28, Jan 2024
A Geographic Perspective: Understanding Italy’s Position In Europe
A Geographic Perspective: Understanding Italy’s Position in Europe
Related Articles: A Geographic Perspective: Understanding Italy’s Position in Europe
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Perspective: Understanding Italy’s Position in Europe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Perspective: Understanding Italy’s Position in Europe
/the-geography-of-italy-4020744-CS-5c3df74a46e0fb00018a8a3a.jpg)
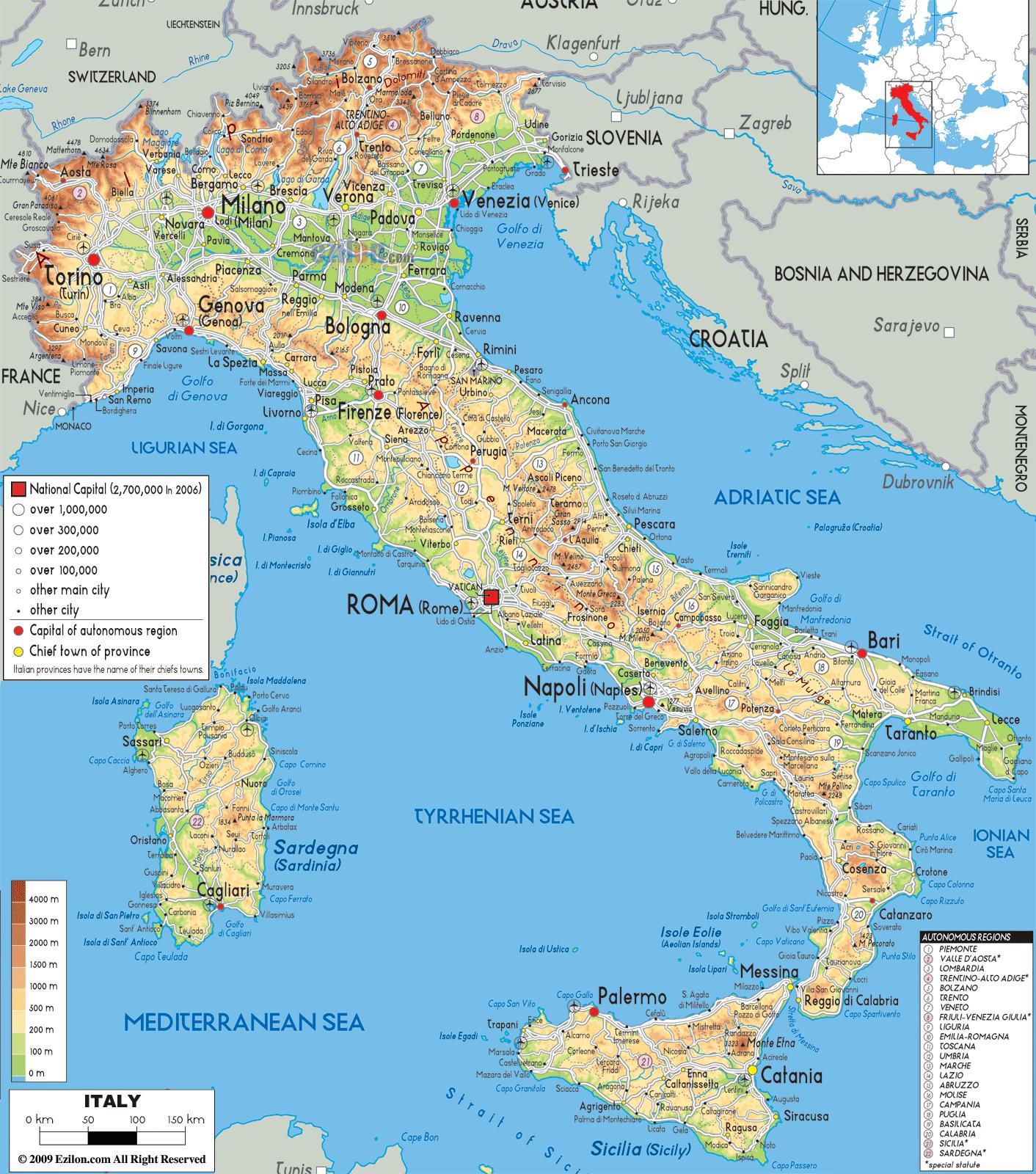
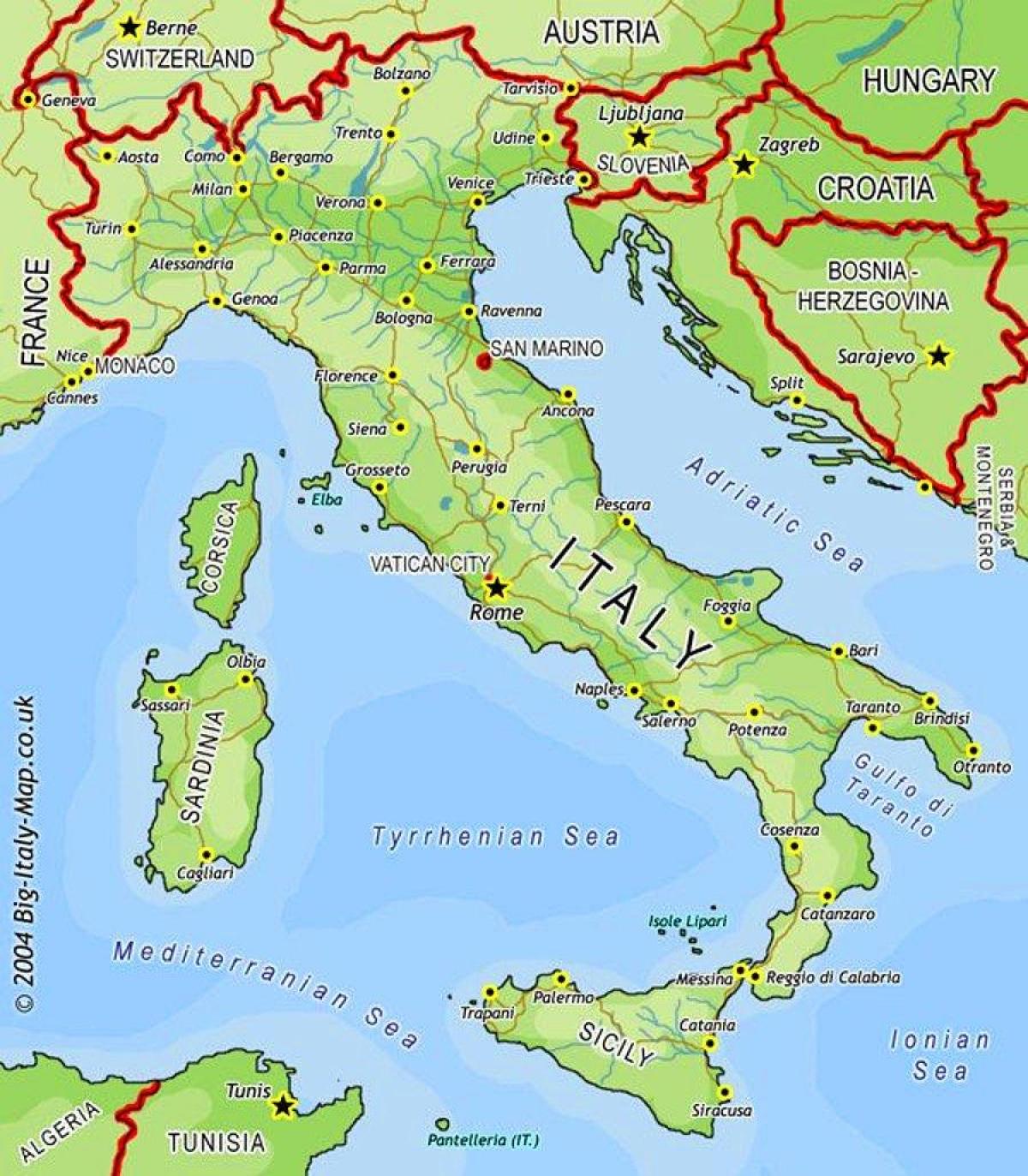
Italy, the "boot-shaped" peninsula jutting into the Mediterranean Sea, holds a unique position within the European landscape. Its geographic location, characterized by diverse landscapes, historical significance, and cultural richness, has profoundly shaped its history, economy, and identity. Examining Italy’s position on a map of European countries reveals a wealth of insights into its multifaceted nature.
A Land of Contrasts: Geographic Features and Their Influence
Italy’s geography is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, from the snow-capped peaks of the Alps in the north to the sun-drenched shores of the Mediterranean in the south. This variety is reflected in the country’s diverse ecosystems, ranging from alpine forests and rolling hills to fertile plains and volcanic islands.
- The Alps: The imposing Alps, forming a natural border with France, Switzerland, Austria, and Slovenia, have historically served as both a barrier and a conduit. They have protected Italy from northern invasions while also facilitating trade routes and cultural exchange.
- The Apennine Mountains: Running the length of the peninsula, the Apennine Mountains have shaped Italy’s internal geography. They create distinct regions with varying climates and agricultural practices. The mountainous terrain also presented challenges for transportation and communication, fostering regional identities and unique cultural traditions.
- The Po Valley: The fertile Po Valley, located in northern Italy, is a major agricultural region. Its rich alluvial soil supports extensive farming activities, making it a vital contributor to the Italian economy.
- The Mediterranean Coastline: Italy boasts a vast coastline, stretching over 7,500 kilometers. This coastline has been a vital artery for trade and cultural exchange throughout history, connecting Italy to the wider Mediterranean world.
Historical Crossroads: Italy’s Position in the European Landscape
Italy’s central location in the Mediterranean has made it a crossroads of civilizations for millennia. This geographic advantage has led to significant cultural exchanges and influences, shaping Italy’s artistic, architectural, and linguistic heritage.
- Roman Empire: Rome, situated in the heart of Italy, became the center of the Roman Empire, which extended its influence across Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East. This historical legacy continues to resonate in Italy’s language, law, and infrastructure.
- Renaissance and Beyond: Italy’s central position facilitated the spread of Renaissance ideas and innovations throughout Europe. Artists, scholars, and thinkers from across the continent flocked to Italian cities like Florence, Rome, and Venice, contributing to a flourishing of arts and sciences.
- European Integration: Italy’s location within the heart of Europe has played a pivotal role in its participation in European integration. As a founding member of the European Union, Italy has actively contributed to the development of European institutions and policies.
Economic Importance: A Gateway to the Mediterranean
Italy’s strategic location has made it a vital hub for trade and commerce. Its access to the Mediterranean Sea, combined with its extensive coastline and well-developed infrastructure, has positioned it as a gateway to the Middle East, North Africa, and other regions.
- Industrial and Agricultural Hub: Italy is a major industrial and agricultural producer, with key sectors including automotive, fashion, food processing, and tourism. Its location facilitates access to raw materials and markets, contributing to its economic success.
- Tourism Powerhouse: Italy’s rich history, cultural heritage, and stunning landscapes have made it a leading tourist destination. Millions of visitors flock to its iconic cities, ancient ruins, and picturesque landscapes, generating significant revenue for the country.
- Strategic Partnerships: Italy’s location has fostered strong economic ties with its neighboring countries and beyond. Its membership in the European Union and its participation in international trade agreements have further strengthened its economic standing.
Cultural Bridge: Connecting Europe and the Mediterranean
Italy’s geographic location has facilitated cultural exchange and integration. Its proximity to other Mediterranean countries has resulted in a blend of influences, shaping its cuisine, language, music, and art.
- Linguistic Diversity: Italy’s regional dialects reflect the country’s diverse history and cultural influences. The Italian language, itself a descendant of Latin, has evolved over centuries, incorporating elements from other languages spoken in the Mediterranean region.
- Artistic Heritage: Italy’s rich artistic heritage, encompassing ancient Roman ruins, Renaissance masterpieces, and Baroque churches, has captivated the world. Its central location facilitated the spread of artistic styles and techniques throughout Europe.
- Culinary Delights: Italian cuisine, renowned for its simplicity and freshness, reflects the country’s diverse agricultural produce. Its culinary traditions, influenced by both northern and southern European flavors, have become a global phenomenon.
FAQs: Exploring Italy’s Position in Europe
Q: What are the main geographical features of Italy?
A: Italy’s geography is characterized by the Alps in the north, the Apennine Mountains running down the peninsula, the fertile Po Valley, and the extensive Mediterranean coastline.
Q: How has Italy’s location influenced its history?
A: Italy’s central location in the Mediterranean has made it a crossroads of civilizations, leading to significant cultural exchanges and influences. Its historical significance is evident in its Roman legacy, Renaissance influence, and role in European integration.
Q: What are the economic benefits of Italy’s location?
A: Italy’s location has made it a vital hub for trade and commerce, positioning it as a gateway to the Mediterranean. It is a major industrial and agricultural producer, a leading tourist destination, and benefits from strong economic ties with its neighbors.
Q: How has Italy’s location shaped its culture?
A: Italy’s central position has facilitated cultural exchange and integration, resulting in a blend of influences. Its linguistic diversity, artistic heritage, and culinary traditions reflect its unique position as a bridge between Europe and the Mediterranean.
Tips for Understanding Italy’s Position on a Map of Europe
- Focus on the Mediterranean: Recognize Italy’s prominent position in the Mediterranean Sea, highlighting its connection to North Africa, the Middle East, and other regions.
- Observe the Borders: Pay attention to Italy’s borders with France, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia, and its neighboring Mediterranean countries. These borders illustrate its geographical connections and historical interactions.
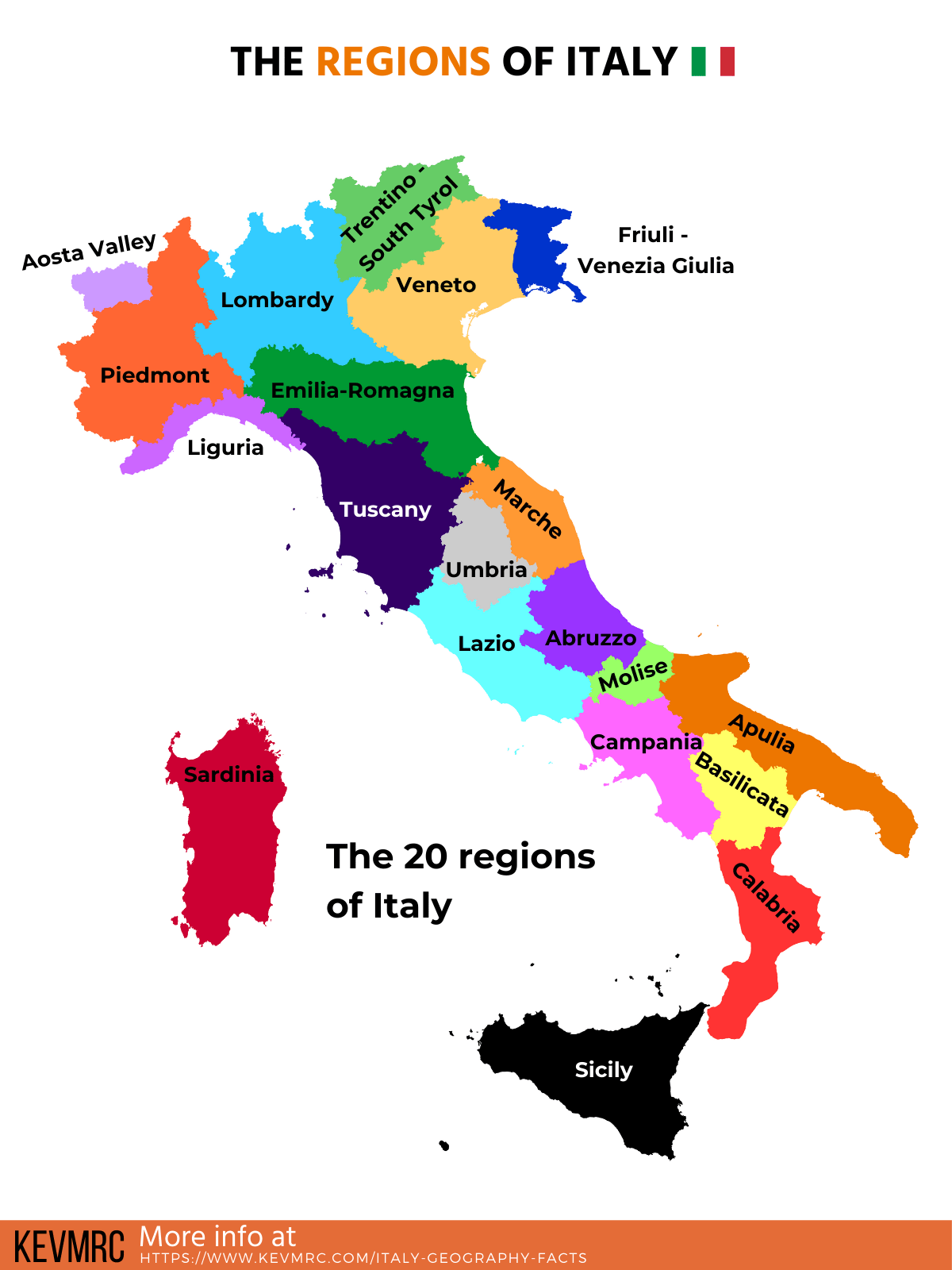
- Explore the Regional Diversity: Identify the distinct regions within Italy, recognizing their unique landscapes, cultural traditions, and economic activities.
- Consider the Historical Context: Reflect on Italy’s historical role as a center of power, a hub of cultural exchange, and a participant in European integration.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Italy’s Location
Italy’s position on a map of European countries reveals a story of interconnectedness, cultural exchange, and historical significance. Its diverse landscapes, strategic location, and rich cultural heritage have shaped its identity and continue to influence its role in the European and global landscape. Understanding Italy’s geographic position provides a deeper appreciation for its multifaceted nature and its enduring contributions to the world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Perspective: Understanding Italy’s Position in Europe. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
