6, Aug 2023
A Shifting Landscape: Europe In 1939 And 2000
A Shifting Landscape: Europe in 1939 and 2000
Related Articles: A Shifting Landscape: Europe in 1939 and 2000
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Shifting Landscape: Europe in 1939 and 2000. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Shifting Landscape: Europe in 1939 and 2000

The map of Europe in 1939 presents a stark contrast to the landscape of the continent in 2000. The period between these two years witnessed profound transformations, driven by war, political upheaval, and the subsequent emergence of new geopolitical realities. Understanding the differences between these maps offers valuable insights into the tumultuous history of the 20th century and its lasting impact on the European landscape.
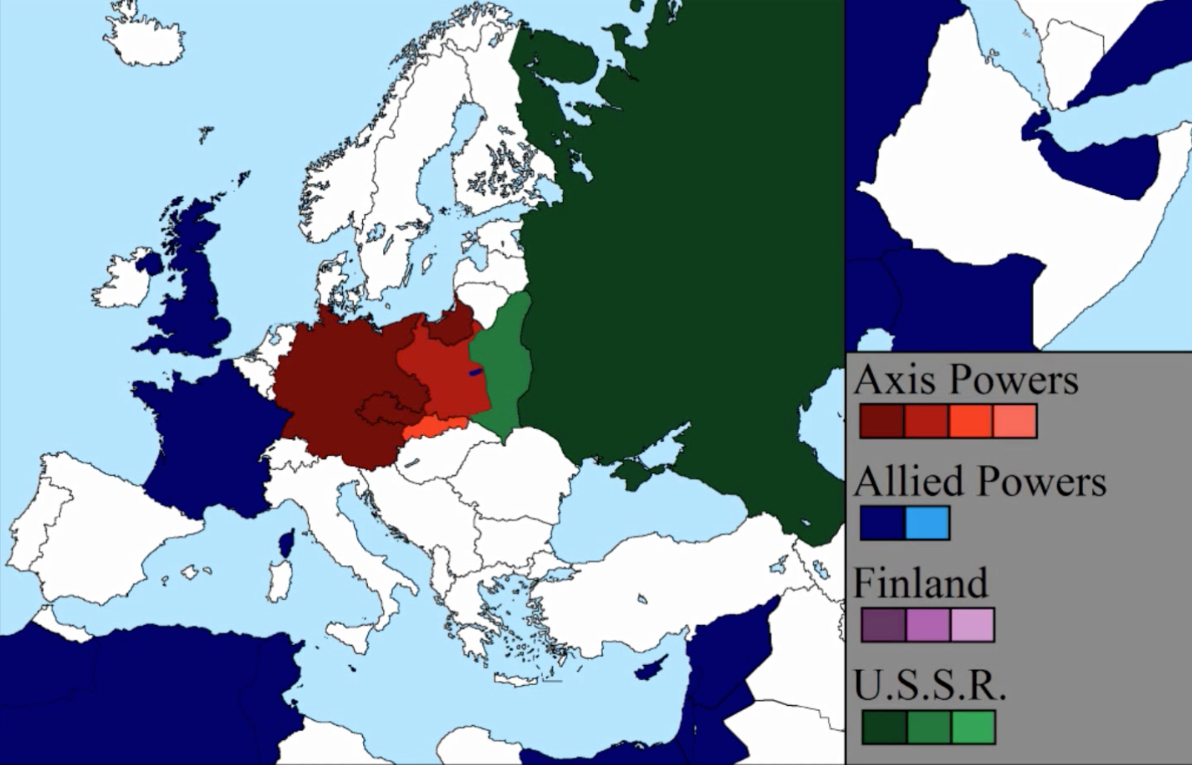
Europe in 1939: A Continent on the Brink
The map of Europe in 1939 reflects a continent on the precipice of war. The shadow of the First World War still loomed large, its unresolved issues fueling tensions and anxieties. The rise of aggressive nationalism, coupled with the growing influence of fascist ideologies, had created a volatile atmosphere.
Key Features of the 1939 Map:
- The Axis Powers: Germany, Italy, and Japan had formed an alliance, posing a significant threat to the existing world order. Germany, under the leadership of Adolf Hitler, had already embarked on a campaign of expansion, annexing Austria and Czechoslovakia.
- The Soviet Union: The Soviet Union, under Joseph Stalin, maintained a powerful military presence and was increasingly assertive in its foreign policy. Its expansionist ambitions, particularly in Eastern Europe, were a source of concern for the West.
- The Allied Powers: The United Kingdom, France, and their allies represented the pre-war status quo. However, their ability to effectively counter the Axis threat was hampered by internal divisions and a lack of decisive action.
- The Collapse of Empires: The Austro-Hungarian Empire, Ottoman Empire, and Russian Empire had all dissolved in the aftermath of World War I, leading to the creation of new nation-states and redrawing of borders. This process was far from complete, leaving many regions vulnerable to instability and conflict.
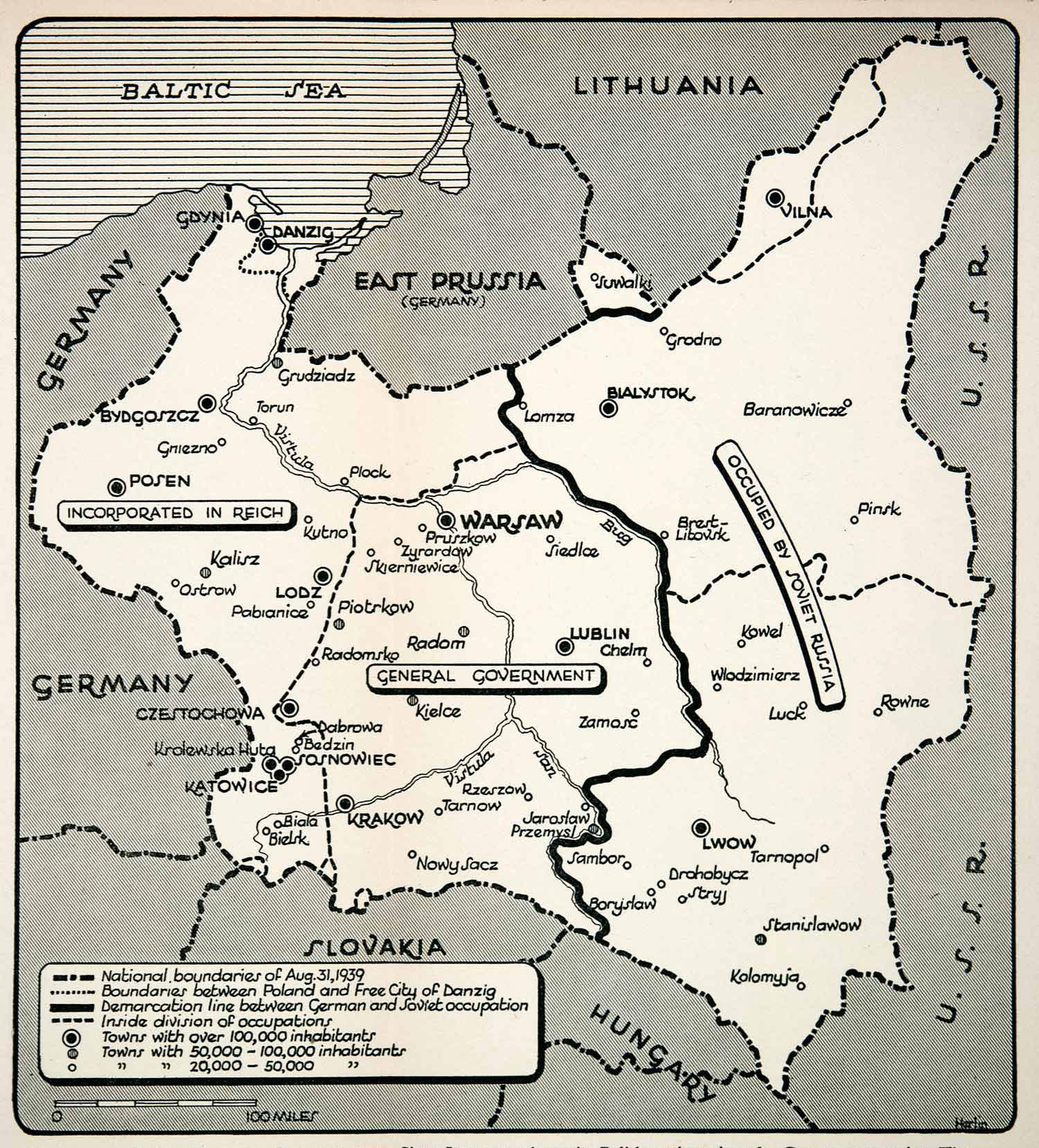
The Second World War and Its Impact:
The outbreak of World War II in 1939 marked a turning point in European history. The conflict, characterized by unprecedented violence and destruction, reshaped the political map of the continent. The war saw the rise of totalitarian regimes, the brutal occupation of numerous countries, and the Holocaust, a horrific genocide that claimed the lives of millions of Jews and other minorities.
Europe in 2000: A New Era of Integration and Cooperation
The map of Europe in 2000 reflects a continent transformed by the events of the 20th century. The Cold War, which had divided Europe into two opposing blocs, had ended in 1991 with the collapse of the Soviet Union. This led to a period of unprecedented political and economic integration, culminating in the creation of the European Union (EU).
Key Features of the 2000 Map:
- The European Union: The EU, a supranational organization, encompassed 15 member states in 2000, representing a significant step towards greater political and economic unity in Europe. The EU aimed to promote peace, stability, and economic prosperity within its member states.
- The Enlargement of the EU: The EU expanded rapidly in the years following 2000, incorporating former Soviet bloc countries and marking a significant shift in the geopolitical landscape of Europe.
- The End of the Cold War: The collapse of the Soviet Union and the end of the Cold War ushered in a new era of democracy and free markets in Eastern Europe. The region experienced a period of rapid economic growth and political reform.
- The Rise of New Challenges: While Europe in 2000 presented a picture of progress and cooperation, new challenges emerged. These included the rise of nationalism, the resurgence of ethnic tensions, and the growing threat of terrorism.
The Significance of the Transformation
The transformation of Europe from 1939 to 2000 is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of the continent. While the period witnessed immense suffering and upheaval, it also saw the emergence of new institutions and ideologies that promoted cooperation and stability.
Benefits of Studying the Transformation:
- Understanding Historical Context: Studying the transformation of Europe between 1939 and 2000 provides valuable insights into the historical context of current events.
- Appreciating the Importance of Peace and Cooperation: The experience of the 20th century highlights the importance of international cooperation and diplomacy in preventing future conflicts.
- Recognizing the Challenges of Integration: The process of European integration has faced numerous challenges, including economic disparities, cultural differences, and the rise of nationalist sentiment. Studying these challenges can provide valuable lessons for future integration efforts.
FAQs
Q: What were the major political changes that occurred in Europe between 1939 and 2000?
A: The period saw the rise and fall of totalitarian regimes, the collapse of empires, the end of the Cold War, and the creation of the European Union.
Q: How did the Second World War impact the map of Europe?
A: The war led to the redrawing of borders, the establishment of new nation-states, and the displacement of millions of people.
Q: What were the key drivers of European integration after the Cold War?
A: The desire for peace, stability, and economic prosperity were major drivers of European integration.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing Europe in the 21st century?
A: Challenges include the rise of nationalism, the resurgence of ethnic tensions, the threat of terrorism, and the increasing influence of external powers.
Tips for Studying the Transformation
- Utilize Maps and Historical Resources: Maps, timelines, and historical documents can provide valuable visual and textual information about the transformation of Europe.
- Focus on Key Events and Personalities: Studying key events, such as the Second World War, the Cold War, and the creation of the EU, can help you understand the major drivers of change.
- Consider the Perspectives of Different Groups: Explore the experiences of various groups, including refugees, minorities, and political leaders, to gain a broader understanding of the transformation.
Conclusion
The transformation of Europe from 1939 to 2000 represents a period of profound change and upheaval. While the continent faced immense challenges, it also witnessed remarkable progress and cooperation. Understanding the historical context of this transformation is crucial for comprehending the current state of Europe and its future prospects. By studying the map of Europe in 1939 and comparing it to the map of 2000, we can gain valuable insights into the forces that have shaped the continent and the challenges that lie ahead.
![Europe's shifting borders, interwar period (1919-1939) [2336x2032] : r/MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/Nip1ed_eVQLZJf6hVuKOs0LD40kDl8TYzqNcCx4ByGM.png?auto=webpu0026s=527af1d31d977e1ad4affa766c13d2f836d310d2)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Shifting Landscape: Europe in 1939 and 2000. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
