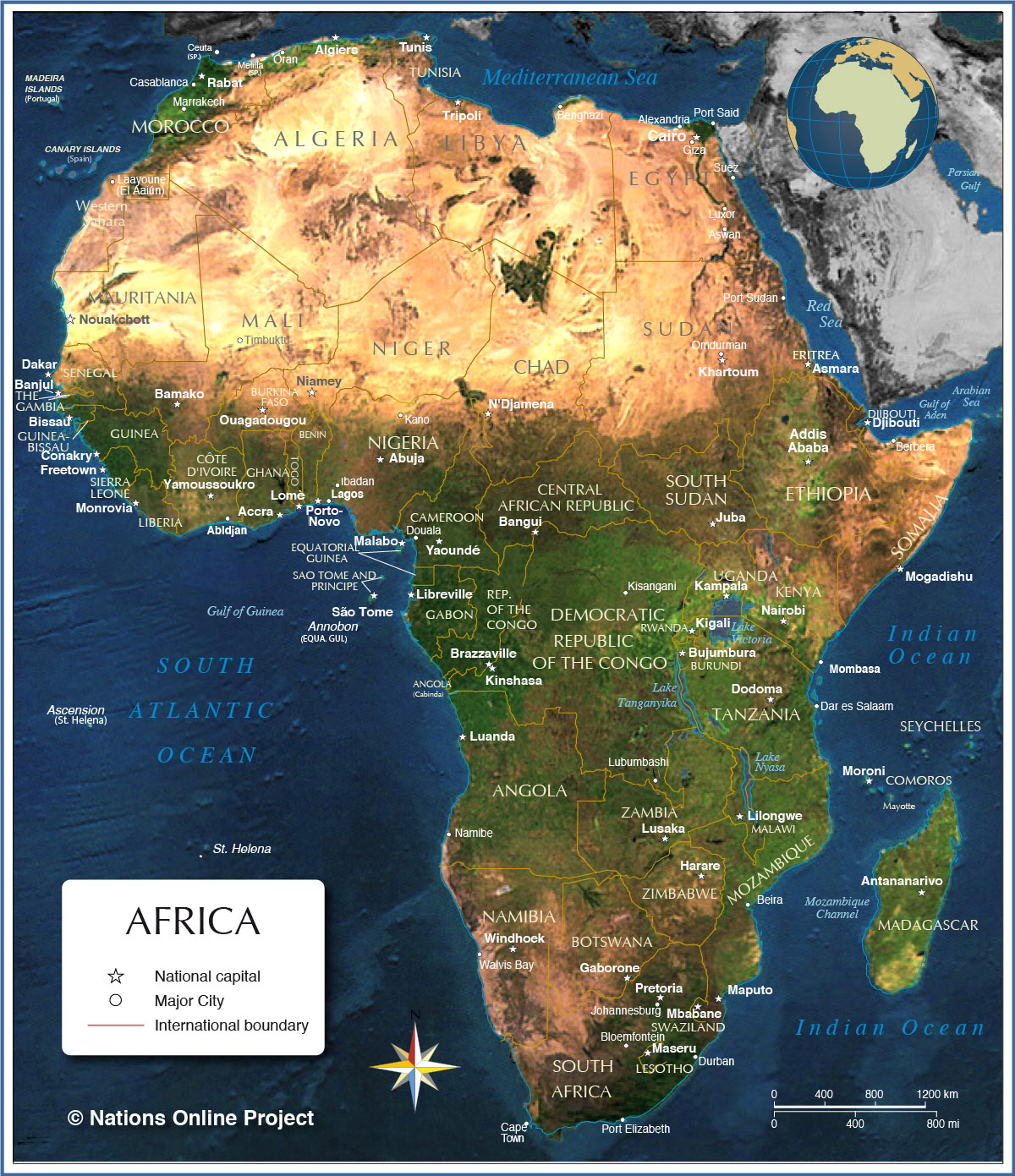
Africa, the second-largest continent in the world, is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, cultures, and histories. Understanding its geography is crucial for appreciating its complexities and appreciating the unique challenges and opportunities facing its nations. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the map of Africa, exploring its diverse features and highlighting the importance of this geographical knowledge.
The Continental Outline:
Africa’s shape, often likened to a giant hand pointing southward, is instantly recognizable. The continent is bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Indian Ocean to the east, and the Southern Ocean to the south. This vast expanse encompasses an area of approximately 30.37 million square kilometers, containing a rich tapestry of biomes, from lush rainforests to arid deserts.
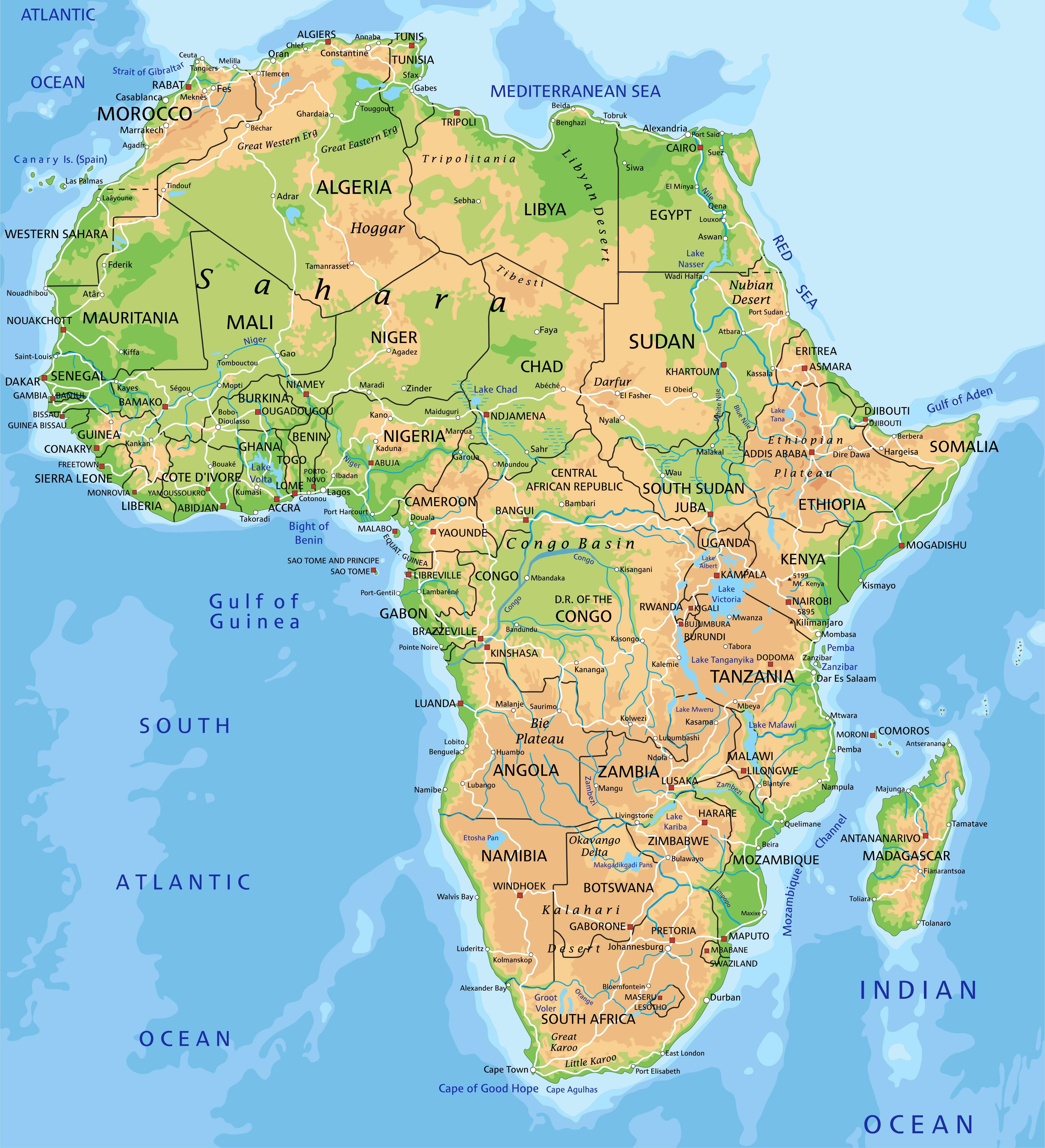
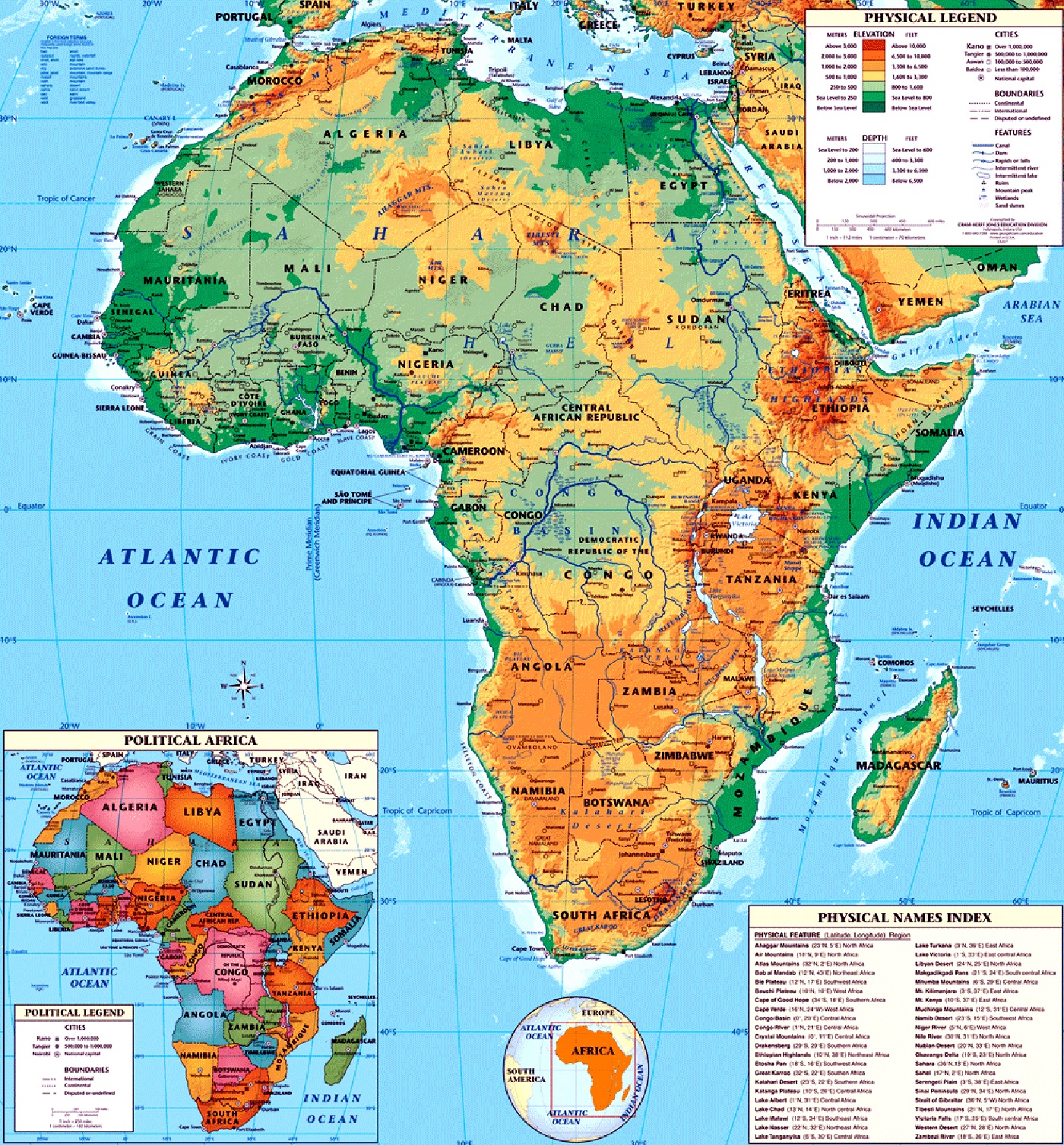
Major Geographical Features:
1. Mountains and Plateaus:
- The Atlas Mountains: Located in North Africa, these mountains form a barrier between the Mediterranean coast and the Sahara Desert.
- The Ethiopian Highlands: This elevated plateau in East Africa is home to the source of the Blue Nile River and boasts diverse ecosystems.
- The Drakensberg Mountains: Stretching along the eastern edge of South Africa, these mountains are known for their dramatic cliffs and scenic beauty.
2. Rivers and Lakes:
- The Nile River: The longest river in the world, the Nile flows through eleven countries, playing a crucial role in agriculture and transportation.
- The Congo River: The second-largest river in Africa, the Congo River is a vital waterway and supports a rich biodiversity.
- Lake Victoria: The largest lake in Africa, Lake Victoria is a vital source of water and sustenance for many communities.
3. Deserts and Savannas:
- The Sahara Desert: The largest hot desert in the world, the Sahara covers a vast area of North Africa, characterized by its arid climate and harsh conditions.
- The Kalahari Desert: Located in southern Africa, the Kalahari is a semi-arid desert with diverse wildlife and unique ecosystems.
- The African Savanna: Covering much of central and southern Africa, the savanna is characterized by grasslands and scattered trees, supporting a vast array of wildlife.
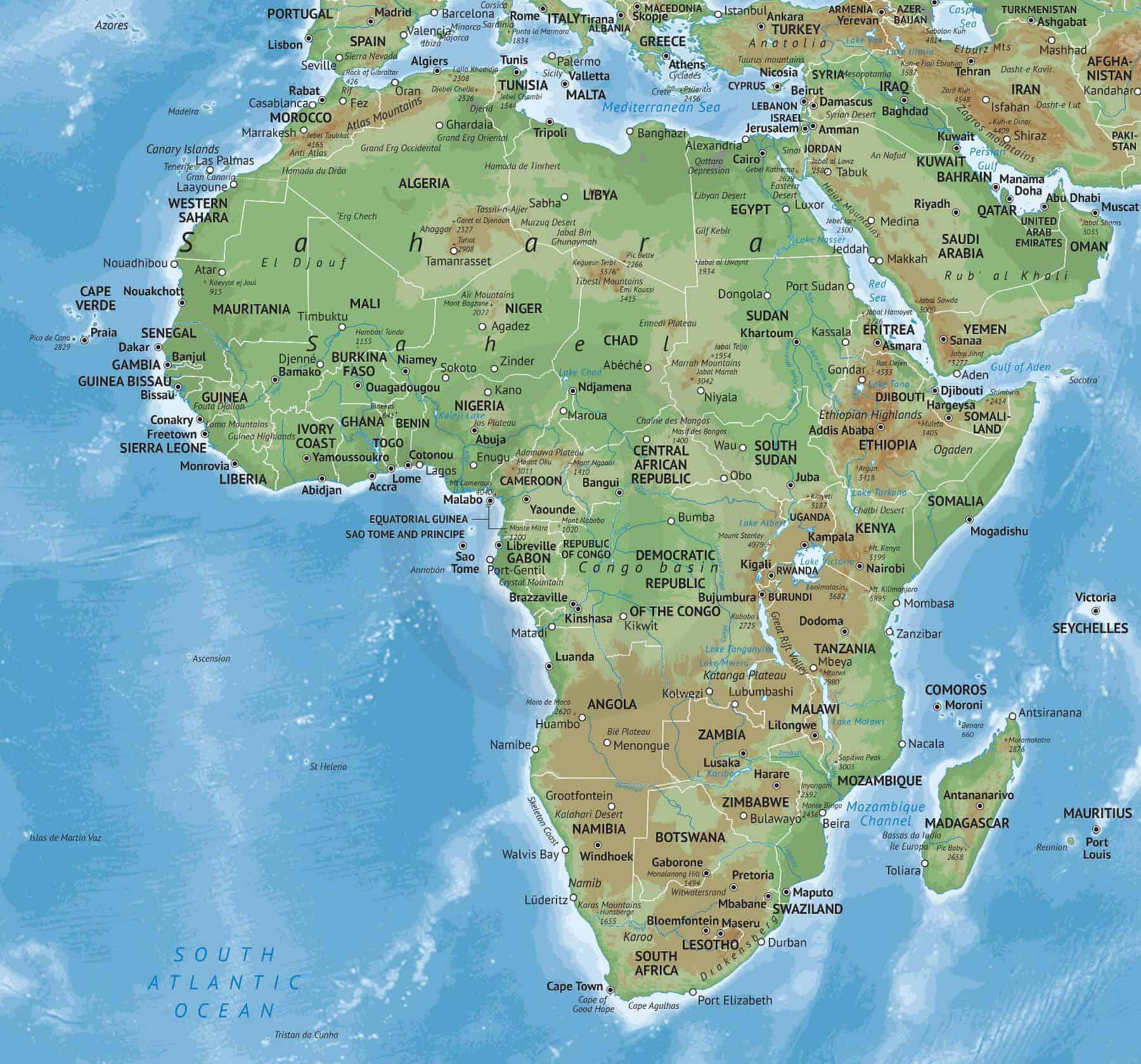
4. Coastal Zones:
- The Mediterranean Coast: This region enjoys a warm, sunny climate and is home to vibrant coastal cities and ancient archaeological sites.
- The Atlantic Coast: With diverse coastal landscapes, the Atlantic coast boasts stunning beaches, mangrove forests, and important fishing grounds.
- The Indian Ocean Coast: This coastline is characterized by its coral reefs, diverse marine life, and vibrant coastal communities.
Understanding the Importance of the Map:
The map of Africa is more than just a geographical representation; it is a vital tool for understanding the continent’s diverse cultures, histories, and challenges.
- Political and Economic Understanding: The map helps visualize the boundaries of African nations, facilitating understanding of their political structures, economic relationships, and regional dynamics.
- Resource Management and Development: Mapping resources like water, minerals, and fertile land is crucial for sustainable development, resource allocation, and environmental conservation.
- Conflict Resolution and Peacebuilding: Understanding the geographical context of conflicts is essential for effective conflict resolution and peacebuilding efforts.
- Cultural Heritage and Tourism: The map highlights the diverse landscapes and cultural heritage of Africa, promoting tourism and fostering appreciation for its unique beauty.
- Climate Change and Environmental Challenges: Mapping climate patterns, deforestation, and resource depletion helps understand the impact of climate change and develop effective mitigation strategies.
Exploring the Map by Country:
This section will delve into the individual countries of Africa, providing a concise overview of their key geographical features, cultural characteristics, and historical significance.
North Africa:
- Egypt: The birthplace of ancient civilization, Egypt is known for its iconic pyramids, the Nile River, and its vast desert landscape.
- Morocco: Situated at the crossroads of Africa and Europe, Morocco boasts a rich cultural heritage, a diverse landscape, and the majestic Atlas Mountains.
- Algeria: The largest country in Africa, Algeria possesses a vast desert landscape, the Saharan Atlas Mountains, and a rich history.
- Tunisia: Located on the Mediterranean coast, Tunisia is known for its ancient Roman ruins, its beautiful beaches, and its vibrant culture.
- Libya: A vast desert country, Libya is rich in oil resources and possesses a diverse landscape, including the Sahara Desert and the Jebel Akhdar mountain range.
West Africa:
- Nigeria: The most populous country in Africa, Nigeria is known for its diverse cultures, its oil wealth, and its bustling cities.
- Ghana: A nation rich in history and culture, Ghana is known for its role in the transatlantic slave trade, its vibrant music and dance traditions, and its cocoa production.
- Senegal: Located on the Atlantic coast, Senegal is known for its beautiful beaches, its vibrant music and dance culture, and its rich history.
- Mali: A landlocked country with a rich cultural heritage, Mali is known for its desert landscapes, its ancient cities, and its traditional music.
- Côte d’Ivoire: Located on the Atlantic coast, Côte d’Ivoire is known for its diverse landscapes, its cocoa production, and its vibrant culture.
Central Africa:
- Democratic Republic of the Congo: Home to the Congo River and a vast rainforest, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is rich in natural resources and biodiversity.
- Republic of the Congo: Located on the Atlantic coast, the Republic of the Congo is known for its oil resources, its rainforest ecosystems, and its diverse wildlife.
- Cameroon: A country with diverse landscapes, Cameroon is known for its rainforest, its mountains, and its vibrant culture.
- Gabon: Located on the Atlantic coast, Gabon is known for its rich biodiversity, its rainforest ecosystems, and its oil resources.
- Central African Republic: A landlocked country with a diverse landscape, the Central African Republic is known for its rainforest, its savanna, and its rich cultural heritage.
East Africa:
- Kenya: Known for its stunning wildlife, its diverse landscapes, and its vibrant culture, Kenya is a popular tourist destination.
- Tanzania: Home to Mount Kilimanjaro, the Serengeti National Park, and Zanzibar, Tanzania is a country of exceptional natural beauty and cultural richness.
- Uganda: Known as the "Pearl of Africa," Uganda is renowned for its diverse wildlife, its beautiful lakes, and its lush rainforest.
- Ethiopia: A country with a rich history and culture, Ethiopia is known for its ancient churches, its unique coffee culture, and its breathtaking landscapes.
- Somalia: Located on the Horn of Africa, Somalia is known for its long coastline, its diverse culture, and its challenging political situation.
Southern Africa:
- South Africa: The most developed country in Africa, South Africa is known for its diverse landscapes, its vibrant culture, and its rich history.
- Botswana: Known for its vast desert landscapes, its abundant wildlife, and its commitment to conservation, Botswana is a popular tourist destination.
- Namibia: A country of dramatic landscapes, Namibia is known for its desert landscapes, its coastal areas, and its diverse wildlife.
- Zimbabwe: A country with a rich history and culture, Zimbabwe is known for its ancient ruins, its diverse wildlife, and its scenic landscapes.
- Mozambique: Located on the Indian Ocean coast, Mozambique is known for its beautiful beaches, its diverse wildlife, and its rich history.
Island Nations:
- Madagascar: The world’s fourth largest island, Madagascar is known for its unique biodiversity, its diverse landscapes, and its rich cultural heritage.
- Seychelles: A group of islands in the Indian Ocean, Seychelles is known for its beautiful beaches, its luxurious resorts, and its diverse marine life.
- Mauritius: An island nation in the Indian Ocean, Mauritius is known for its beautiful beaches, its diverse culture, and its thriving tourism industry.
FAQs about the Map of Africa:
1. What are the major geographical features of Africa?
Africa is a continent of diverse landscapes, including mountains, plateaus, rivers, lakes, deserts, savannas, and coastal zones. Key features include the Atlas Mountains, the Ethiopian Highlands, the Nile River, the Congo River, Lake Victoria, the Sahara Desert, the Kalahari Desert, and the African Savanna.
2. Why is the map of Africa important?
The map of Africa is vital for understanding the continent’s diverse cultures, histories, and challenges. It aids in political and economic understanding, resource management, conflict resolution, cultural heritage preservation, and tackling environmental challenges like climate change.
3. How can I use the map of Africa to learn about its countries?
The map helps visualize the location and boundaries of each country, allowing you to research their individual geographical features, cultural characteristics, historical significance, and current challenges.
4. What are some of the key challenges facing Africa?
Africa faces significant challenges, including poverty, inequality, conflict, climate change, and environmental degradation. Understanding these challenges requires knowledge of the continent’s geography and the unique circumstances of each country.
5. How can I explore the map of Africa further?
Online resources like Google Maps, interactive atlases, and geographical databases offer detailed information about Africa’s geography. You can also consult books, documentaries, and academic journals for in-depth exploration.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Africa:
- Use interactive maps: Explore online resources like Google Maps and interactive atlases to zoom in on specific regions and countries.
- Focus on key features: Pay attention to major geographical features like mountains, rivers, deserts, and coastal zones to understand the continent’s landscape and its impact on human settlements.
- Read about the countries: Research individual countries to learn about their history, culture, economy, and challenges.
- Explore cultural resources: Dive into books, documentaries, and online resources to learn about Africa’s diverse cultures, languages, and traditions.
- Connect geography to current events: Relate geographical information to current events in Africa to gain a deeper understanding of the continent’s complexities.
Conclusion:
The map of Africa is a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s diverse landscapes, cultures, histories, and challenges. It serves as a visual guide to its vastness, highlighting the interconnectedness of its nations and the importance of collaboration in tackling shared challenges. By engaging with the map and exploring the individual countries, we gain a deeper appreciation for Africa’s rich tapestry and the vital role it plays in the global landscape.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Africa: Understanding the Continent’s Diverse Landscape. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
