2, Aug 2023
A Seismic Landscape: Understanding Earthquakes In California And Nevada
A Seismic Landscape: Understanding Earthquakes in California and Nevada
Related Articles: A Seismic Landscape: Understanding Earthquakes in California and Nevada
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Seismic Landscape: Understanding Earthquakes in California and Nevada. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Seismic Landscape: Understanding Earthquakes in California and Nevada
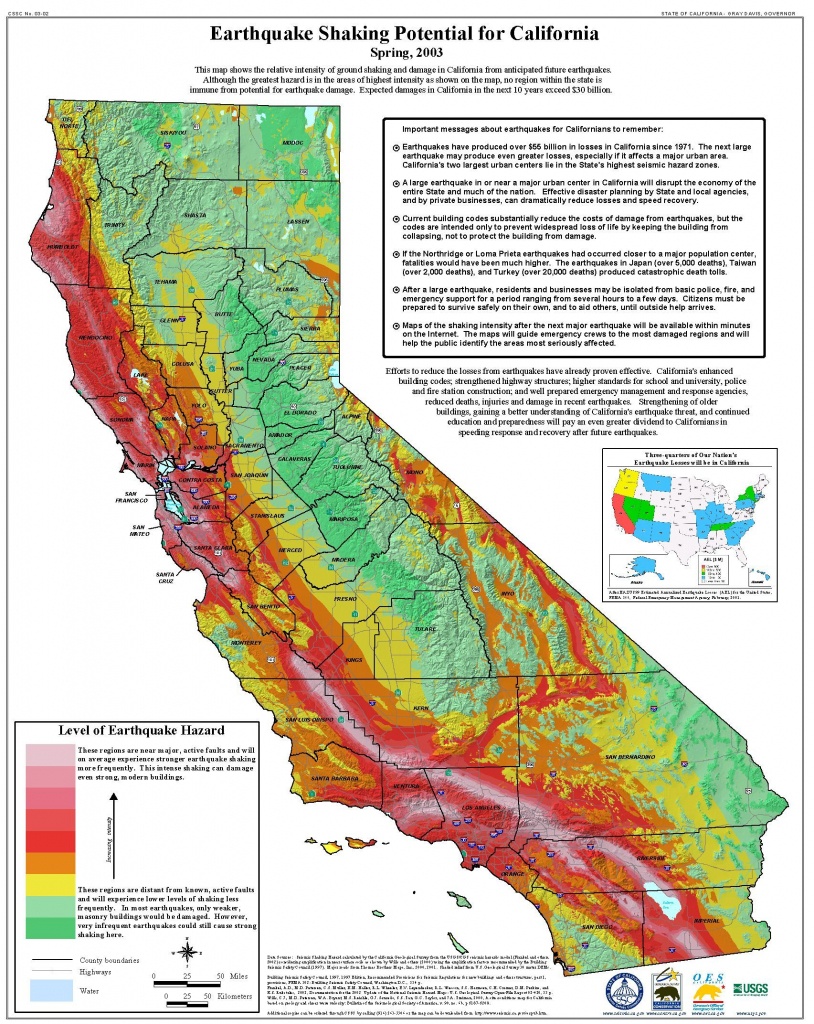
California and Nevada, nestled along the western edge of North America, are renowned for their dramatic landscapes and vibrant ecosystems. Beneath the surface, however, lies a dynamic and restless environment, characterized by a constant interplay of tectonic forces that manifest as frequent earthquakes. The region’s seismic activity is a defining characteristic, shaping its geology, influencing its infrastructure, and reminding its inhabitants of the powerful forces at play beneath their feet.
Understanding the Tectonic Setting
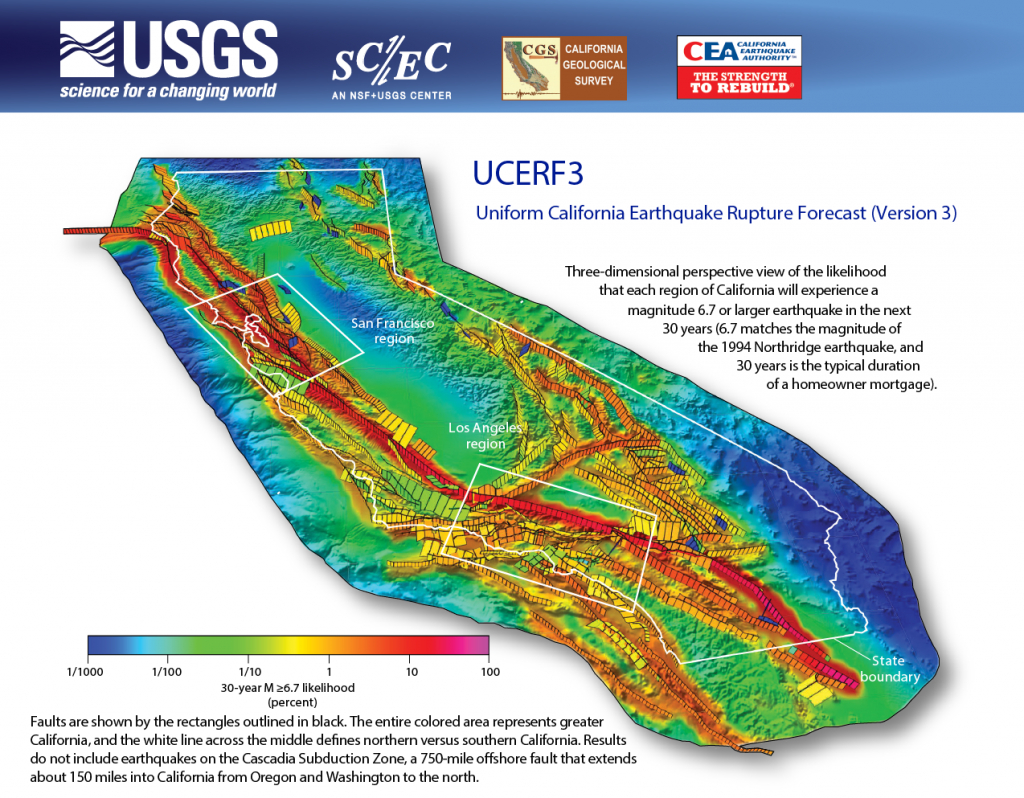
The primary driver of earthquake activity in California and Nevada is the San Andreas Fault, a major transform fault extending over 800 miles along the western edge of the North American Plate. This fault marks the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate, where they slide horizontally past each other. The Pacific Plate is moving northwestward relative to the North American Plate, causing the landmass of California to slide northward.
The San Andreas Fault is not a single, continuous rupture. It is a complex system of interconnected faults, with several branches and smaller faults extending outward. These subsidiary faults, along with the San Andreas Fault itself, are responsible for the vast majority of earthquakes in California and Nevada.
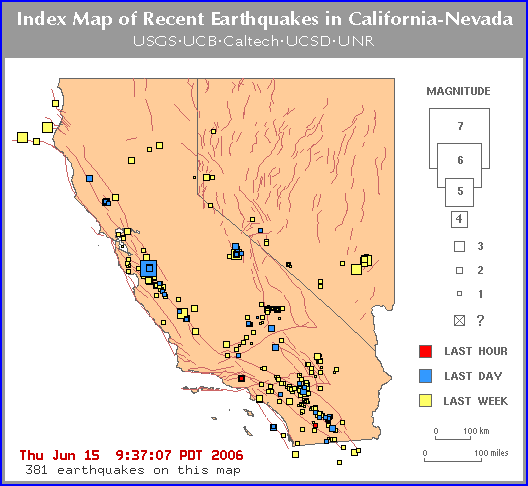
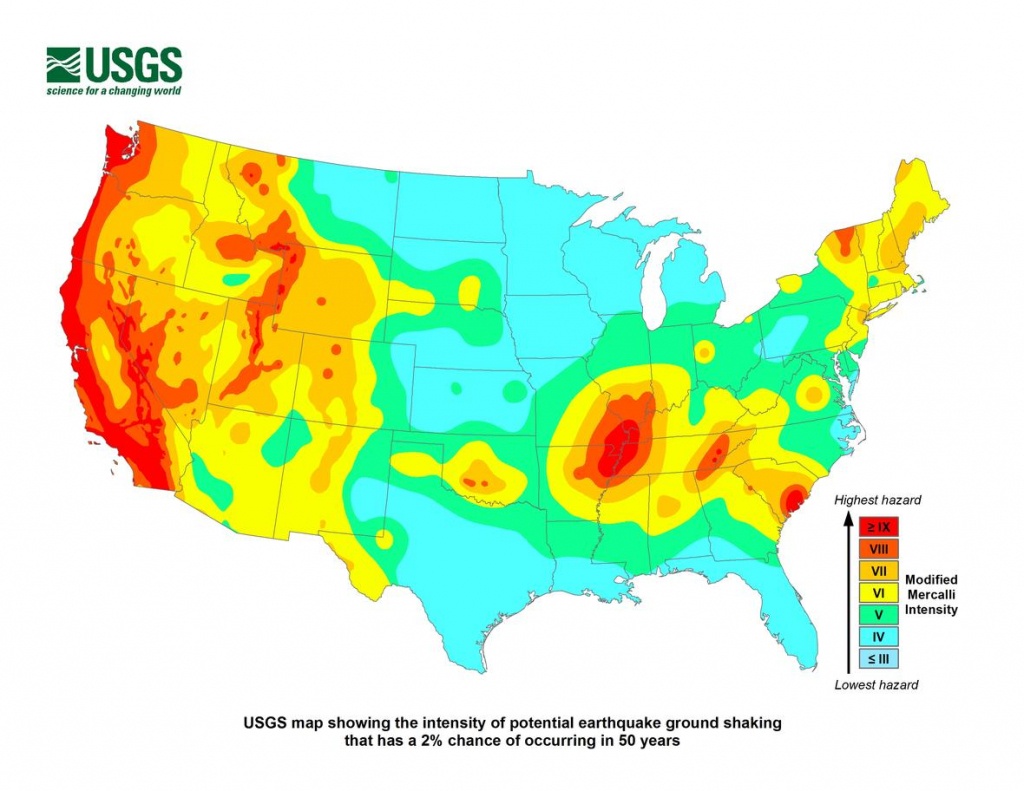
Mapping the Tremors: A Visual Representation of Seismic Activity
Maps of earthquakes in California and Nevada provide a critical visual representation of seismic activity. These maps, typically colored according to earthquake magnitude, offer valuable insights into:
- Earthquake Frequency: The maps highlight areas with higher concentrations of earthquakes, indicating zones of heightened seismic activity. These areas often correspond to fault lines, where the movement of tectonic plates creates the most stress.
- Earthquake Distribution: By illustrating the spatial distribution of earthquakes, the maps reveal the extent and pattern of seismic activity across the region. This information is crucial for understanding the interconnectedness of different fault systems and identifying potential areas of future seismic events.
- Magnitude and Intensity: The size and intensity of earthquakes are visually represented by the size and color of markers on the map. This allows for a quick assessment of the potential impact of an earthquake, with larger earthquakes typically indicating a greater risk of damage.
The Importance of Earthquake Mapping
Earthquake maps serve as essential tools for various purposes:
- Scientific Research: Scientists use these maps to study earthquake patterns, identify active fault zones, and gain a deeper understanding of the region’s seismic history. This knowledge is crucial for developing accurate earthquake hazard models and improving earthquake prediction capabilities.
- Emergency Management: Emergency responders rely on earthquake maps to prepare for potential earthquakes, assess the impact of seismic events, and prioritize resources for disaster relief efforts. The maps help to identify areas most vulnerable to earthquake damage, allowing for targeted preparedness strategies.
- Infrastructure Development: Engineers and architects use earthquake maps to design and construct buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure that can withstand seismic forces. Understanding the seismic hazard of a particular location is critical for ensuring the safety and resilience of structures.
- Public Awareness: Earthquake maps play a vital role in raising public awareness of the seismic risks in California and Nevada. They provide a visual representation of the potential for earthquakes, encouraging individuals to prepare for these events and adopt safe practices.
Beyond the San Andreas Fault: Other Sources of Seismic Activity
While the San Andreas Fault is the most prominent seismic feature in California and Nevada, other fault systems also contribute to earthquake activity. These include:
- The Sierra Nevada Fault System: This fault system runs along the eastern edge of the Sierra Nevada mountain range, extending from the southern tip of California into Nevada. It is responsible for a significant number of earthquakes in the region, including the 1954 Owens Valley earthquake.
- The Eastern California Shear Zone: This zone, located in eastern California, is a broad region of complex faulting that extends from the San Andreas Fault eastward. It is characterized by a network of smaller faults and has been the source of numerous earthquakes, including the 1992 Landers earthquake.
- The Walker Lane Fault Zone: Located in western Nevada, the Walker Lane Fault Zone is a major fault system that runs parallel to the San Andreas Fault. It is responsible for a significant amount of earthquake activity in Nevada, including the 1915 Pleasant Valley earthquake.
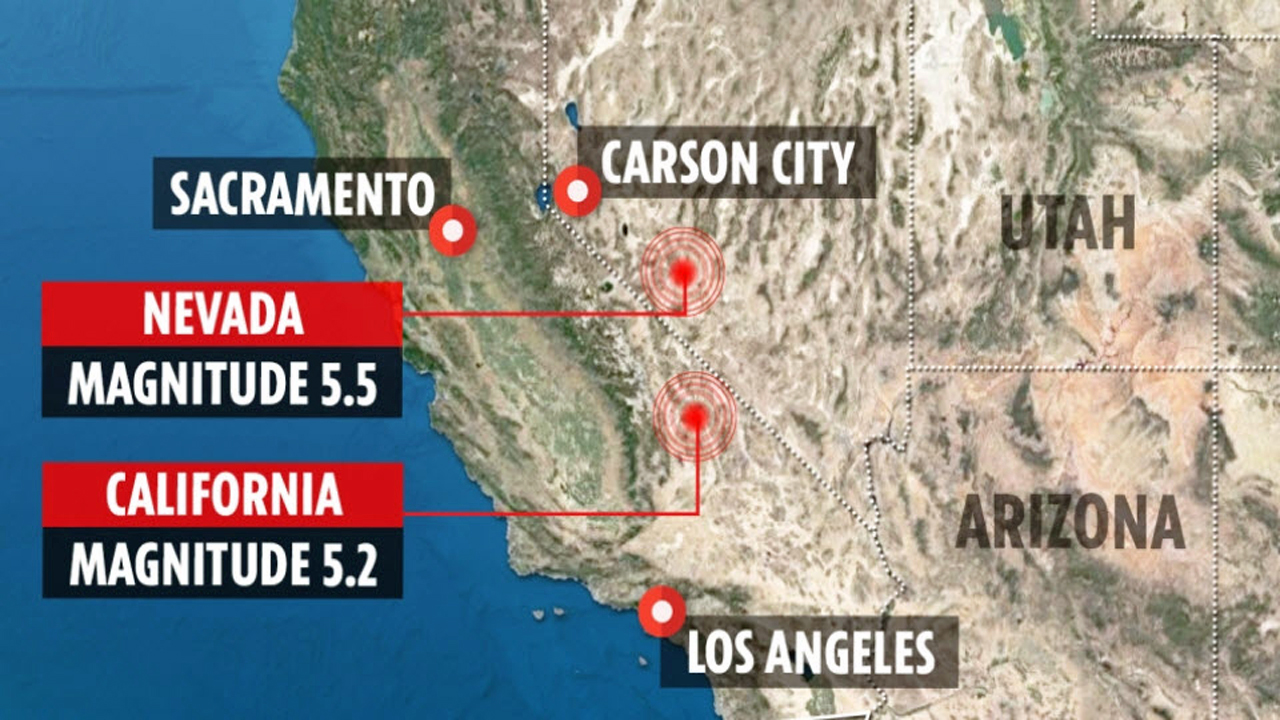
A Look at Recent Seismic Activity
The past few decades have witnessed several notable earthquakes in California and Nevada, highlighting the ongoing seismic activity in the region:
- 1994 Northridge Earthquake: This magnitude 6.7 earthquake struck the San Fernando Valley region of Los Angeles, causing significant damage and resulting in 57 fatalities.
- 1999 Hector Mine Earthquake: This magnitude 7.1 earthquake occurred in the Mojave Desert, causing widespread damage and triggering numerous aftershocks.
- 2010 Baja California Earthquake: This magnitude 7.2 earthquake struck near the border of California and Mexico, generating a tsunami that caused minor damage along the California coast.
- 2019 Ridgecrest Earthquakes: A series of earthquakes, including a magnitude 7.1 event, struck near the town of Ridgecrest, California, causing significant damage to infrastructure and prompting a widespread response from emergency services.
FAQs about Earthquakes in California and Nevada
Q: How often do earthquakes occur in California and Nevada?
A: California and Nevada experience thousands of earthquakes each year, ranging from small tremors barely perceptible to humans to powerful earthquakes that can cause widespread damage. The frequency of earthquakes varies depending on the location and the activity of nearby fault lines.
Q: What is the largest earthquake recorded in California and Nevada?
A: The largest earthquake recorded in California was the 1906 San Francisco earthquake, which had a magnitude of 7.8. The largest earthquake recorded in Nevada was the 1915 Pleasant Valley earthquake, which had a magnitude of 7.3.
Q: Are there any warning systems for earthquakes?
A: While there is no reliable method for predicting earthquakes, advanced warning systems are being developed to provide seconds or minutes of lead time before ground shaking begins. These systems utilize sensors to detect the initial seismic waves of an earthquake, allowing for automated alerts and responses.
Q: What should I do during an earthquake?
A: During an earthquake, the most important thing is to stay safe. If indoors, drop, cover, and hold on to a sturdy object. If outdoors, move away from buildings and overhead power lines. Once the shaking stops, check for injuries and damage.
Tips for Earthquake Preparedness
- Secure heavy objects: Secure heavy objects, such as bookcases and mirrors, to prevent them from falling during an earthquake.
- Have an emergency plan: Develop an emergency plan with your family, including designated meeting points and communication strategies.
- Prepare an emergency kit: Assemble an emergency kit that includes food, water, first-aid supplies, and other essential items.
- Learn CPR and first aid: Knowing basic first-aid and CPR techniques can be vital in an emergency situation.
- Practice earthquake drills: Conduct regular earthquake drills with your family to familiarize them with safety procedures.
Conclusion
The maps of earthquakes in California and Nevada provide a vital visual representation of the region’s dynamic and restless geology. These maps serve as essential tools for scientific research, emergency management, infrastructure development, and public awareness. By understanding the patterns and frequency of earthquakes, we can better prepare for these events, mitigate their impact, and ensure the safety and resilience of communities living in this seismically active region. The ongoing study of earthquake activity in California and Nevada is crucial for furthering our understanding of these natural phenomena, improving earthquake prediction capabilities, and fostering a culture of preparedness among residents.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Seismic Landscape: Understanding Earthquakes in California and Nevada. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
