2, Aug 2023
A Geographic Exploration Of Europe: Understanding The Continent’s Diverse Landscape And Nations
A Geographic Exploration of Europe: Understanding the Continent’s Diverse Landscape and Nations
Related Articles: A Geographic Exploration of Europe: Understanding the Continent’s Diverse Landscape and Nations
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Exploration of Europe: Understanding the Continent’s Diverse Landscape and Nations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Exploration of Europe: Understanding the Continent’s Diverse Landscape and Nations

Europe, a continent rich in history, culture, and natural beauty, comprises a diverse tapestry of nations, each with its unique identity and contribution to the global landscape. Understanding the geographical layout of Europe, its countries, and their respective characteristics is crucial for comprehending the continent’s political, economic, and social dynamics. This article delves into the intricacies of the European map, exploring its nations, their geographical features, and the significance of their interconnectedness.
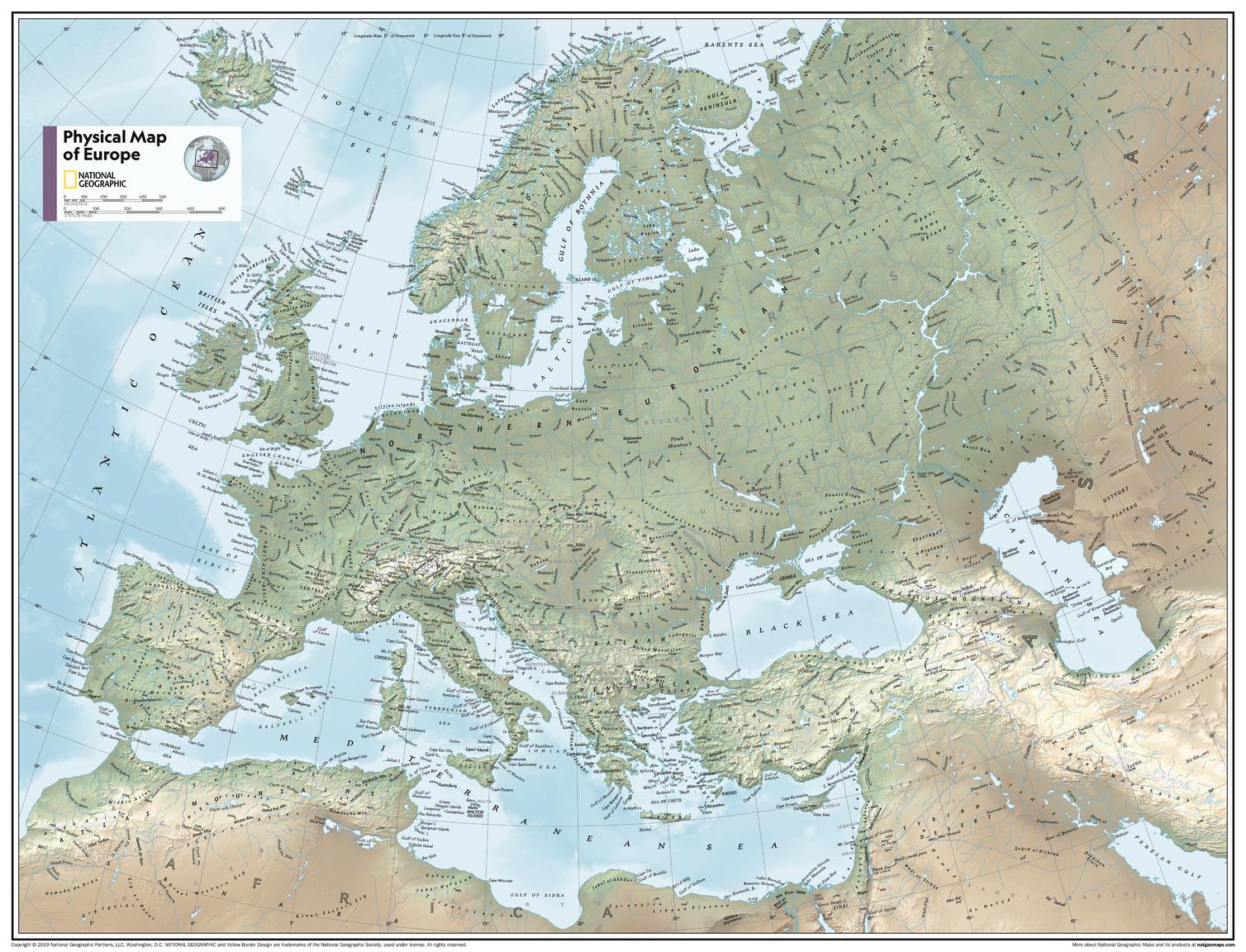
The European Landscape: A Mosaic of Diverse Terrain
Europe, situated on the westernmost portion of the Eurasian landmass, is a peninsula surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the Arctic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Black Sea. Its diverse geography encompasses a wide range of landscapes, from the towering Alps and Pyrenees to the vast plains of Eastern Europe and the rugged coastlines of Scandinavia.
The Western European Landscape: Characterized by rolling hills, fertile valleys, and extensive coastlines, Western Europe is home to some of the continent’s most prominent nations. The British Isles, with their distinct island geography, hold a unique position, while the Iberian Peninsula, home to Spain and Portugal, boasts a diverse landscape of mountains, plains, and coastal regions. France, known for its rolling vineyards and picturesque countryside, shares a border with the Alps, which extend into Italy, a country renowned for its stunning coastline, volcanic landscapes, and alpine peaks.
The Central European Landscape: This region is defined by the presence of the Carpathian Mountains, the Bohemian Massif, and the Danube River, which flows through several countries, serving as a vital transportation route. The Central European landscape is a blend of forests, plains, and rolling hills, providing a rich tapestry of natural beauty.
The Eastern European Landscape: Eastern Europe is characterized by vast plains, known as the East European Plain, which stretch from the Baltic Sea to the Black Sea. The region is also home to the Ural Mountains, which mark the traditional boundary between Europe and Asia. The Eastern European landscape includes diverse ecosystems, from the dense forests of Belarus and Ukraine to the steppes of Russia and the Carpathian Mountains.
The Nordic Landscape: The Scandinavian Peninsula, home to Norway, Sweden, and Finland, is a region of towering mountains, deep fjords, and vast forests. The Baltic Sea, surrounded by several countries, including Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, is a vital waterway connecting the region to the North Sea.
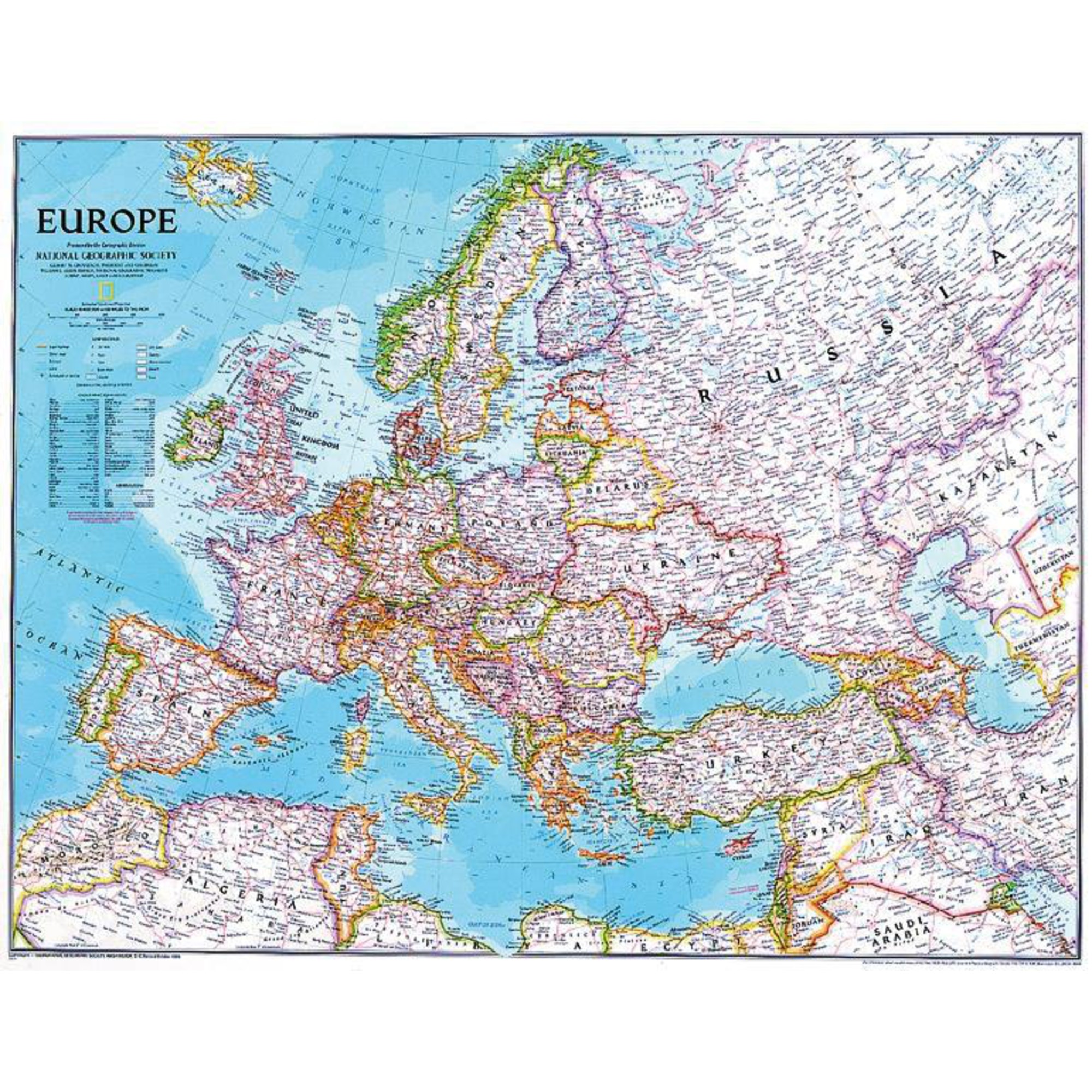
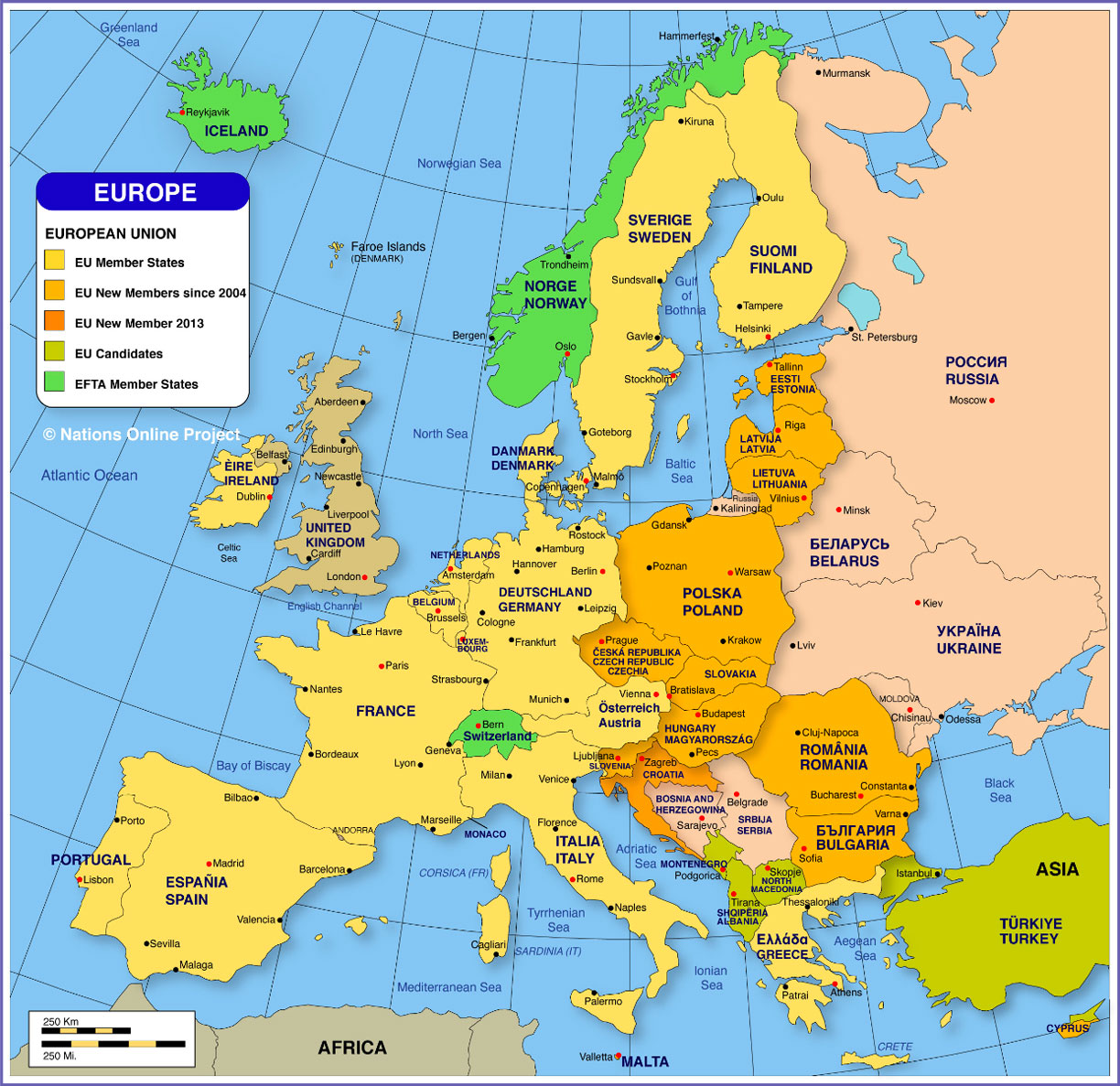
Understanding the Countries of Europe
Europe is home to 50 sovereign states, each with its unique history, culture, and political system. While the exact number of countries in Europe can vary depending on the criteria used for inclusion, the following list highlights some of the most prominent and influential nations:
Western Europe:
- United Kingdom: A constitutional monarchy comprised of England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. Known for its rich history, diverse culture, and global influence.
- France: A republic with a strong central government. Renowned for its art, fashion, gastronomy, and its role in European politics.
- Germany: A federal republic, a major economic powerhouse in Europe, known for its technological advancements and cultural heritage.
- Italy: A republic with a diverse landscape, a rich history, and a significant contribution to art, music, and fashion.
- Spain: A constitutional monarchy, known for its vibrant culture, beautiful beaches, and historical sites.
- Portugal: A republic with a history of exploration and colonization, known for its beautiful beaches, traditional cuisine, and cultural heritage.
- Belgium: A federal constitutional monarchy with a diverse population, known for its chocolate, beer, and its role in international diplomacy.
- Netherlands: A constitutional monarchy, renowned for its canals, windmills, and its role in international trade and finance.
- Luxembourg: A constitutional monarchy, a small country with a strong financial sector and a significant role in European politics.
- Ireland: A republic with a rich Celtic heritage, known for its vibrant culture, scenic landscapes, and its growing economy.
Central Europe:
- Austria: A federal republic, known for its classical music, architecture, and its role in European history.
- Switzerland: A federal republic, known for its neutrality, its banking sector, and its stunning alpine landscapes.
- Czech Republic: A parliamentary republic, known for its beer, its rich history, and its vibrant culture.
- Slovakia: A parliamentary republic, known for its natural beauty, its historical sites, and its growing economy.
- Hungary: A parliamentary republic, known for its thermal baths, its rich history, and its cultural heritage.
- Poland: A republic with a rich history and culture, known for its vibrant cities, its natural beauty, and its growing economy.
Eastern Europe:
- Russia: A federation, the largest country in the world by land area, with a rich history and a complex political system.
- Ukraine: A republic, known for its fertile land, its diverse culture, and its role in European history.
- Belarus: A republic, known for its forests, its agricultural resources, and its cultural heritage.
- Moldova: A parliamentary republic, known for its vineyards, its agricultural resources, and its cultural heritage.
- Romania: A parliamentary republic, known for its Carpathian Mountains, its rich history, and its cultural heritage.
- Bulgaria: A parliamentary republic, known for its Black Sea coastline, its historical sites, and its cultural heritage.
- Serbia: A republic, known for its historical sites, its natural beauty, and its cultural heritage.
- Croatia: A republic, known for its Adriatic coastline, its historical sites, and its cultural heritage.
- Slovenia: A republic, known for its Alps, its historical sites, and its cultural heritage.
Nordic Europe:
- Sweden: A constitutional monarchy, known for its welfare state, its innovative technology, and its beautiful natural landscapes.
- Norway: A constitutional monarchy, known for its fjords, its oil and gas industry, and its stunning natural landscapes.
- Finland: A republic, known for its forests, its lakes, and its innovative technology.
- Denmark: A constitutional monarchy, known for its design, its food, and its role in European politics.
- Iceland: A republic, known for its glaciers, its volcanoes, and its unique culture.
- Estonia: A republic, known for its technology sector, its beautiful coastline, and its historical sites.
- Latvia: A republic, known for its forests, its beaches, and its historical sites.
- Lithuania: A republic, known for its Baltic coastline, its historical sites, and its cultural heritage.
The Importance of the European Map
The map of Europe serves as a vital tool for understanding the continent’s diverse geography, history, and culture. It provides a visual representation of the interconnectedness of the European nations, highlighting their shared history, cultural influences, and economic relationships. By studying the map, we can gain insights into:
- Political Boundaries and Relationships: The map reveals the geographical borders of each European country, highlighting their proximity to one another and the potential for cooperation or conflict.
- Economic Interdependence: The map demonstrates the interconnectedness of European economies, highlighting trade routes, transportation networks, and the flow of goods and services across borders.
- Cultural Influences: The map provides a visual representation of the diverse cultural influences that have shaped Europe, showcasing the spread of languages, religions, and artistic traditions across the continent.
- Environmental Challenges: The map highlights the geographical features that contribute to environmental challenges in Europe, such as climate change, pollution, and deforestation.
- Historical Events: The map can be used to understand the historical events that have shaped Europe, such as wars, migrations, and empires.
FAQs about the Map of Europe and its Countries
Q: What is the largest country in Europe?
A: Russia is the largest country in Europe by land area, encompassing a vast territory spanning across the continent’s eastern portion.
Q: What is the smallest country in Europe?
A: The title of the smallest country in Europe is often attributed to Vatican City, an independent city-state located within Rome, Italy.
Q: What are the most populous countries in Europe?
A: The most populous countries in Europe are Russia, Germany, Turkey, Ukraine, and France.
Q: What are the most densely populated countries in Europe?
A: The Netherlands, Belgium, and Germany are among the most densely populated countries in Europe.
Q: What are the official languages spoken in Europe?
A: Europe is a continent with a rich linguistic diversity. The official languages spoken in Europe include English, French, German, Italian, Spanish, Russian, Polish, Portuguese, Romanian, and many others.
Q: What are the major religions practiced in Europe?
A: Christianity is the dominant religion in Europe, with Catholicism, Protestantism, and Eastern Orthodoxy being the main branches. Islam, Judaism, and other faiths are also practiced in various regions.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Europe
- Engage with Interactive Maps: Utilize online interactive maps to explore the geographical features, political boundaries, and cultural landmarks of Europe.
- Focus on Key Regions: Divide Europe into key regions, such as Western Europe, Central Europe, Eastern Europe, and Northern Europe, to facilitate your understanding of the continent’s diverse geography.
- Explore Historical Maps: Examining historical maps can provide insights into how the map of Europe has evolved over time, highlighting changes in political boundaries, empires, and cultural influences.
- Connect Geography and History: Relate geographical features to historical events, understanding how landscapes have shaped human settlements, trade routes, and conflicts.
- Utilize Travel Guides and Resources: Consult travel guides and online resources to gain a deeper understanding of the individual countries, their cultures, and their attractions.
Conclusion
The map of Europe serves as a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s diverse geography, history, and culture. By exploring the map, we can gain insights into the interconnectedness of European nations, their political relationships, their economic interdependence, and the shared cultural influences that have shaped the continent. The map provides a visual representation of the continent’s rich tapestry of nations, each with its unique identity and contribution to the global landscape. Through a deeper understanding of the European map, we can appreciate the complexities and the richness of this fascinating continent.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Exploration of Europe: Understanding the Continent’s Diverse Landscape and Nations. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
