3, Jan 2024
A Journey Through Africa: Exploring The Continent’s Geography And Diversity
A Journey Through Africa: Exploring the Continent’s Geography and Diversity
Related Articles: A Journey Through Africa: Exploring the Continent’s Geography and Diversity
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Africa: Exploring the Continent’s Geography and Diversity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Africa: Exploring the Continent’s Geography and Diversity

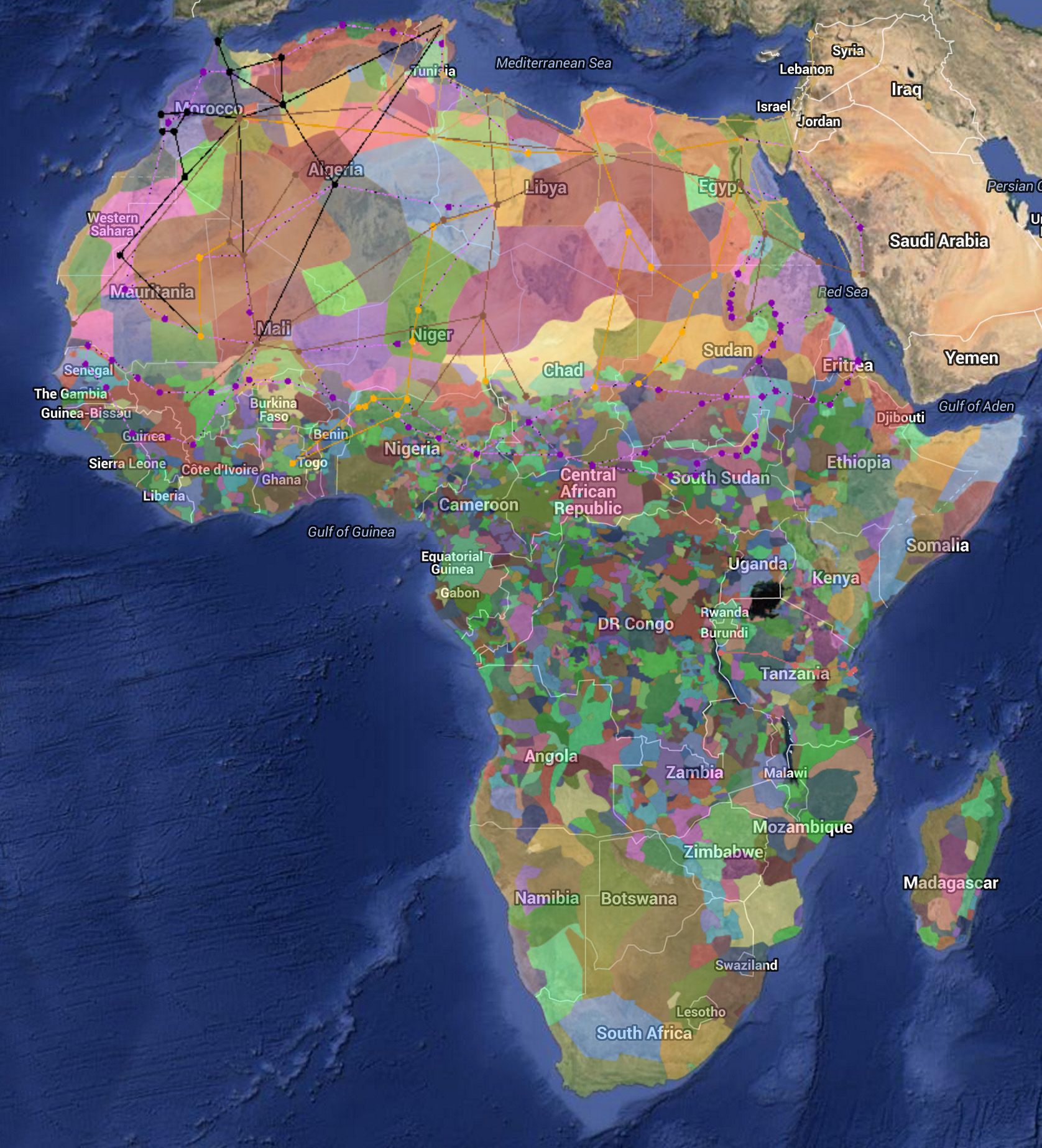
Africa, the second-largest continent on Earth, is a land of immense diversity, boasting a rich tapestry of cultures, landscapes, and ecosystems. Understanding the continent’s geography, including its intricate network of countries and the surrounding oceans, is crucial for appreciating its history, present-day challenges, and potential for the future. This article delves into the intricate map of Africa, providing a comprehensive overview of its countries, oceans, and their profound significance.
A Mosaic of Nations:
Africa is home to 54 sovereign states, each with its unique identity and history. The continent’s diverse geography has shaped its political boundaries, leading to a complex patchwork of nations. The northern region is dominated by the vast Sahara Desert, while the southern portion features the iconic savannas and rainforests. Coastal regions are characterized by diverse ecosystems, from mangrove swamps to vibrant coral reefs.
Delving Deeper into the Countries:
- North Africa: This region, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, is home to countries such as Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Egypt. These nations share a rich history, influenced by Arab and Berber cultures. The region is characterized by vast deserts and fertile oases.
- West Africa: West Africa is a region of immense cultural and economic diversity. Countries like Senegal, Mali, Ghana, Nigeria, and Côte d’Ivoire are prominent members. The region boasts a rich history of trade, influenced by the trans-Saharan trade routes and the Atlantic slave trade.
- Central Africa: This region, encompassing countries like Cameroon, Gabon, the Democratic Republic of Congo, and the Republic of Congo, is renowned for its dense rainforests and abundant biodiversity. It is also home to the Congo Basin, the world’s second-largest rainforest.
- East Africa: East Africa is a region of dramatic landscapes, including the Great Rift Valley, Mount Kilimanjaro, and the Serengeti National Park. It is home to countries such as Ethiopia, Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, and Rwanda, each with its unique cultural heritage.
- Southern Africa: Southern Africa encompasses countries like South Africa, Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, and Mozambique. The region is characterized by diverse landscapes, from the arid Kalahari Desert to the lush Drakensberg Mountains.
The Encircling Oceans:
Africa is surrounded by three major oceans: the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and the Mediterranean Sea. These bodies of water have played a pivotal role in shaping the continent’s history, culture, and economy.
- The Atlantic Ocean: The Atlantic Ocean forms the western boundary of Africa, influencing the continent’s climate and coastal ecosystems. It has been a vital trade route for centuries, connecting Africa to Europe and the Americas.
- The Indian Ocean: The Indian Ocean forms the eastern boundary of Africa, influencing the climate of the eastern and southern regions. It has been a major trading route for centuries, connecting Africa to Asia and the Middle East.
- The Mediterranean Sea: The Mediterranean Sea forms the northern boundary of Africa, influencing the climate and culture of North Africa. It has been a significant trade route for millennia, connecting Africa to Europe and Asia.
The Significance of the Map:
The map of Africa, with its intricate network of countries and surrounding oceans, is a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s diverse geography, history, and challenges. It highlights the interconnectedness of African nations and their relationship with the global community. By studying the map, we can gain insights into:
- Cultural Diversity: The map reveals the vast cultural diversity of Africa, showcasing the unique traditions, languages, and beliefs of its various nations.
- Economic Development: The map provides a visual representation of the continent’s economic landscape, highlighting key industries, trade routes, and areas of potential growth.
- Environmental Challenges: The map helps us understand the environmental challenges facing Africa, including deforestation, desertification, and climate change.
- Political Landscape: The map showcases the political landscape of Africa, highlighting the diverse political systems, regional alliances, and potential areas of conflict.
- Resource Distribution: The map reveals the distribution of natural resources across the continent, including minerals, oil, and water, which are vital for economic development.
FAQs about the Map of Africa:
1. What is the largest country in Africa by land area?
The largest country in Africa by land area is Algeria, with a total area of 2,381,741 square kilometers.
2. Which African country has the longest coastline?
The African country with the longest coastline is Somalia, with a total coastline of approximately 3,333 kilometers.
3. What is the highest point in Africa?
The highest point in Africa is Mount Kilimanjaro, located in Tanzania, with a summit elevation of 5,895 meters.
4. What are the main rivers in Africa?
Some of the major rivers in Africa include the Nile River, the Congo River, the Niger River, and the Zambezi River.
5. What are the main deserts in Africa?
The main deserts in Africa are the Sahara Desert, the Namib Desert, and the Kalahari Desert.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Africa:
- Use a detailed map: A detailed map with clear country borders, major cities, and geographical features is essential for a comprehensive understanding.
- Study the physical features: Pay attention to mountains, rivers, lakes, and deserts, as these features have significantly shaped the continent’s history and development.
- Explore the cultural diversity: Research the various cultures, languages, and traditions of African nations to gain a deeper appreciation for the continent’s rich heritage.
- Focus on economic activities: Identify key industries, trade routes, and areas of economic potential to understand the continent’s economic landscape.
- Analyze environmental challenges: Consider the environmental challenges facing Africa, including climate change, deforestation, and desertification.
Conclusion:
The map of Africa is a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s diverse geography, history, and challenges. By studying the map and its intricate network of countries and surrounding oceans, we gain a deeper appreciation for the continent’s rich cultural heritage, its unique landscapes, and its immense potential for the future. The map serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of African nations and their shared responsibility for preserving the continent’s natural resources and promoting sustainable development.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Africa: Exploring the Continent’s Geography and Diversity. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
