19, Sep 2023
A Geographic Tapestry: Exploring The Countries Of Europe
A Geographic Tapestry: Exploring the Countries of Europe
Related Articles: A Geographic Tapestry: Exploring the Countries of Europe
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Tapestry: Exploring the Countries of Europe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Tapestry: Exploring the Countries of Europe

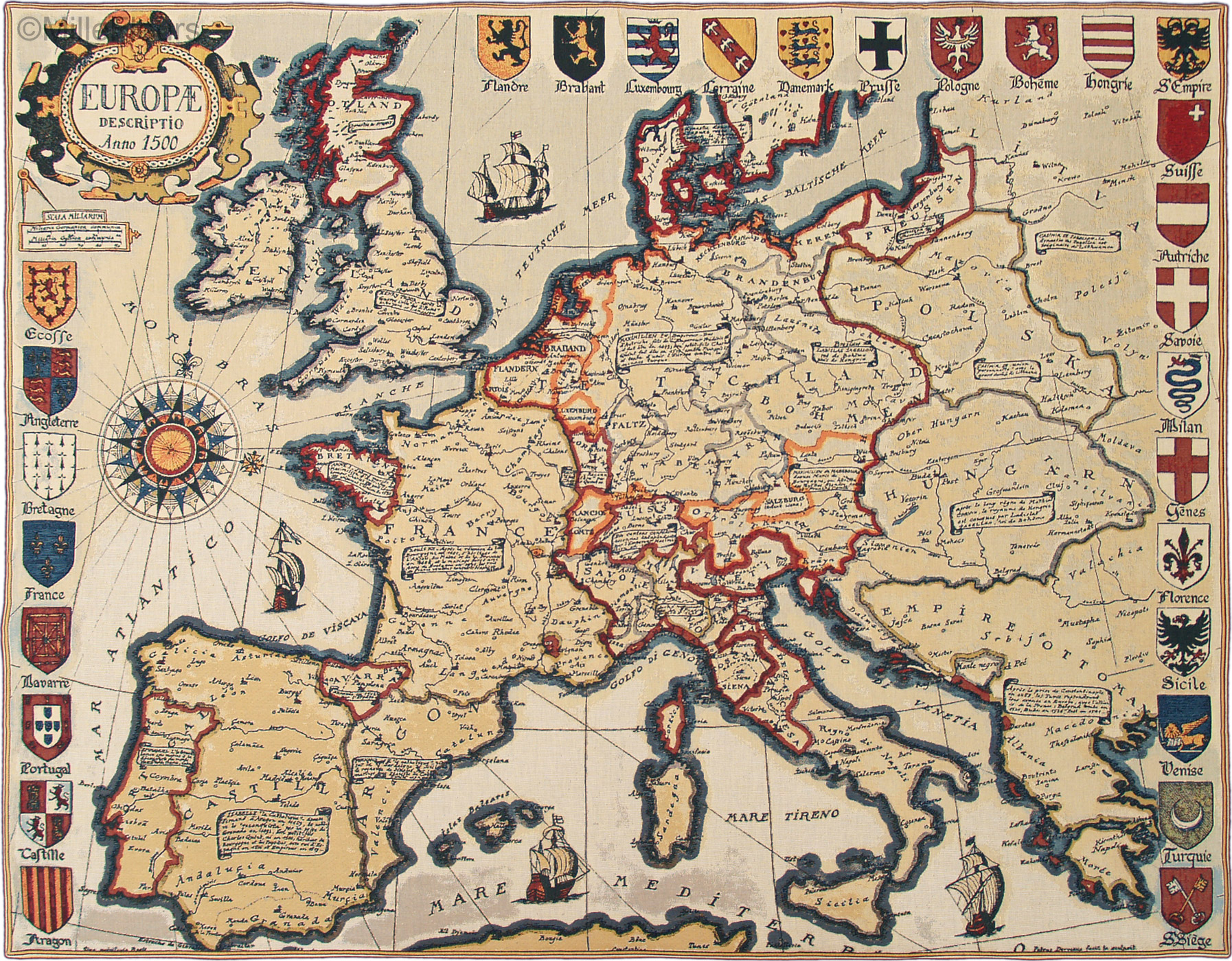
The map of Europe, a continent steeped in history, culture, and diverse landscapes, is a visual representation of a complex tapestry of nations. Its intricate network of borders, from the rugged peaks of the Alps to the sun-drenched shores of the Mediterranean, reflects centuries of political evolution, cultural exchange, and shifting power dynamics. Understanding this map is not merely a matter of memorizing names and locations, but rather an exploration of the intricate relationships that shape the continent’s identity.
A Mosaic of Nations:
Europe is home to 44 countries, each with its own distinct history, language, traditions, and cultural heritage. From the bustling metropolises of London and Paris to the charming villages of the countryside, each country offers unique experiences. The map is a visual testament to this diversity, showcasing the geographical distribution of these distinct entities.
The Western Bloc:
The Western European countries, including the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and Portugal, have historically been at the forefront of European development. They boast strong economies, vibrant cultures, and influential political systems. The map reveals their geographical proximity and interconnectedness, highlighting the historical and cultural ties that bind them.
The Eastern Bloc:
Eastern Europe, once dominated by the Soviet Union, has undergone significant transformation since the fall of the Iron Curtain. Countries like Poland, Ukraine, Russia, Belarus, and the Baltic states have embarked on their own journeys of political and economic development. The map reflects this dynamic shift, showcasing the geographical separation that defined the Cold War era and the evolving relationships that define the post-Soviet landscape.
The Balkan Peninsula:
The Balkan Peninsula, a region known for its complex history and diverse ethnicities, is a fascinating microcosm of Europe’s cultural richness. Countries like Greece, Serbia, Bulgaria, Albania, and Romania share a common heritage yet boast distinct identities. The map highlights their geographical proximity and the historical and cultural connections that bind them.
The Nordic Countries:
The Nordic countries, including Sweden, Finland, Norway, Denmark, and Iceland, stand out for their social welfare systems, democratic traditions, and strong economies. They share a geographical proximity and a common cultural heritage rooted in Viking history and mythology. The map reveals their location at the northern edge of the continent, showcasing their unique cultural and geographical identity.
The Importance of the Map:
The map of Europe serves as a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s past, present, and future. It provides a visual framework for comprehending:
- Historical Connections: The map reveals the intricate network of historical relationships between European nations, from ancient empires to modern alliances. It highlights the geographical factors that shaped these connections, from trade routes to conquest.
- Cultural Diversity: The map showcases the rich tapestry of cultures that make up Europe. It highlights the geographical distribution of different languages, religions, and traditions, demonstrating the continent’s remarkable diversity.
- Political Dynamics: The map reflects the changing political landscape of Europe, from the rise and fall of empires to the formation of the European Union. It provides a visual representation of the geographical forces that shape political alliances and conflicts.
- Economic Interdependence: The map highlights the interconnectedness of European economies, showcasing the geographical distribution of trade routes, industrial centers, and financial hubs. It demonstrates the vital role that geography plays in economic development.
Understanding the Map: A Guide to Exploration
To fully appreciate the significance of the map of Europe, consider these key points:
- Scale and Proportion: The map’s scale and proportion are crucial for understanding the relative size and location of different countries. A map that accurately reflects these factors provides a better understanding of the geographical relationships between nations.
- Geographical Features: Understanding the major geographical features, such as mountain ranges, rivers, and coastlines, is essential for grasping the continent’s physical landscape and its impact on human settlements and development.
- Historical Context: The map is not static but a dynamic representation of historical evolution. Understanding the historical events that shaped the map, such as wars, treaties, and migrations, provides a deeper understanding of the continent’s present-day landscape.
- Cultural Influences: The map reflects the cultural diversity of Europe, highlighting the geographical distribution of different languages, religions, and traditions. Understanding these cultural influences provides a richer perspective on the continent’s history and identity.
FAQs: The Countries of Europe Map
Q: What is the largest country in Europe?
A: Russia, although a significant portion of its territory lies in Asia, is considered the largest country in Europe by land area.
Q: What is the smallest country in Europe?
A: Vatican City, located within Rome, is the smallest country in Europe by both land area and population.
Q: What is the most densely populated country in Europe?
A: Monaco, a city-state on the French Riviera, is the most densely populated country in Europe.
Q: What is the official language of the European Union?
A: The European Union has 24 official languages, reflecting the linguistic diversity of its member states.
Q: What is the currency of the European Union?
A: The euro is the official currency of 19 out of 27 European Union member states.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Europe
- Use a Detailed Map: Choose a map with a detailed level of detail that includes major cities, rivers, and mountain ranges.
- Study the Geography: Familiarize yourself with the major geographical features of Europe, such as the Alps, the Danube River, and the Mediterranean Sea.
- Explore Historical Maps: Compare historical maps with modern maps to understand how the boundaries and political landscape of Europe have changed over time.
- Research Individual Countries: Delve into the history, culture, and geography of individual countries to gain a deeper understanding of the continent’s diversity.
Conclusion:
The map of Europe is not simply a collection of lines and borders; it is a dynamic representation of a continent rich in history, culture, and interconnectedness. It serves as a powerful tool for understanding the complex relationships between nations, the forces that have shaped the continent’s development, and the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. By studying the map and understanding its nuances, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate tapestry of Europe and its profound impact on the world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Tapestry: Exploring the Countries of Europe. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
