6, Jan 2024
A Journey Through Time: Understanding The Volcanic Landscape Of New Mexico
A Journey Through Time: Understanding the Volcanic Landscape of New Mexico
Related Articles: A Journey Through Time: Understanding the Volcanic Landscape of New Mexico
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Time: Understanding the Volcanic Landscape of New Mexico. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Time: Understanding the Volcanic Landscape of New Mexico
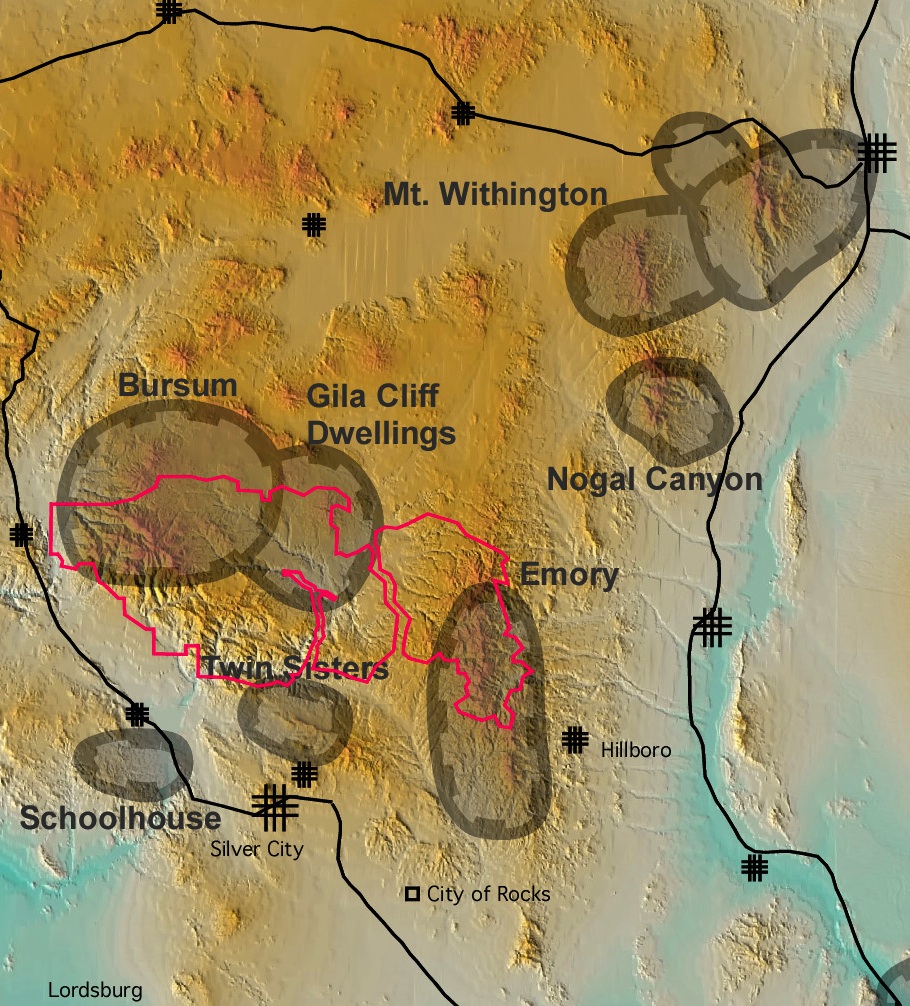
New Mexico, a state renowned for its diverse landscapes and rich history, harbors a secret beneath its surface: a volcanic past that continues to shape its present. The state’s geological history is intricately woven with volcanic activity, leaving behind a tapestry of dormant volcanoes, lava flows, and volcanic ash deposits. Understanding this history requires a careful examination of the New Mexico Volcano Map, a vital tool for comprehending the state’s unique landscape and its potential for future volcanic activity.
A Glimpse into the Past: New Mexico’s Volcanic History
The volcanic landscape of New Mexico is a testament to the dynamic forces that have shaped the Earth for millions of years. The state’s volcanic history spans a vast timeframe, from the ancient Precambrian era to the relatively recent Quaternary period. This history is evident in the diverse volcanic features that dot the state, ranging from towering volcanic peaks to vast fields of volcanic ash.
-
Precambrian Era: The earliest volcanic activity in New Mexico occurred during the Precambrian era, over 540 million years ago. This period witnessed the formation of the Zuni-San Juan volcanic field, a vast area characterized by ancient volcanic rocks and remnants of extinct volcanoes.
-
Mesozoic Era: During the Mesozoic era, approximately 250 to 66 million years ago, volcanic activity continued in New Mexico. This period saw the formation of the Jemez Mountains, a region dominated by volcanic features like the Valles Caldera, a massive volcanic crater formed by a catastrophic eruption.
-
Cenozoic Era: The Cenozoic era, spanning the last 66 million years, saw a resurgence of volcanic activity in New Mexico. This period witnessed the eruption of numerous volcanoes, including the iconic Mount Taylor, the state’s highest peak, and the Raton-Clayton volcanic field, a region characterized by cinder cones and lava flows.
The New Mexico Volcano Map: A Window into the State’s Volcanic Past
The New Mexico Volcano Map serves as a vital tool for understanding the state’s volcanic history and its potential for future volcanic activity. It provides a detailed overview of the location and types of volcanic features present in the state, offering valuable insights into the geological processes that have shaped the landscape.
-
Identifying Volcanic Features: The map clearly identifies various volcanic features, such as volcanoes, lava flows, ash deposits, and volcanic vents. This information allows researchers and scientists to study the distribution and characteristics of volcanic activity throughout the state’s history.
-
Understanding Volcanic Hazards: The map highlights areas prone to volcanic hazards, such as lava flows, ashfall, and volcanic gases. This information is crucial for planning mitigation strategies and ensuring public safety in case of future eruptions.
-
Analyzing Volcanic Activity: The map provides valuable data for analyzing volcanic activity patterns, identifying areas of potential future eruptions, and understanding the processes that drive volcanic events. This information is vital for monitoring volcanic activity and predicting potential hazards.
The Importance of the New Mexico Volcano Map
The New Mexico Volcano Map plays a crucial role in various aspects of life in the state, impacting the following:
-
Resource Management: The map helps identify areas with potential geothermal energy resources, providing valuable information for sustainable energy development.
-
Land Use Planning: The map guides land use planning by identifying areas with potential volcanic hazards, ensuring safe and sustainable development.
-
Disaster Preparedness: The map provides vital information for disaster preparedness, allowing authorities to develop effective response strategies and evacuation plans in case of volcanic eruptions.
-
Scientific Research: The map serves as a valuable tool for scientists studying volcanic processes, providing essential data for understanding the Earth’s dynamic nature.
FAQs about the New Mexico Volcano Map
1. Are there any active volcanoes in New Mexico?
While no volcanoes in New Mexico are currently erupting, some are considered potentially active, meaning they have the potential to erupt in the future. The Jemez Mountains Volcanic Field, including the Valles Caldera, is one such area.
2. How often do volcanoes erupt in New Mexico?
Volcanic eruptions in New Mexico are relatively infrequent, but they have occurred throughout history. The most recent eruption is estimated to have occurred about 600 years ago in the Raton-Clayton volcanic field.
3. What are the potential hazards associated with volcanic eruptions in New Mexico?
Potential hazards associated with volcanic eruptions in New Mexico include lava flows, ashfall, volcanic gases, and pyroclastic flows. These hazards can pose significant risks to human life, infrastructure, and the environment.
4. What are the signs of an impending volcanic eruption?
Signs of an impending volcanic eruption can include increased seismic activity, ground deformation, changes in gas emissions, and changes in heat flow. Monitoring these parameters helps scientists predict and prepare for potential eruptions.
5. How can I stay informed about volcanic activity in New Mexico?
The New Mexico Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources (NMBGMR) provides updates on volcanic activity and hazards. You can access their website and social media platforms for the latest information and resources.
Tips for Using the New Mexico Volcano Map
- Understand the map’s symbols and legends: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and legends used on the map to interpret the information accurately.
- Identify areas of volcanic activity: Locate areas on the map where volcanic features are present, such as volcanoes, lava flows, and ash deposits.
- Assess potential hazards: Determine potential hazards associated with volcanic activity in different areas, such as lava flows, ashfall, and volcanic gases.
- Consult additional resources: Use the map in conjunction with other resources, such as scientific reports and online databases, for a more comprehensive understanding.
- Stay informed about volcanic activity: Regularly check for updates on volcanic activity from official sources like the NMBGMR.
Conclusion
The New Mexico Volcano Map is a valuable tool for understanding the state’s volcanic history, identifying potential hazards, and promoting safe and sustainable development. By utilizing this map, researchers, scientists, policymakers, and the public can gain valuable insights into the dynamic forces that have shaped the state’s unique landscape and prepare for potential future volcanic activity. The map serves as a reminder of the Earth’s constant evolution and the importance of understanding and respecting its power.

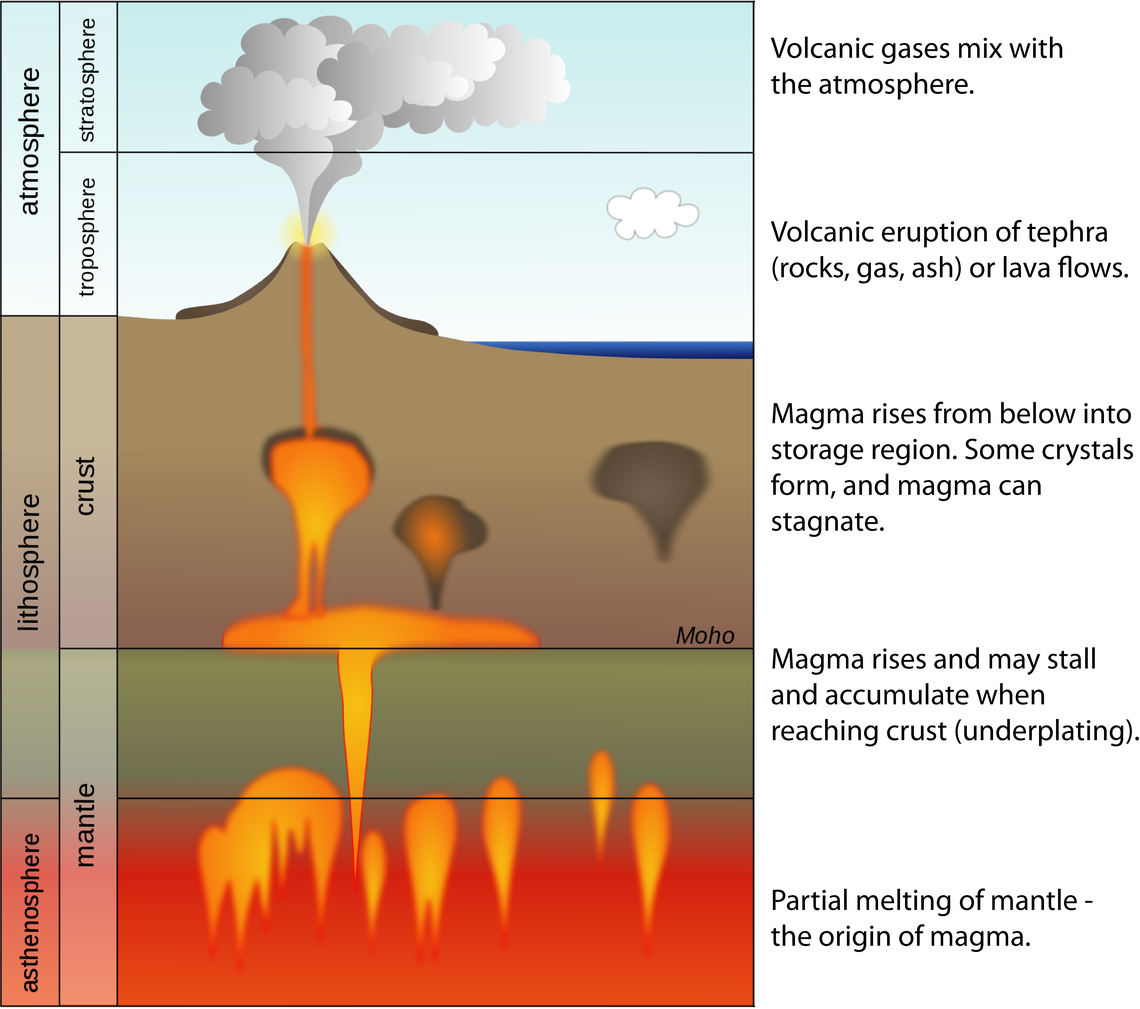






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Time: Understanding the Volcanic Landscape of New Mexico. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
