7, Mar 2024
A Look Beyond The EU: Understanding Europe’s Non-Member States
A Look Beyond the EU: Understanding Europe’s Non-Member States
Related Articles: A Look Beyond the EU: Understanding Europe’s Non-Member States
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Look Beyond the EU: Understanding Europe’s Non-Member States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Look Beyond the EU: Understanding Europe’s Non-Member States
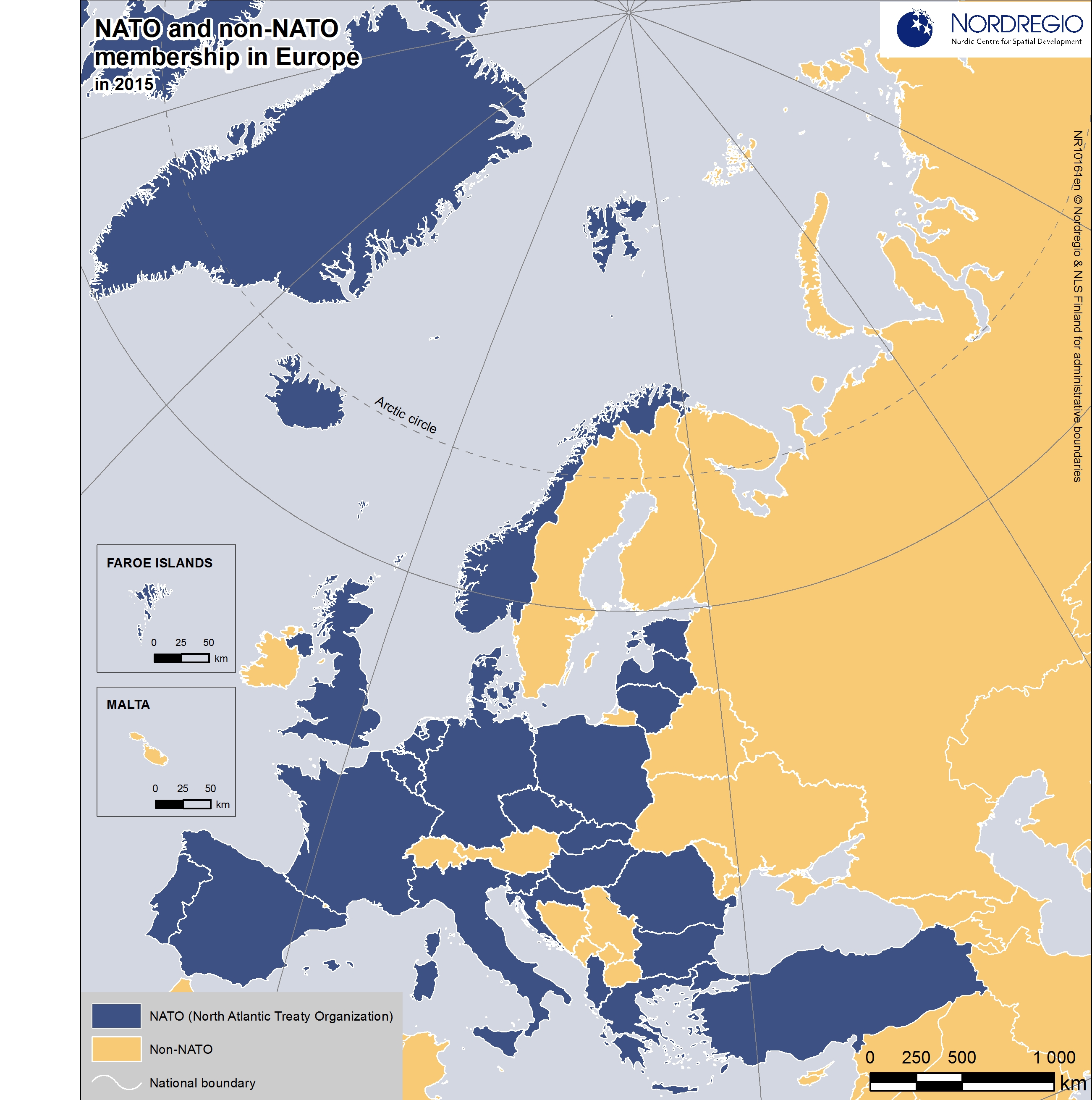
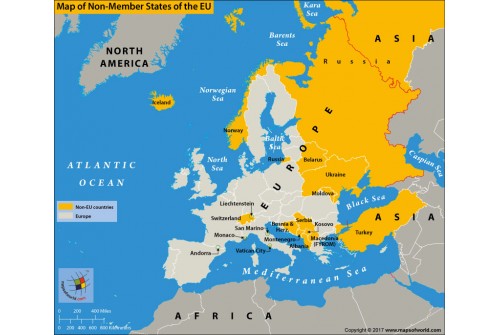
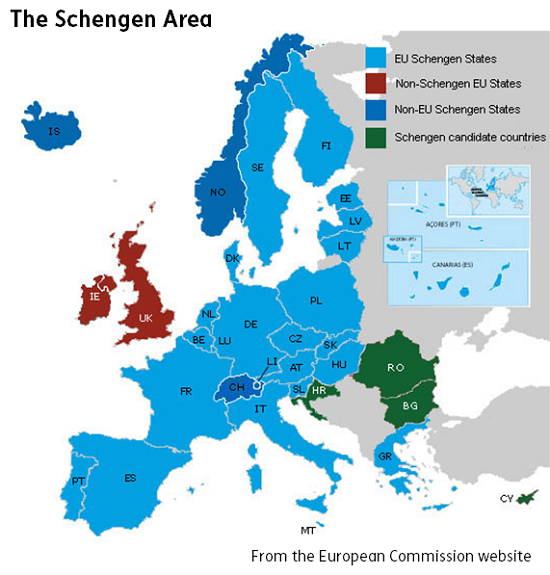
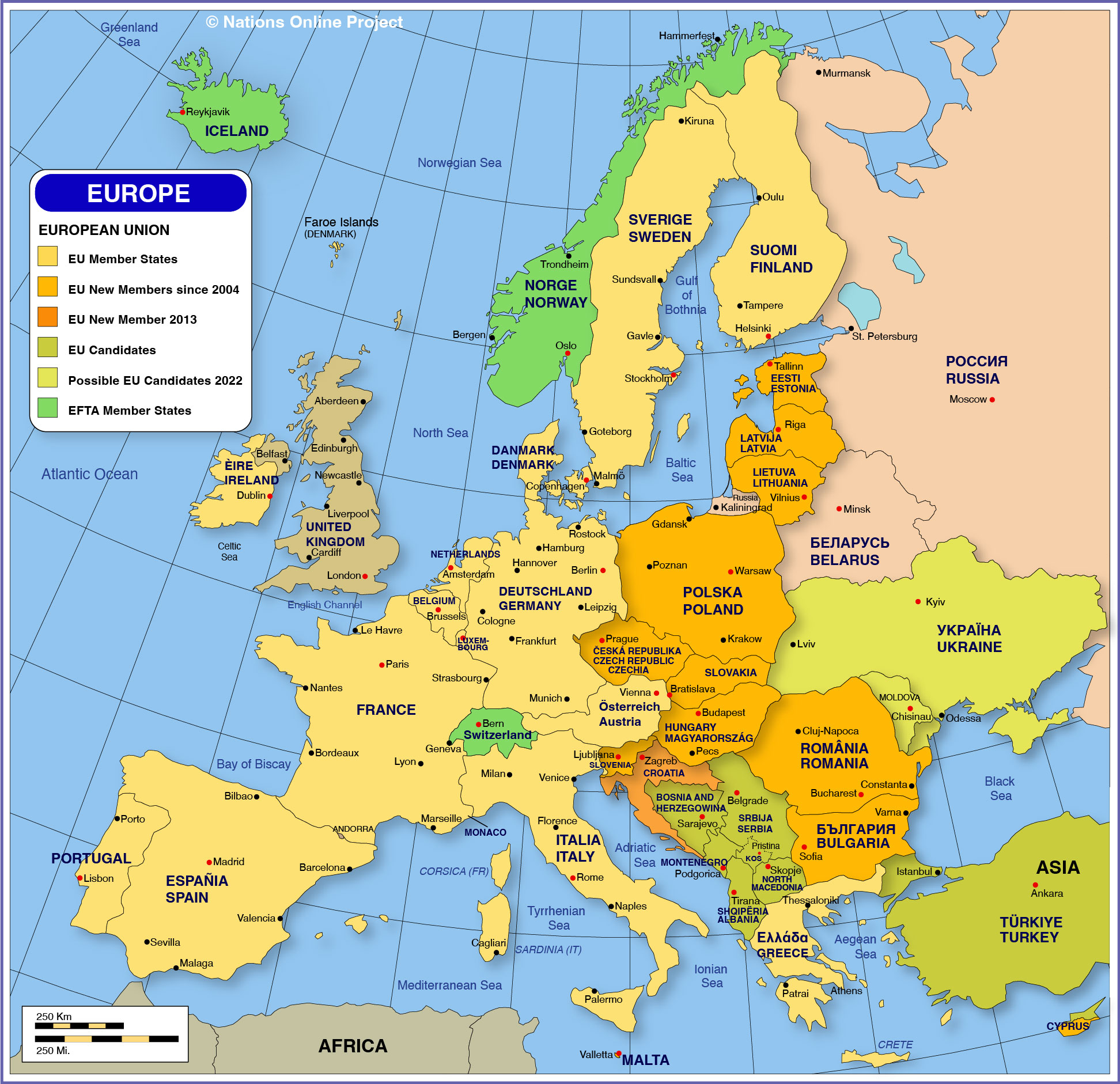
The European Union (EU) is a prominent force in contemporary Europe, encompassing 27 member states. However, a significant number of countries within the continent remain outside the Union, each possessing unique historical, cultural, and political identities. Understanding the geographical and political landscape of these non-EU countries is crucial for comprehending the complexities of modern Europe.
Mapping Europe’s Diversity: A Geographical Perspective
A map of Europe excluding EU member states reveals a diverse array of nations scattered across the continent:
-
The Western Balkans: This region, situated in southeastern Europe, includes Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, and Serbia. These countries are characterized by their turbulent past, marked by conflict and the transition from communist rule. While some, like Montenegro, have expressed interest in EU membership, others face significant political and economic challenges hindering their path towards accession.
-
The Caucasus: Located at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, the Caucasus region is home to Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia. These countries share a rich history and cultural heritage, but also grapple with complex geopolitical dynamics, including territorial disputes and lingering ethnic tensions. While Azerbaijan and Georgia have pursued closer ties with the EU, Armenia maintains a delicate balance between its strategic partnership with Russia and its aspirations for European integration.
-
The Eastern Partnership: This initiative, launched by the EU in 2009, aims to strengthen ties with six countries in Eastern Europe: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Moldova, and Ukraine. While the initiative has fostered economic and political cooperation, the region remains politically volatile, with Russia exerting significant influence. Ukraine’s ongoing conflict with Russia has further complicated the political landscape, highlighting the challenges of navigating between East and West.
-
Other Non-EU States: Several other countries in Europe remain outside the EU, including:
- Iceland: A Nordic island nation, known for its stunning natural beauty and strong economic performance, Iceland has chosen to maintain its sovereignty and independence outside the EU.
- Norway: A prosperous nation with a strong social welfare system, Norway opted out of EU membership in 1994, preferring to maintain control over its natural resources and fishing rights.
- Switzerland: A highly developed and neutral country, Switzerland has long maintained a policy of non-alignment, choosing to prioritize its own national interests over EU membership.
- Turkey: A strategically important country spanning Europe and Asia, Turkey’s accession process has stalled due to concerns over human rights, democracy, and rule of law.
- Russia: A major geopolitical power with a vast territory spanning Europe and Asia, Russia has a complex relationship with the EU, marked by periods of cooperation and tension.
The Importance of Understanding Non-EU Countries
Understanding the political, economic, and social realities of non-EU countries is crucial for several reasons:
-
Regional Security and Stability: The stability of the European continent is intricately linked to the well-being of all its nations, including those outside the EU. Conflicts or instability in non-EU countries can have significant spillover effects, impacting regional security and economic prosperity.
-
Economic Cooperation and Integration: Non-EU countries play a vital role in the European economy, serving as trading partners and sources of investment. Strengthening economic ties with these countries can benefit both sides, fostering economic growth and prosperity.
-
Cultural Exchange and Diversity: Europe’s rich cultural heritage is shaped by the diversity of its nations. Engaging with non-EU countries promotes cultural exchange, fostering understanding and tolerance.
-
Global Diplomacy and Cooperation: Non-EU countries often play key roles in international affairs, contributing to global security, development, and peace. Maintaining strong relationships with these countries is essential for promoting international cooperation and tackling global challenges.
Navigating the Complexities: FAQs about Non-EU Countries
Q: Why do some European countries choose not to join the EU?
A: Reasons for remaining outside the EU vary widely, ranging from historical and cultural factors to economic concerns and political considerations. Some countries, like Switzerland, value their neutrality and independence. Others, like Norway, prioritize control over their natural resources. In some cases, political and economic reforms required for EU membership may be perceived as too challenging or undesirable.
Q: What are the benefits of being a non-EU member?
A: Non-EU membership offers certain advantages, including:
- Sovereignty and Independence: Non-EU countries retain full control over their domestic policies and decision-making processes.
- Flexibility in Trade and Economic Policies: Non-EU members are not bound by EU regulations and can tailor their economic policies to their specific needs.
- Control over Natural Resources: Non-EU countries retain full control over their natural resources, including fishing rights and energy reserves.
Q: What are the challenges faced by non-EU countries?
A: Non-EU membership also presents certain challenges:
- Limited Access to EU Markets: Non-EU countries may face trade barriers and restrictions when exporting goods and services to the EU.
- Exclusion from EU Funding and Programs: Non-EU members are not eligible for EU funding and programs, which can limit their access to resources for development and innovation.
- Potential for Political Isolation: Non-EU countries may face difficulties participating in EU decision-making processes and influencing EU policies.
Q: What is the future of non-EU countries in Europe?
A: The future of non-EU countries in Europe is uncertain and subject to ongoing political and economic developments. Some countries, like North Macedonia and Albania, are actively pursuing EU membership, while others, like Switzerland and Norway, have chosen to remain outside the Union. The future relationship between the EU and non-EU countries will depend on a range of factors, including:
- The EU’s Enlargement Policy: The EU’s willingness to expand its membership will have a significant impact on the future of non-EU countries.
- Economic and Political Developments: Economic growth, political stability, and democratic reforms in non-EU countries will influence their relationship with the EU.
- Geopolitical Dynamics: The changing geopolitical landscape, including the rise of China and Russia, will also shape the future of non-EU countries in Europe.
Tips for Understanding Non-EU Countries in Europe
- Engage with Diverse Perspectives: Seek out information from a variety of sources, including academic research, news reports, and firsthand accounts from individuals living in non-EU countries.
- Focus on Context: Understand the historical, cultural, and political context that shapes the experiences of non-EU countries.
- Embrace Complexity: Recognize that the relationship between the EU and non-EU countries is complex and multifaceted, with no simple solutions or generalizations.
- Encourage Dialogue: Engage in discussions and debates about the future of Europe, recognizing the importance of collaboration and understanding between all its nations.
Conclusion: A Europe of Interdependence
The map of Europe excluding EU member states reveals a diverse and dynamic continent. These non-EU countries play a vital role in shaping the political, economic, and cultural landscape of Europe. Understanding their unique perspectives, challenges, and aspirations is crucial for fostering cooperation, promoting stability, and building a more inclusive and prosperous future for all European nations. The future of Europe lies in embracing interdependence, recognizing the shared interests and common challenges that unite all its countries, regardless of their membership status.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Look Beyond the EU: Understanding Europe’s Non-Member States. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
