5, Oct 2023
A Geographical Overview Of Europe And Its Surrounding Countries
A Geographical Overview of Europe and its Surrounding Countries
Related Articles: A Geographical Overview of Europe and its Surrounding Countries
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Overview of Europe and its Surrounding Countries. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Overview of Europe and its Surrounding Countries

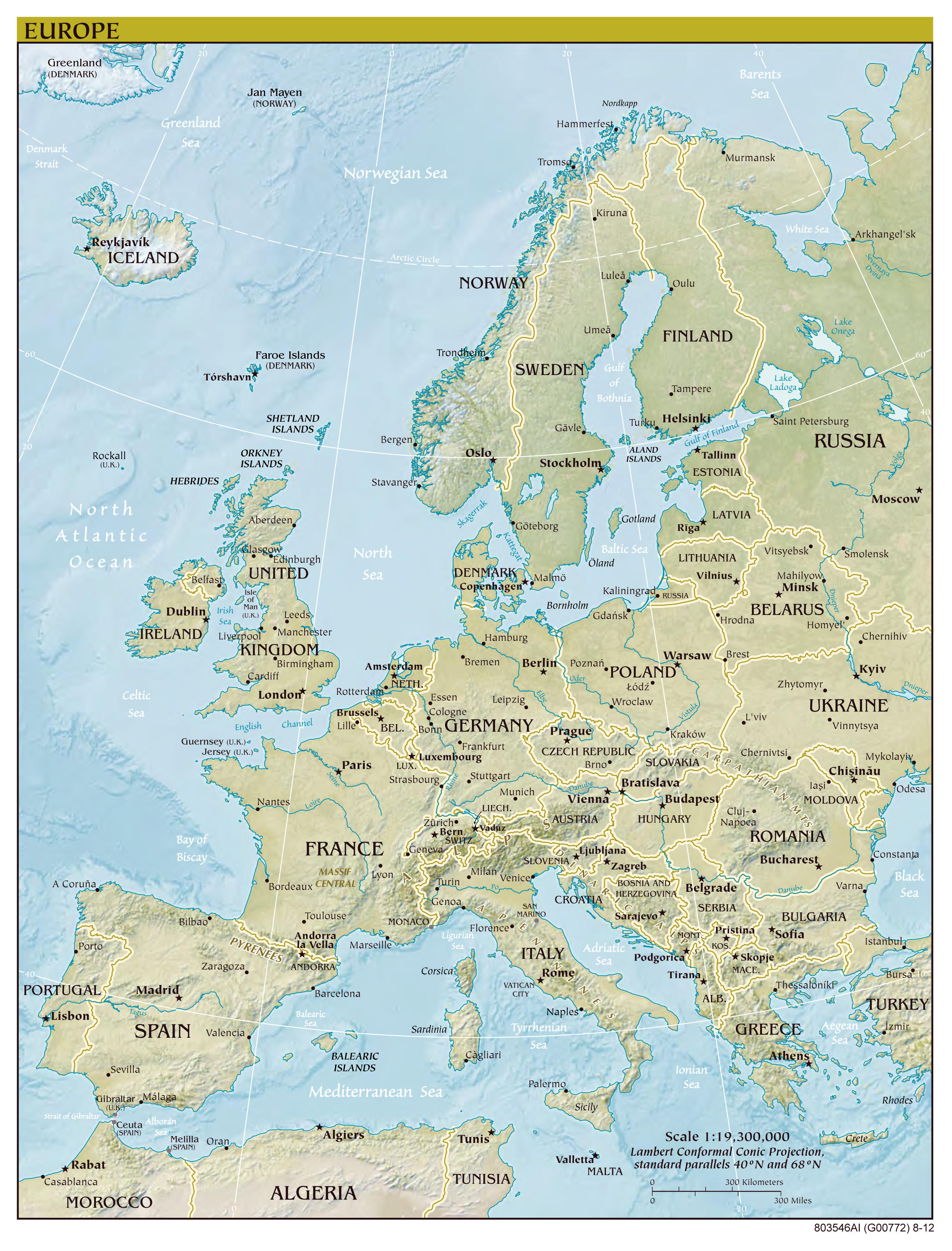
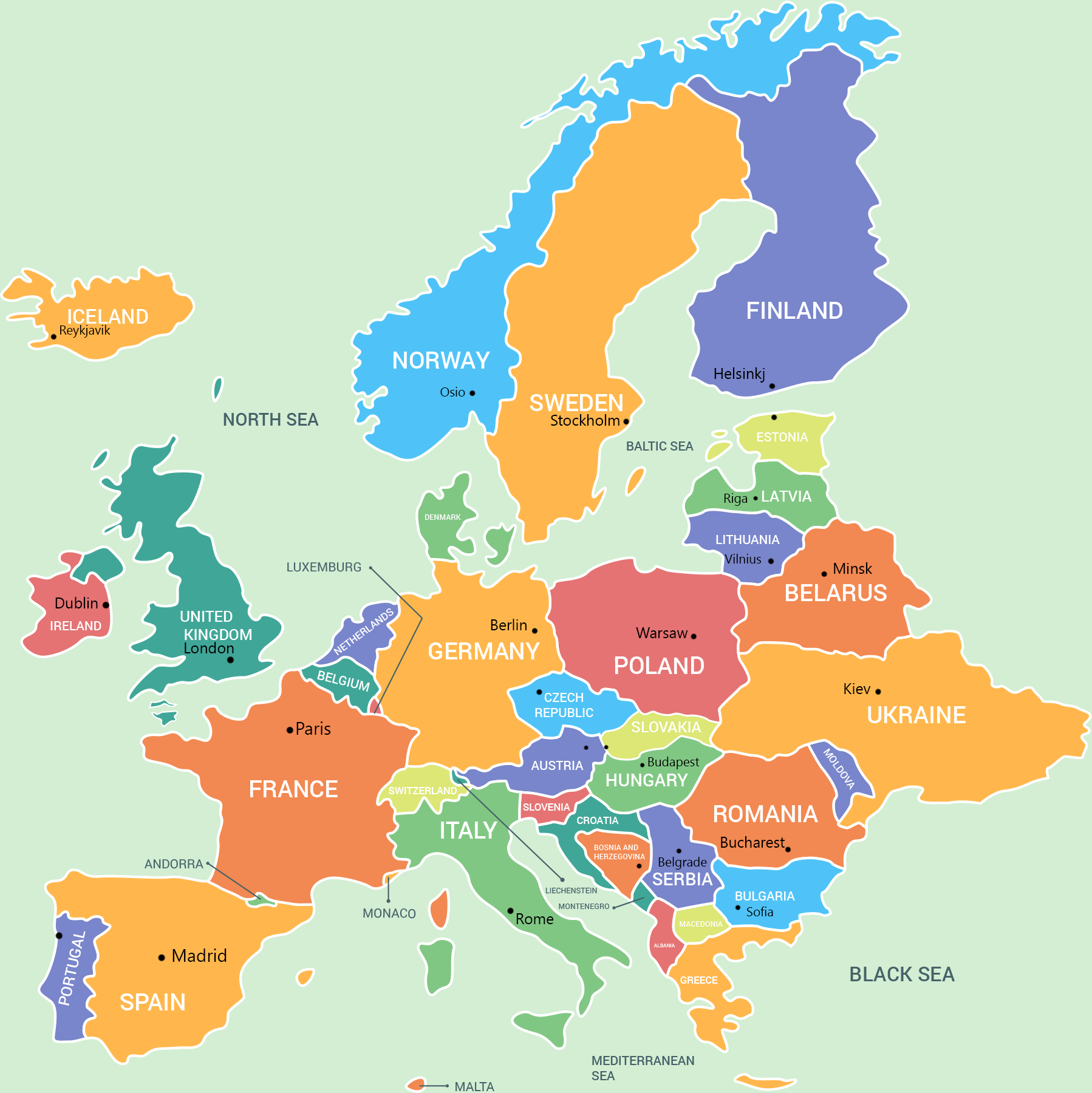
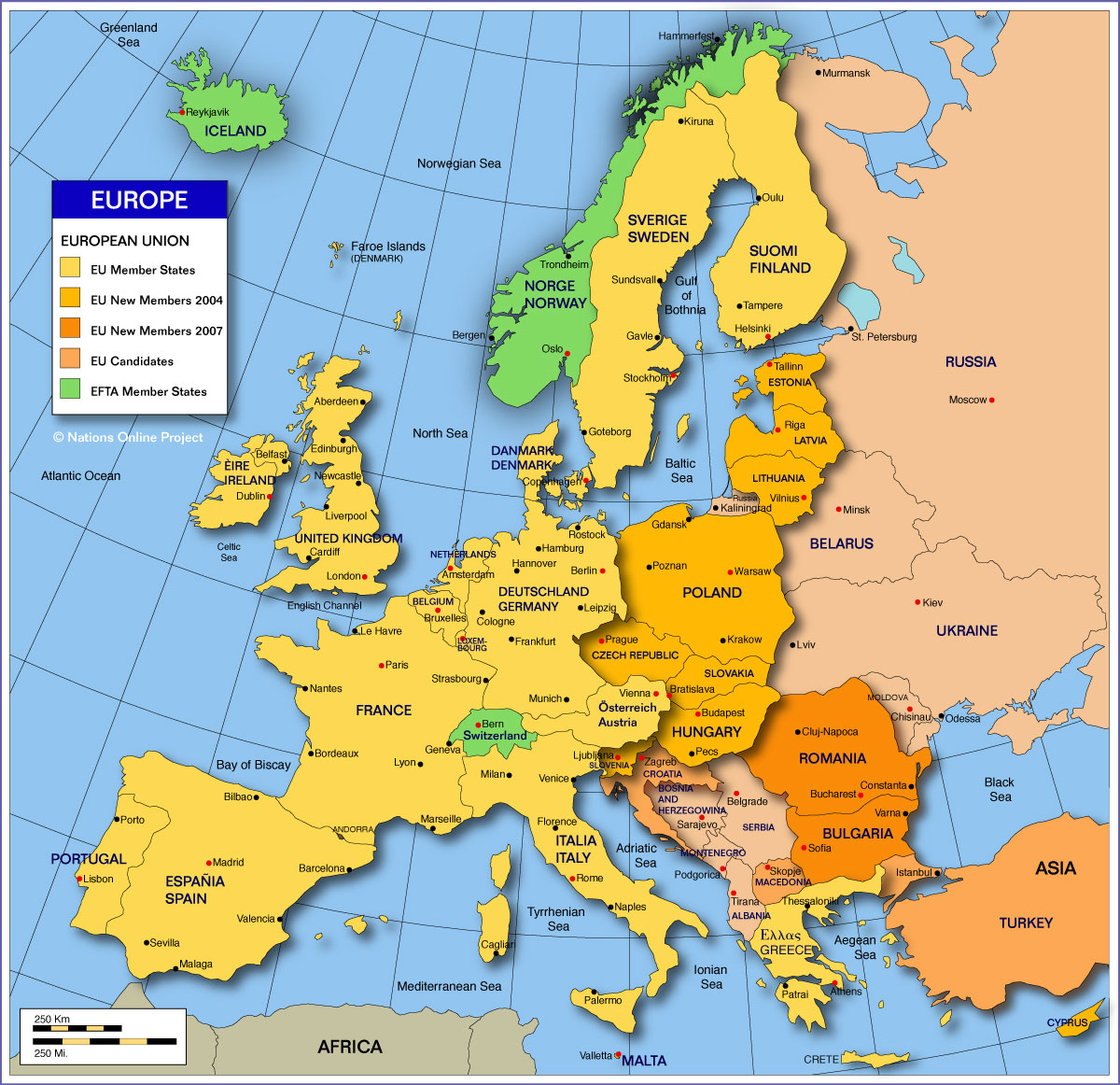
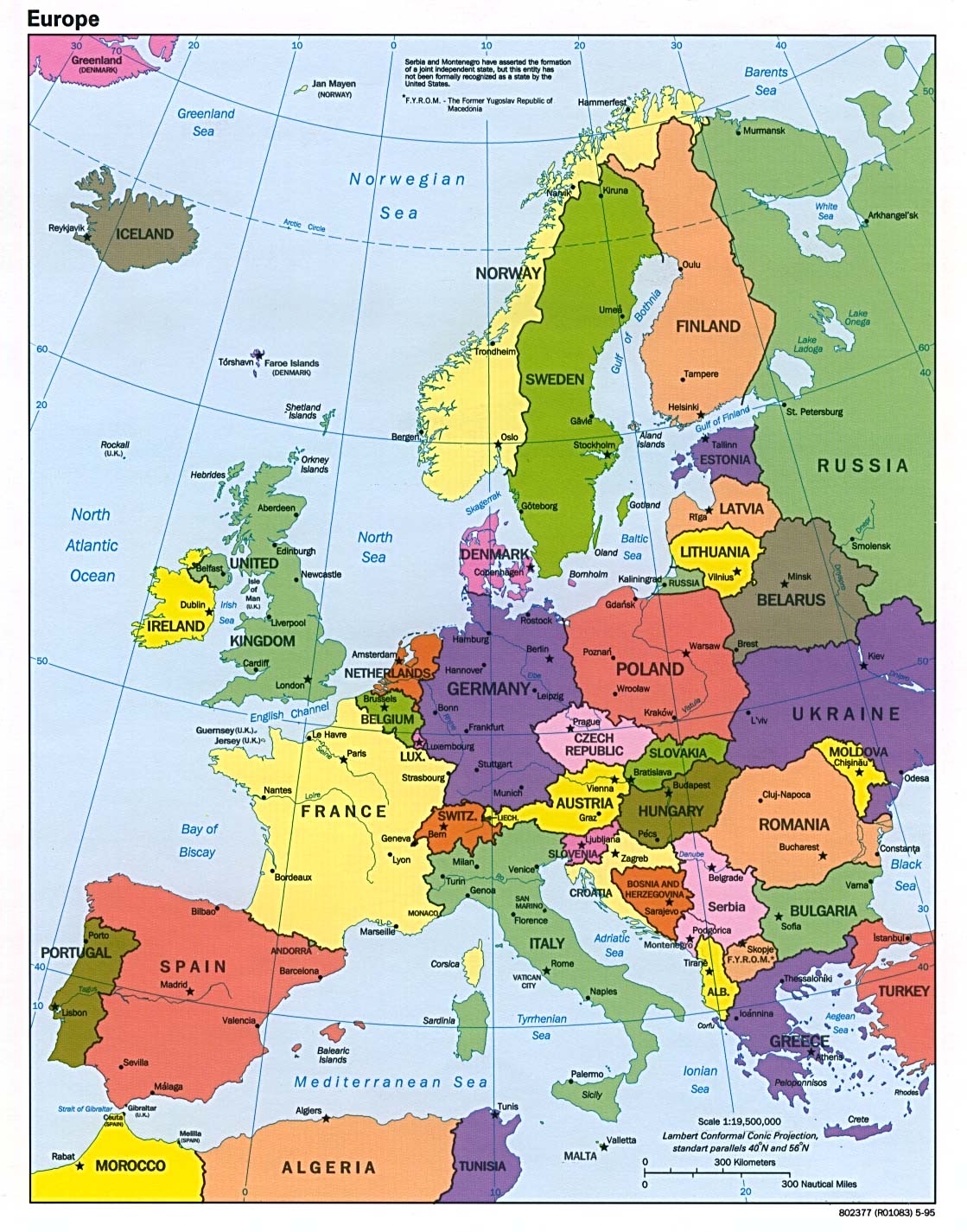
Europe, a continent steeped in history, culture, and diverse landscapes, occupies the westernmost part of the Eurasian landmass. Its geographical boundaries are fluid, often defined by cultural and political factors rather than strict geographical lines. This article explores the geographical features of Europe and its surrounding countries, highlighting their significance and interconnectedness.
The European Peninsula:
The heart of Europe lies on a vast peninsula, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea to the east. This peninsula is further divided into smaller peninsulas, each with its distinct characteristics:
- The Iberian Peninsula: Home to Spain and Portugal, this peninsula is marked by the Pyrenees Mountains in the north, the rugged terrain of the Iberian Meseta, and the fertile Andalusian plains in the south.
- The Italian Peninsula: Known for its boot-shaped coastline, the Italian Peninsula is dominated by the Apennine Mountains, which run the length of the peninsula.
- The Balkan Peninsula: This peninsula, home to countries like Greece, Bulgaria, and Romania, is characterized by its mountainous terrain and the Danube River, which flows through its northern region.
- The Scandinavian Peninsula: Comprising Norway and Sweden, this peninsula is renowned for its dramatic fjords, vast forests, and the majestic Scandinavian Mountains.
Surrounding Countries and Islands:
Beyond the European peninsula, several countries and islands are considered part of the European continent, either geographically or historically:
- Russia: The largest country in the world, Russia occupies a vast expanse of land in both Europe and Asia, with the Ural Mountains serving as a geographical dividing line. While its European portion is significant, Russia is often considered a transcontinental country.
- Turkey: Situated at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, Turkey straddles the Bosporus Strait, connecting the Black Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. While Turkey’s cultural and historical ties are deeply rooted in Europe, it is geographically considered part of Asia.
- The British Isles: Comprising the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, these islands are separated from mainland Europe by the English Channel and the North Sea.
- Iceland: Located in the North Atlantic Ocean, Iceland is a volcanic island nation with a unique landscape shaped by glaciers and volcanic activity.
The Importance of Geographical Features:
The geographical features of Europe and its surrounding countries play a significant role in shaping its history, culture, and economy:
- Mountains: Mountains like the Alps, Pyrenees, and Carpathians have historically served as natural barriers, influencing trade routes and political boundaries. They also provide valuable resources like timber and minerals and are popular destinations for tourism.
- Rivers: Major rivers like the Danube, Rhine, and Volga have facilitated trade and transportation, connecting different regions and fostering economic development. They also provide essential water resources for agriculture and industry.
- Coastlines: Europe’s extensive coastlines have played a crucial role in its maritime history, facilitating trade and exploration. They are also important for fishing, tourism, and transportation.
- Climate: Europe experiences a diverse range of climates, from the Mediterranean climate in the south to the cold, snowy climate in the north. This climate diversity has influenced the development of different agricultural practices and cultural traditions.
Understanding the Interconnectedness:
The geographical features of Europe and its surrounding countries are interconnected in various ways:
- Trade Routes: Historically, major trade routes traversed Europe and its surrounding regions, connecting different cultures and facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas.
- Migration Patterns: Throughout history, people have migrated across Europe and its surrounding regions, contributing to the diverse cultural tapestry of the continent.
- Environmental Challenges: Issues like climate change and pollution affect the entire continent, highlighting the interconnectedness of its ecosystems.
Conclusion:
The map of Europe and its surrounding countries is not simply a representation of geographical boundaries; it is a testament to the continent’s rich history, cultural diversity, and interconnectedness. Understanding the geographical features of this region is crucial for comprehending its past, present, and future. From the towering mountains to the flowing rivers, each feature contributes to the unique character of Europe and its surrounding countries, shaping their societies, economies, and cultures.
FAQs
Q: What is the largest country in Europe by land area?
A: Russia, though geographically considered a transcontinental country, is the largest country in Europe by land area.
Q: What is the smallest country in Europe?
A: Vatican City, an independent city-state located within Rome, Italy, is the smallest country in Europe.
Q: What is the most populous country in Europe?
A: Russia is also the most populous country in Europe, with a population of over 146 million people.
Q: What is the highest mountain in Europe?
A: Mount Elbrus, located in the Caucasus Mountains, is the highest mountain in Europe, with a summit elevation of 5,642 meters (18,510 feet).
Q: What is the longest river in Europe?
A: The Volga River, flowing through Russia, is the longest river in Europe, with a length of approximately 3,690 kilometers (2,294 miles).
Tips
- Use a detailed map: A detailed map of Europe and its surrounding countries can help you visualize the geographical features and understand their relationships.
- Explore different map types: Different map types, such as physical maps, political maps, and thematic maps, can provide different insights into the region.
- Research specific regions: Focus on specific regions of interest, such as the Balkans, the Scandinavian Peninsula, or the British Isles, to gain a deeper understanding of their unique characteristics.
- Consider historical context: Understanding the historical context of geographical features can provide valuable insights into their significance.
- Connect with other disciplines: Explore connections between geography and other disciplines, such as history, economics, and culture.
Conclusion:
The map of Europe and its surrounding countries is a valuable tool for understanding the continent’s complex and interconnected landscape. By studying its geographical features, we can gain insights into its history, culture, and ongoing challenges, fostering a deeper appreciation for this diverse and dynamic region.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Overview of Europe and its Surrounding Countries. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
