7, Feb 2024
A Geographic Tapestry: Understanding The Map Of Europe And North Africa
A Geographic Tapestry: Understanding the Map of Europe and North Africa
Related Articles: A Geographic Tapestry: Understanding the Map of Europe and North Africa
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Tapestry: Understanding the Map of Europe and North Africa. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Tapestry: Understanding the Map of Europe and North Africa

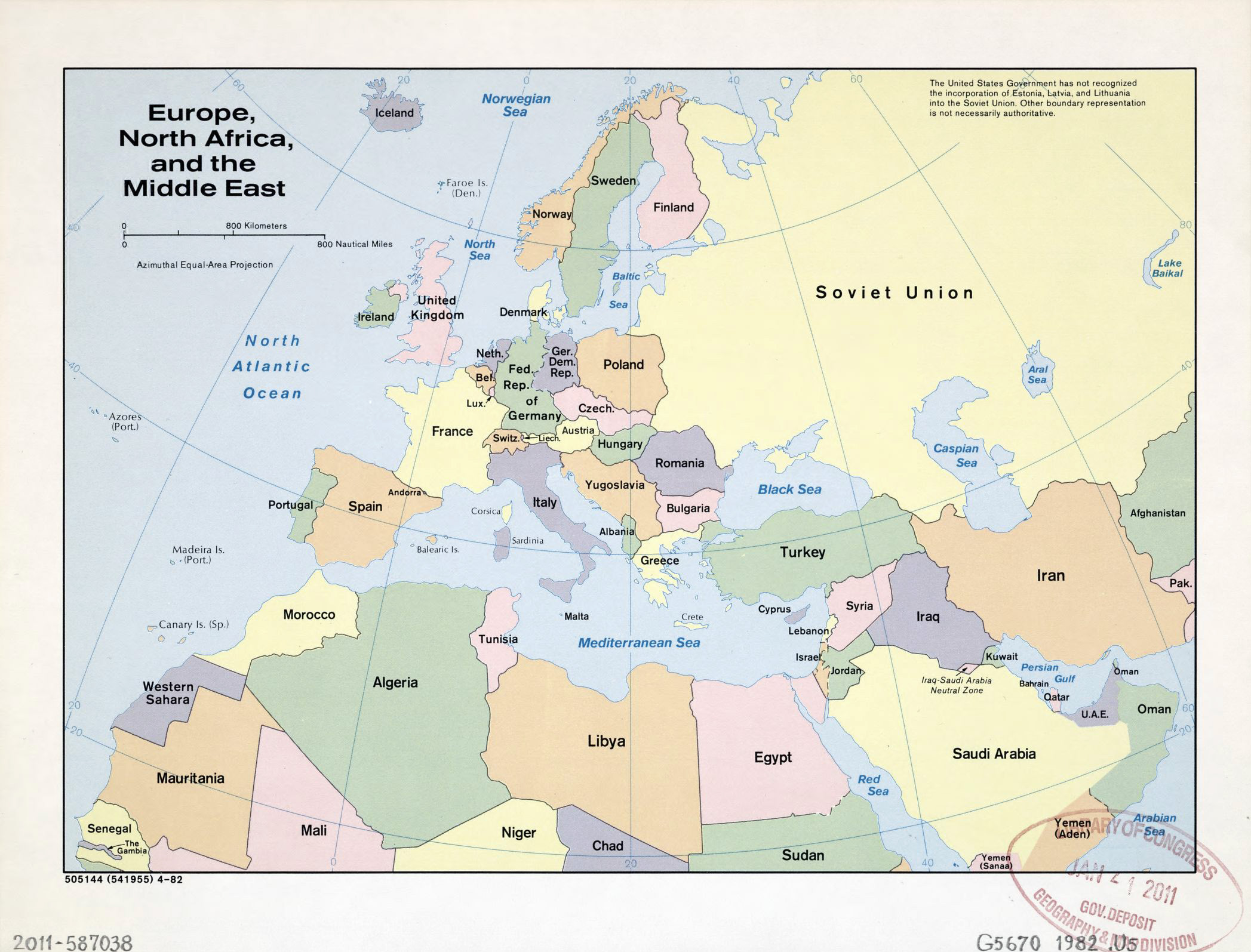
The map of Europe and North Africa is a vibrant tapestry woven with diverse landscapes, rich histories, and interconnected cultures. Understanding its intricate geography unveils a complex web of relationships, shaping the political, economic, and social dynamics of the region. This exploration delves into the key features of this map, highlighting its significance in the global context.
A Continent of Contrasts: Europe’s Diverse Landscape
Europe, the second-smallest continent, is a geographical paradox. Its compact size belies its incredible diversity. From the rugged peaks of the Alps to the rolling plains of the Danube Basin, from the windswept shores of the Atlantic to the sun-drenched Mediterranean coast, Europe presents a mosaic of landscapes.
Peninsulas and Islands: The continent’s fragmented coastline, characterized by numerous peninsulas and islands, has historically shaped its cultural and political landscape. The Iberian Peninsula, home to Spain and Portugal, boasts a distinct identity rooted in its geographical isolation. Similarly, the Italian Peninsula, with its boot-shaped silhouette, has a rich history of independent states. Islands like Britain and Ireland, separated from the mainland, have developed unique cultural identities.
Major Rivers and Waterways: Europe’s extensive network of rivers, including the Danube, Rhine, and Volga, has served as vital trade routes throughout history. These waterways facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and people, fostering economic growth and cultural interconnectedness. The presence of navigable rivers has also influenced the development of major cities, such as Paris on the Seine and London on the Thames.
Mountain Ranges and Plateaus: The Alps, Pyrenees, and Carpathian Mountains act as natural barriers, shaping the distribution of populations and influencing historical movements. They have also been a source of inspiration for art, literature, and folklore. Plateaus like the Iberian Plateau and the Massif Central in France offer unique ecosystems and cultural landscapes.
North Africa: A Gateway to the Mediterranean
North Africa, a region bridging the Mediterranean Sea and the Sahara Desert, is a land of contrasts. Its diverse geography ranges from fertile coastal plains to vast, arid deserts.
The Maghreb: A Region of Shared History and Culture
The Maghreb, encompassing Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, and Libya, is a region with a shared history and culture deeply intertwined with the Mediterranean world. This region, characterized by its fertile coastal plains and the Atlas Mountains, has been a crossroads of trade routes for centuries.
The Sahara Desert: A Vast and Arid Landscape
The Sahara Desert, the world’s largest hot desert, covers a significant portion of North Africa. This vast and unforgiving landscape presents unique challenges and opportunities, shaping the lives of the nomadic peoples who inhabit it. Despite its harsh conditions, the Sahara holds immense cultural and historical significance.
The Nile River: A Lifeline for Civilization
The Nile River, one of the longest rivers in the world, flows through Egypt, providing a vital source of water and fertile land for agriculture. This river has been the backbone of Egyptian civilization for millennia, shaping its history, culture, and economy.
Interconnectedness: The Importance of Geographic Proximity
The proximity of Europe and North Africa has fostered a complex interplay of cultural, economic, and political influences. Throughout history, these regions have engaged in trade, migration, and conflict, shaping their respective societies.
Trade and Migration: The Mediterranean Sea has served as a vital trade route connecting Europe and North Africa for centuries. This exchange of goods, ideas, and people has enriched both regions, contributing to cultural exchange and economic development. Migration flows across the Mediterranean have also played a significant role in shaping the demographics and cultural landscapes of both regions.
Historical Intertwining: The history of Europe and North Africa is deeply intertwined. From the Roman Empire’s expansion into North Africa to the Arab conquests of the Iberian Peninsula, these regions have experienced periods of both conflict and cooperation. This shared history has left an enduring legacy on both sides of the Mediterranean.
Political and Economic Ties: In the modern era, Europe and North Africa are linked by a complex web of political and economic ties. The European Union, with its expanding membership, has fostered closer relations with North African countries, particularly in the areas of trade, investment, and development cooperation.
Challenges and Opportunities: The map of Europe and North Africa also highlights the challenges and opportunities facing these regions in the 21st century. Climate change, political instability, and economic disparities are among the pressing issues that require collaborative solutions.
Climate Change: The Mediterranean region is particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, with rising sea levels, increased drought, and extreme weather events posing significant threats. This shared challenge requires coordinated efforts to mitigate the impacts of climate change and adapt to its consequences.
Political Instability: The Arab Spring uprisings of 2011 highlighted the political instability in North Africa, with ongoing conflicts and transitions impacting the region’s stability and economic development. Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach that promotes democratic governance, human rights, and economic opportunity.
Economic Disparities: The economic disparities between Europe and North Africa present a major challenge. The gap in income, development, and access to resources creates a complex web of issues, including migration, inequality, and social unrest. Bridging these disparities requires collaborative efforts to promote economic growth, investment, and social inclusion.
FAQs
Q: What are the major geographical features of Europe?
A: Europe is characterized by its diverse landscapes, including rugged mountains, fertile plains, extensive rivers, and fragmented coastlines with numerous peninsulas and islands. The Alps, Pyrenees, and Carpathian Mountains serve as natural barriers, while rivers like the Danube, Rhine, and Volga have been vital trade routes throughout history.
Q: What are the key geographical features of North Africa?
A: North Africa is a region of contrasts, encompassing fertile coastal plains, the vast Sahara Desert, and the Atlas Mountains. The Maghreb region, with its shared history and culture, is located along the Mediterranean coast. The Nile River, flowing through Egypt, is a vital source of water and fertile land for agriculture.
Q: How has the proximity of Europe and North Africa shaped their relationship?
A: The proximity of these regions has fostered a complex interplay of cultural, economic, and political influences. The Mediterranean Sea has served as a vital trade route, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and people. Migration flows across the Mediterranean have also played a significant role in shaping the demographics and cultural landscapes of both regions.
Q: What are the major challenges facing Europe and North Africa in the 21st century?
A: These regions face a range of challenges, including climate change, political instability, and economic disparities. Climate change poses significant threats to the Mediterranean region, while political instability in North Africa impacts the region’s stability and economic development. Economic disparities create a complex web of issues, including migration, inequality, and social unrest.
Tips
- Use a physical map to visualize the geographical features of Europe and North Africa. This will help you understand the relative positions of countries, mountain ranges, rivers, and other key features.
- Research the history of these regions to understand the complex interplay of cultural, economic, and political influences. This will provide context for the current relationship between Europe and North Africa.
- Explore the diverse cultures and landscapes of these regions through travel, literature, and documentaries. This will help you gain a deeper appreciation for the rich tapestry of human experience in this part of the world.
Conclusion
The map of Europe and North Africa is a powerful tool for understanding the complex web of relationships that shape this region. From its diverse landscapes to its shared history and cultural exchanges, the geography of this region has played a vital role in shaping its identity and destiny. Understanding the map is not just about memorizing names and locations; it is about comprehending the interconnectedness of these regions and the challenges and opportunities they face in the 21st century.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Tapestry: Understanding the Map of Europe and North Africa. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
