7, Jun 2024
A Geographic Exploration Of Africa And Its Surrounding Territories
A Geographic Exploration of Africa and Its Surrounding Territories
Related Articles: A Geographic Exploration of Africa and Its Surrounding Territories
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Exploration of Africa and Its Surrounding Territories. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Exploration of Africa and Its Surrounding Territories

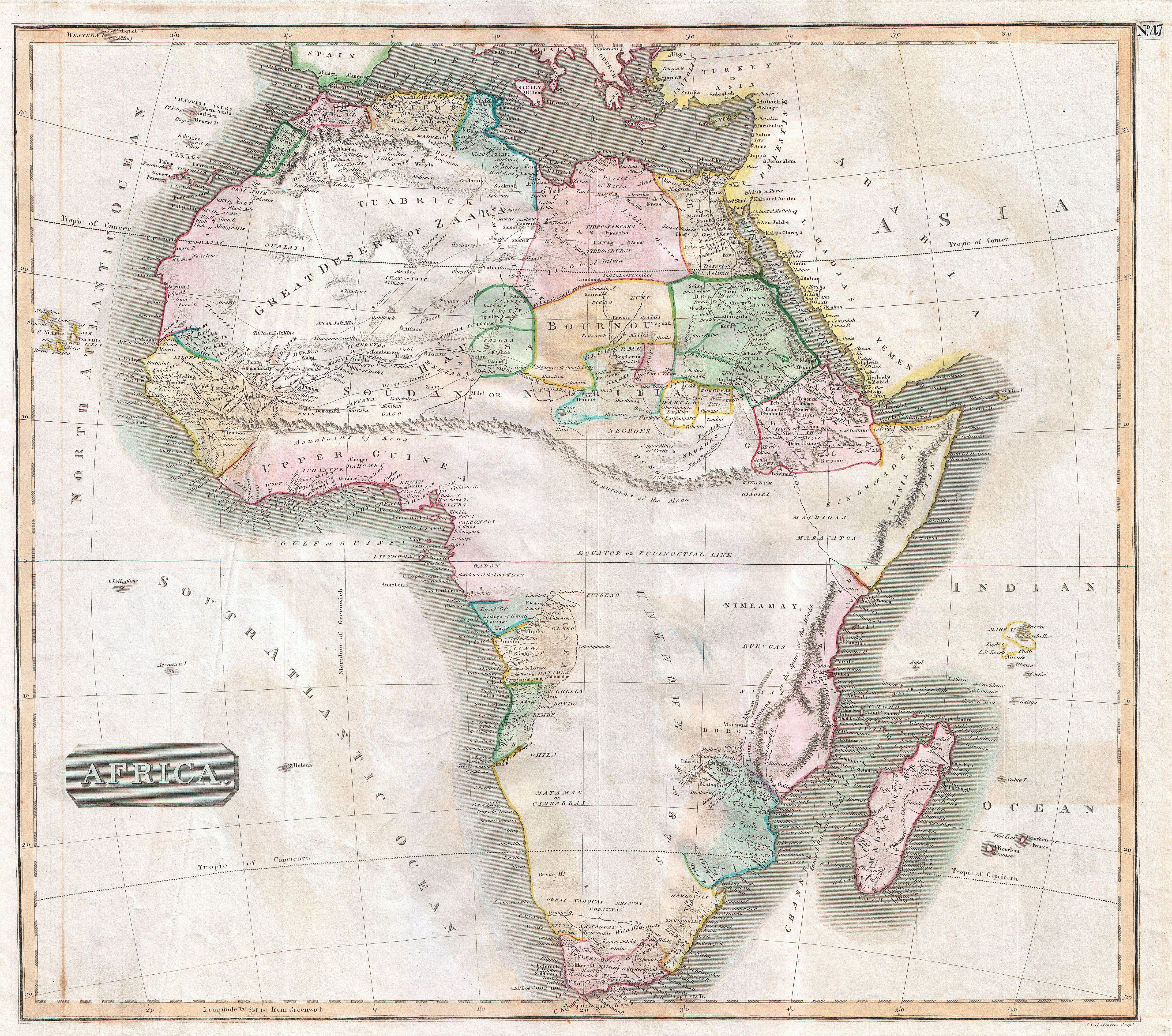
Africa, the second-largest continent on Earth, is a vast and diverse landmass with a rich history, diverse cultures, and a complex geopolitical landscape. Understanding its geography, including the surrounding countries, is crucial for appreciating its history, challenges, and opportunities. This article delves into the intricate tapestry of Africa’s map, exploring its physical features, political boundaries, and the interconnectedness of its diverse regions.
The African Continent: A Land of Extremes
Africa’s geography is characterized by dramatic contrasts, from the towering peaks of Mount Kilimanjaro to the vast expanse of the Sahara Desert. The continent is home to a diverse array of ecosystems, including lush rainforests, arid savannas, fertile river valleys, and coastal plains.
The Physical Geography of Africa:
- Mountains: The Atlas Mountains in North Africa, the Ethiopian Highlands, and the Drakensberg Mountains in South Africa are significant mountain ranges that shape the continent’s landscape.
- Rivers: The Nile River, the longest river in the world, flows through eleven countries, while the Congo River, the second-largest river in the world by volume, drains a vast rainforest region. Other major rivers include the Niger, Zambezi, and Orange rivers.
- Deserts: The Sahara Desert, the largest hot desert in the world, covers a significant portion of North Africa. The Namib Desert along the west coast and the Kalahari Desert in the south are also prominent desert regions.
- Lakes: Lake Victoria, the largest lake in Africa, is a source of water for millions of people and a vital part of the Nile River basin. Other major lakes include Lake Tanganyika, Lake Malawi, and Lake Chad.
Political Boundaries and Surrounding Countries:
Africa is comprised of 54 independent nations, each with its unique history, culture, and political system. The continent’s political boundaries are often complex and have been influenced by colonial legacies, historical conflicts, and economic factors.
Surrounding Countries:
While Africa is a continent unto itself, it shares borders with several countries outside its continental boundaries:
- Europe: Morocco and Algeria share land borders with Spain and the Spanish enclave of Ceuta. Tunisia shares a maritime border with Italy.
- Asia: Egypt shares a land border with Israel.
- Oceania: Madagascar, an island nation off the coast of southeast Africa, is considered part of Oceania.
Understanding the Importance of the Map of Africa:
The map of Africa provides a crucial framework for understanding the continent’s complex history, its diverse cultures, and the challenges it faces. By studying the map, we can gain insights into:
- Resource Distribution: The map reveals the locations of vital resources such as oil, minerals, and fertile land, highlighting the potential for economic development and the challenges of managing these resources sustainably.
- Climate Patterns: The map illustrates the different climate zones across the continent, from the tropical rainforests of Central Africa to the arid deserts of the north. This understanding is essential for addressing climate change impacts and promoting sustainable land management practices.
- Historical Influences: The map reveals the colonial legacies that shaped Africa’s political boundaries, ethnic divisions, and economic development. This understanding is crucial for addressing historical injustices and promoting reconciliation.
- Regional Cooperation: The map highlights the interconnectedness of African nations, emphasizing the importance of regional cooperation for addressing common challenges such as poverty, disease, and conflict.
FAQs about the Map of Africa and Surrounding Countries:
- What are the major geographical features of Africa?
- What are the major countries surrounding Africa?
- What are the most important rivers in Africa?
- What are the challenges and opportunities presented by Africa’s geography?
- How has the map of Africa been shaped by colonial history?
Tips for Understanding the Map of Africa:
- Use a detailed map that includes both physical and political features.
- Pay attention to the scale of the map to understand the relative sizes of different regions.
- Research the history of colonial boundaries and their impact on modern Africa.
- Explore the diverse cultures and languages represented on the map.
- Consider the impact of climate change on Africa’s geography and its people.
Conclusion:
The map of Africa is a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s diverse geography, rich history, and complex challenges. By studying the map, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of its people, resources, and ecosystems. Understanding the map of Africa is not just about memorizing locations; it’s about grasping the continent’s dynamic history, its potential for development, and the importance of regional cooperation in addressing its challenges. Through a comprehensive understanding of Africa’s map, we can foster greater awareness, appreciation, and engagement with this vital region of the world.
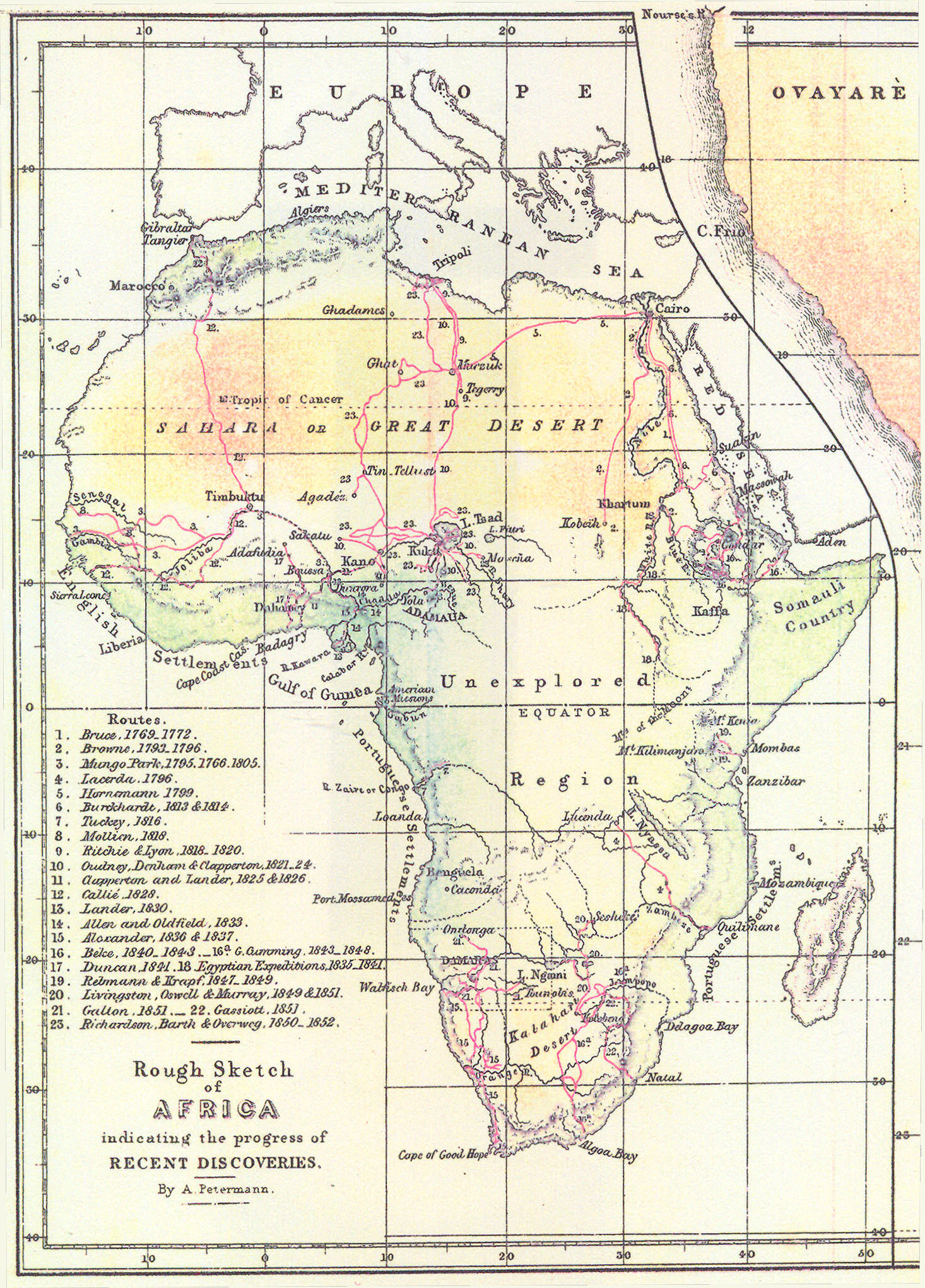

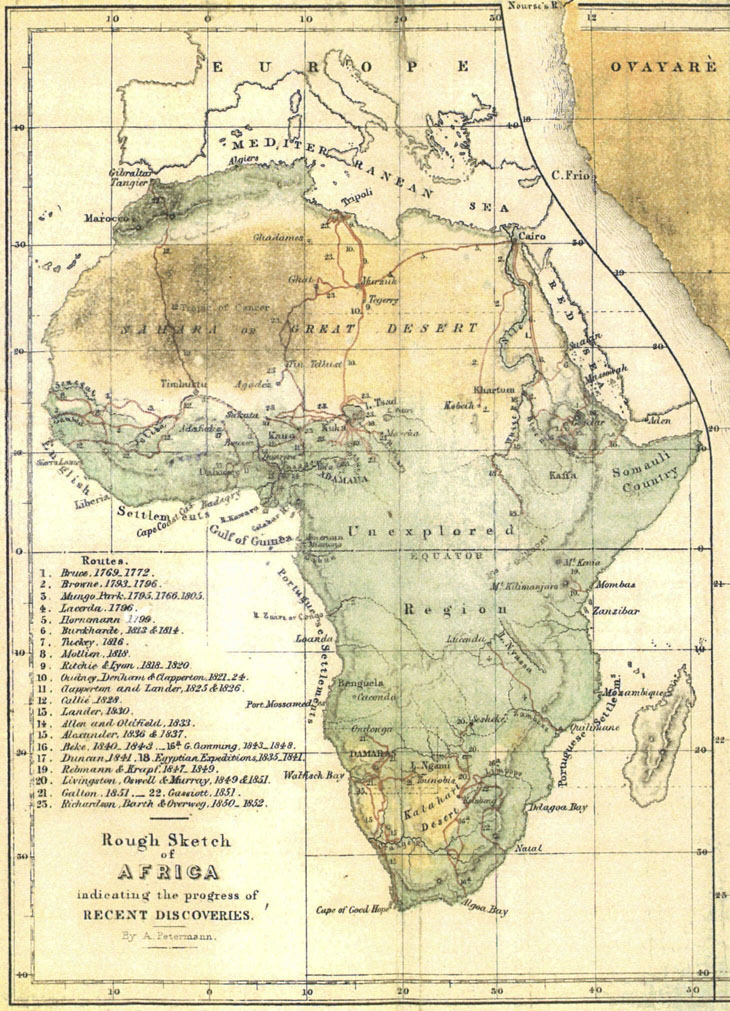
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/map-of-africa-in-1891-showing-routes-of-explorers--artist--unknown--918996998-5b786eb846e0fb0050d5b8e3.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Exploration of Africa and Its Surrounding Territories. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
