21, May 2024
A Journey Through The Eastern European Landscape: Understanding The Map And Its Significance
A Journey Through the Eastern European Landscape: Understanding the Map and Its Significance
Related Articles: A Journey Through the Eastern European Landscape: Understanding the Map and Its Significance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through the Eastern European Landscape: Understanding the Map and Its Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through the Eastern European Landscape: Understanding the Map and Its Significance
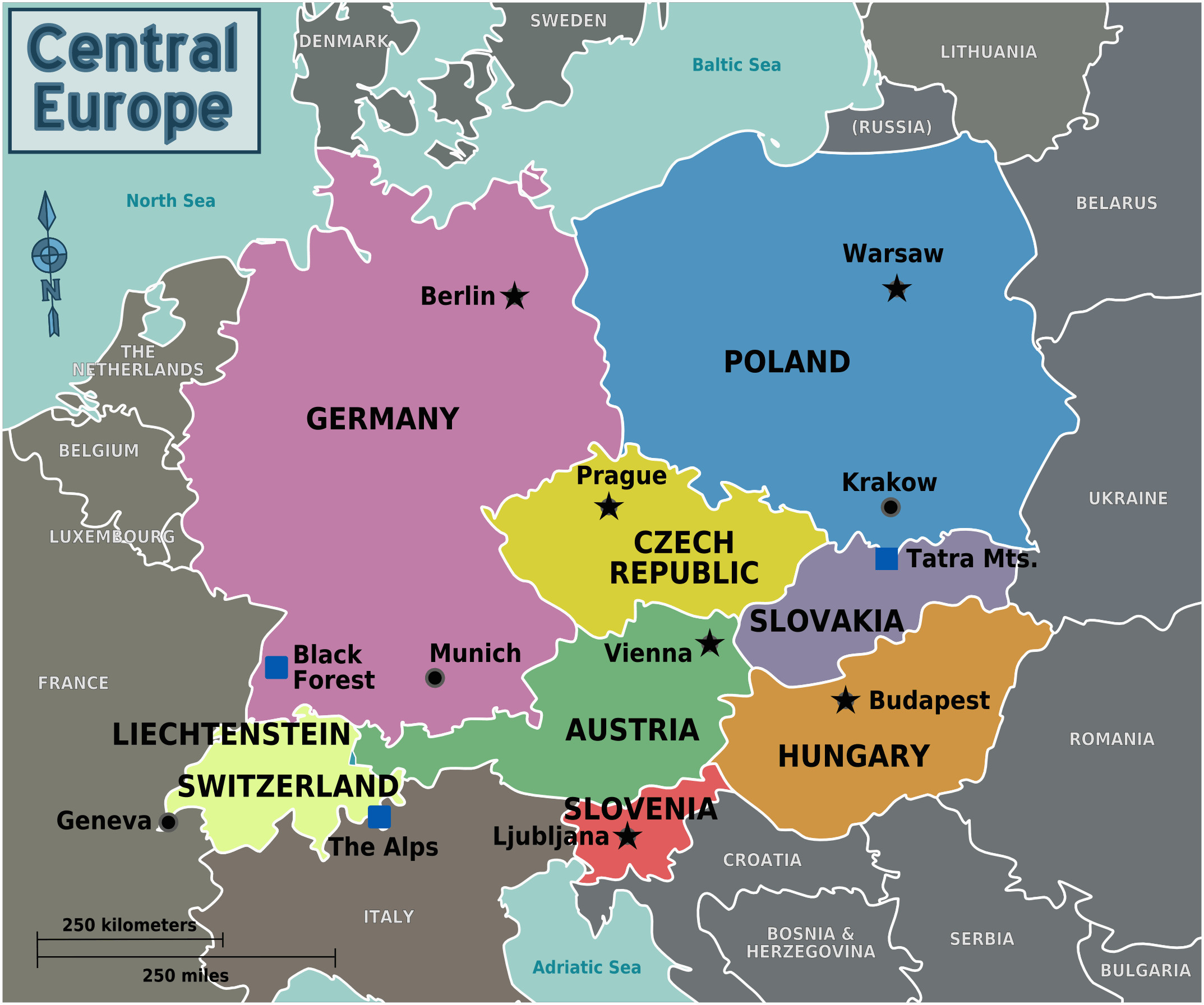
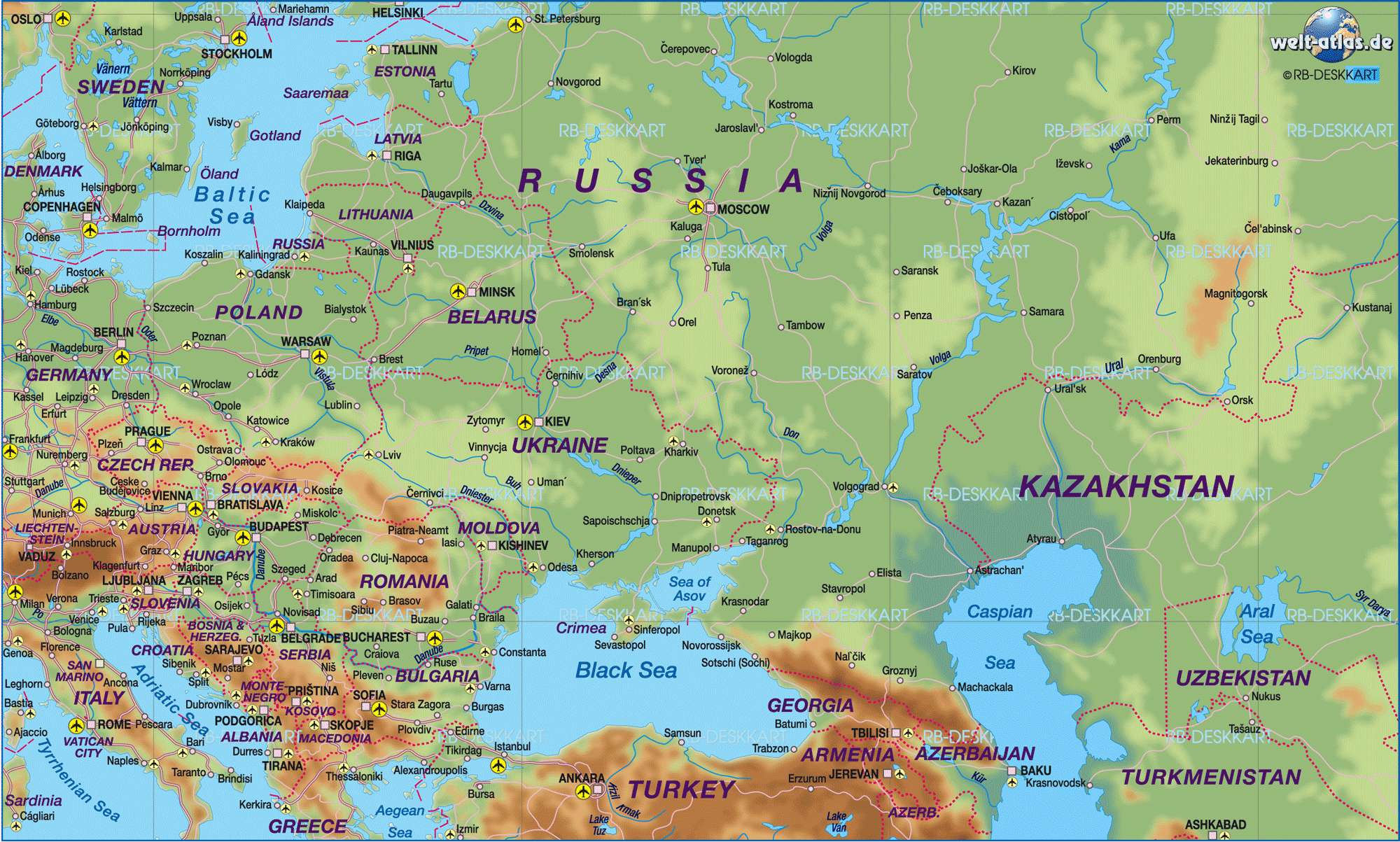
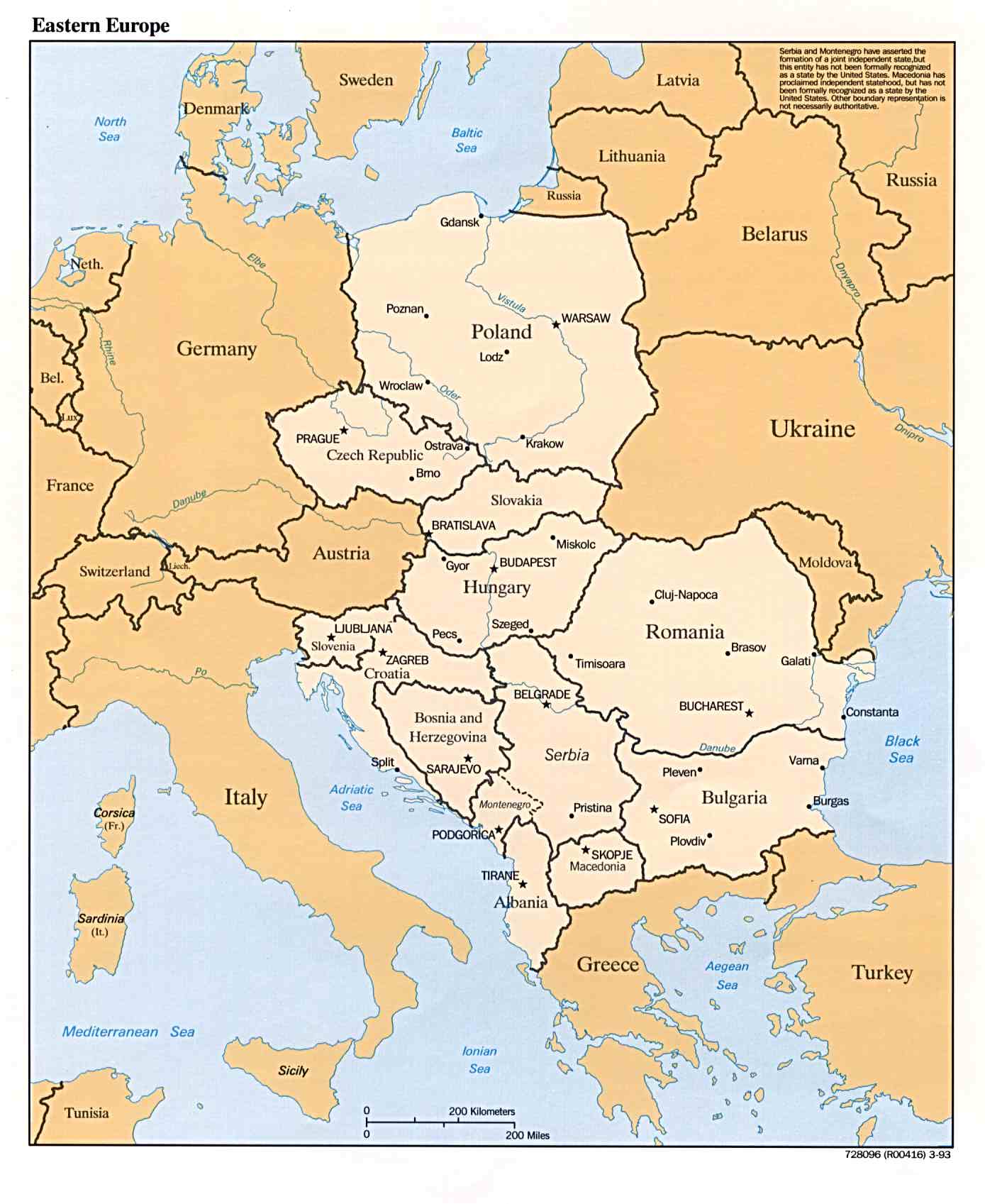
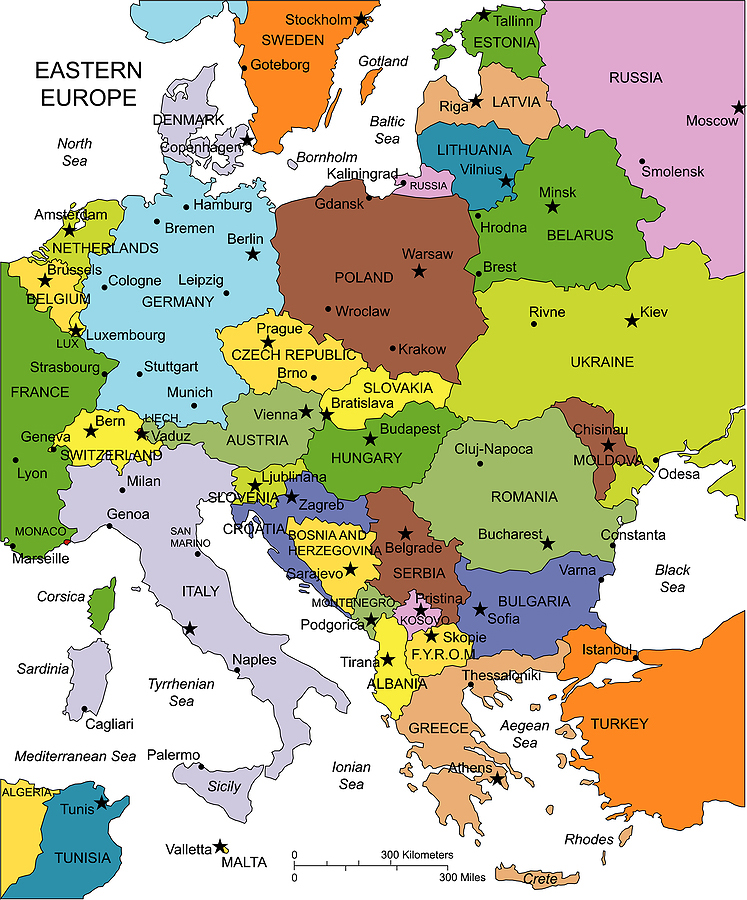
The Eastern European landscape, a tapestry woven with rich history, diverse cultures, and breathtaking natural beauty, presents a unique geographical and political puzzle. Understanding the Eastern European map is crucial for navigating its intricacies, appreciating its complexities, and recognizing its profound impact on global affairs.
Defining Eastern Europe: A Geographical and Historical Perspective
Defining Eastern Europe is a nuanced process, as the term itself carries historical, cultural, and political baggage. While geographical boundaries can be objectively defined, the region’s identity is fluid, shaped by shifting alliances, historical events, and evolving cultural narratives.
Geographical Boundaries:
Traditionally, Eastern Europe is considered to encompass the countries east of Germany and the Baltic Sea, stretching to the Ural Mountains and the Black Sea. This geographical definition includes:
- Baltic States: Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania
- Eastern Slavic States: Belarus, Ukraine, Russia (partially)
- Central European States: Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary
- Southeastern European States: Romania, Moldova, Bulgaria
Historical and Political Considerations:
However, the "Eastern European" label has been historically intertwined with the political and economic systems of the Soviet Union and its satellite states. The fall of the Soviet Union in 1991 marked a significant shift, leading to the emergence of new independent nations and the redefinition of Eastern Europe’s identity.
The Impact of the Soviet Era:
The Soviet era left a lasting imprint on the Eastern European landscape. The region’s political, economic, and social structures were heavily influenced by Soviet ideology and policies. This influence is evident in the region’s infrastructure, industrial development, and cultural landscape.
Post-Soviet Transition and the European Union:
The fall of the Soviet Union ushered in a period of transition, with many Eastern European countries seeking integration into the European Union (EU). This process has brought economic prosperity, political stability, and cultural exchange, but it has also presented challenges, particularly in terms of economic disparities and social adjustments.
Understanding the Eastern European Map: A Key to Navigating the Region’s Complexities
The Eastern European map is not merely a collection of lines and borders; it represents a dynamic region with a rich history, diverse cultures, and unique challenges. Examining the map allows us to:
- Identify key geographical features: The map reveals the region’s vast plains, rolling hills, and extensive river systems, highlighting its natural resources and agricultural potential.
- Analyze historical connections: The map provides insights into historical migrations, empires, and conflicts that have shaped the region’s cultural tapestry.
- Understand political affiliations: The map showcases the region’s diverse political landscape, including its membership in the EU, NATO, and other international organizations.
- Recognize economic disparities: The map highlights the economic differences between countries, reflecting their historical development, access to resources, and participation in global markets.
- Appreciate cultural diversity: The map underscores the region’s vibrant cultural heritage, encompassing a multitude of languages, religions, and artistic traditions.
Navigating the Eastern European Map: A Journey of Exploration and Understanding
Exploring the Eastern European map is an engaging journey, offering insights into the region’s past, present, and future. By delving into its details, we can:
- Trace the footsteps of history: From the ancient civilizations of the Black Sea region to the medieval empires of the Balkans, the map reveals the region’s rich history and the diverse influences that have shaped its identity.
- Discover vibrant cultures: The map invites us to explore the region’s vibrant cultural mosaic, encountering diverse languages, traditions, and artistic expressions.
- Witness the rise of new identities: The map showcases the emergence of new national identities and the region’s ongoing quest for self-determination.
- Explore the challenges of integration: The map reveals the complexities of the region’s integration into the EU and the challenges of reconciling national identities with European aspirations.
- Engage with the future: The map provides a framework for understanding the region’s potential and the challenges it faces in navigating the complexities of the 21st century.
FAQs by Eastern European Countries Map
1. What is the largest country in Eastern Europe?
The largest country in Eastern Europe is Ukraine, with a land area of approximately 603,628 square kilometers.
2. Which Eastern European countries are members of the European Union?
The following Eastern European countries are members of the European Union:
- Baltic States: Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania
- Central European States: Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary
- Southeastern European States: Romania, Bulgaria
3. What are the major languages spoken in Eastern Europe?
The major languages spoken in Eastern Europe include:
- Slavic Languages: Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian, Polish, Czech, Slovak, Slovene, Serbian, Croatian, Bulgarian, Macedonian
- Baltic Languages: Estonian, Latvian, Lithuanian
- Hungarian
- Romanian
- Moldovan
4. What are the major religions practiced in Eastern Europe?
The major religions practiced in Eastern Europe include:
- Eastern Orthodox Christianity: Predominant in Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Bulgaria, Romania, Moldova, Serbia, Montenegro, North Macedonia
- Roman Catholicism: Predominant in Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Lithuania, Latvia, Croatia, Slovenia
- Protestantism: Significant in Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Romania
- Islam: Significant in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Albania, Kosovo, Bulgaria, Turkey (partially)
- Judaism: Historically significant in many Eastern European countries, with a smaller but still vibrant presence today
5. What are the major economic sectors in Eastern Europe?
The major economic sectors in Eastern Europe include:
- Agriculture: A significant sector in many countries, particularly Ukraine and Romania
- Manufacturing: A growing sector, with strong automotive, electronics, and aerospace industries
- Tourism: A rapidly developing sector, particularly in countries like Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, and Croatia
- Energy: A crucial sector, with significant reserves of oil, gas, and coal in Russia and Ukraine
Tips by Eastern European Countries Map
- Start with a basic understanding of geographical boundaries: Familiarize yourself with the key countries and their locations on the map.
- Explore historical maps: Examining historical maps can provide insights into the region’s shifting borders, empires, and cultural influences.
- Read about the region’s history and culture: Gaining knowledge about the region’s rich history and diverse cultures will enhance your understanding of the map.
- Consider the political context: Analyze the map in relation to the region’s political landscape, including its membership in international organizations.
- Look for patterns and connections: Identify geographical features, historical events, and cultural influences that connect different parts of the region.
- Engage with the people: Traveling to Eastern Europe and interacting with its people can provide invaluable firsthand experiences and deepen your understanding of the map.
Conclusion by Eastern European Countries Map
The Eastern European map is a powerful tool for understanding the region’s unique complexities. By delving into its details, we can gain insights into its rich history, diverse cultures, and ongoing transformations. The map serves as a gateway to a vibrant region with a fascinating past and a promising future, inviting us to explore its landscapes, embrace its cultural richness, and engage with its people. Through a deeper understanding of the Eastern European map, we can foster appreciation for this dynamic region and its vital role in shaping the global landscape.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through the Eastern European Landscape: Understanding the Map and Its Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
