29, Feb 2024
A Shifting Landscape: Europe Under The Shadow Of World War II
A Shifting Landscape: Europe Under the Shadow of World War II
Related Articles: A Shifting Landscape: Europe Under the Shadow of World War II
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Shifting Landscape: Europe Under the Shadow of World War II. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Shifting Landscape: Europe Under the Shadow of World War II
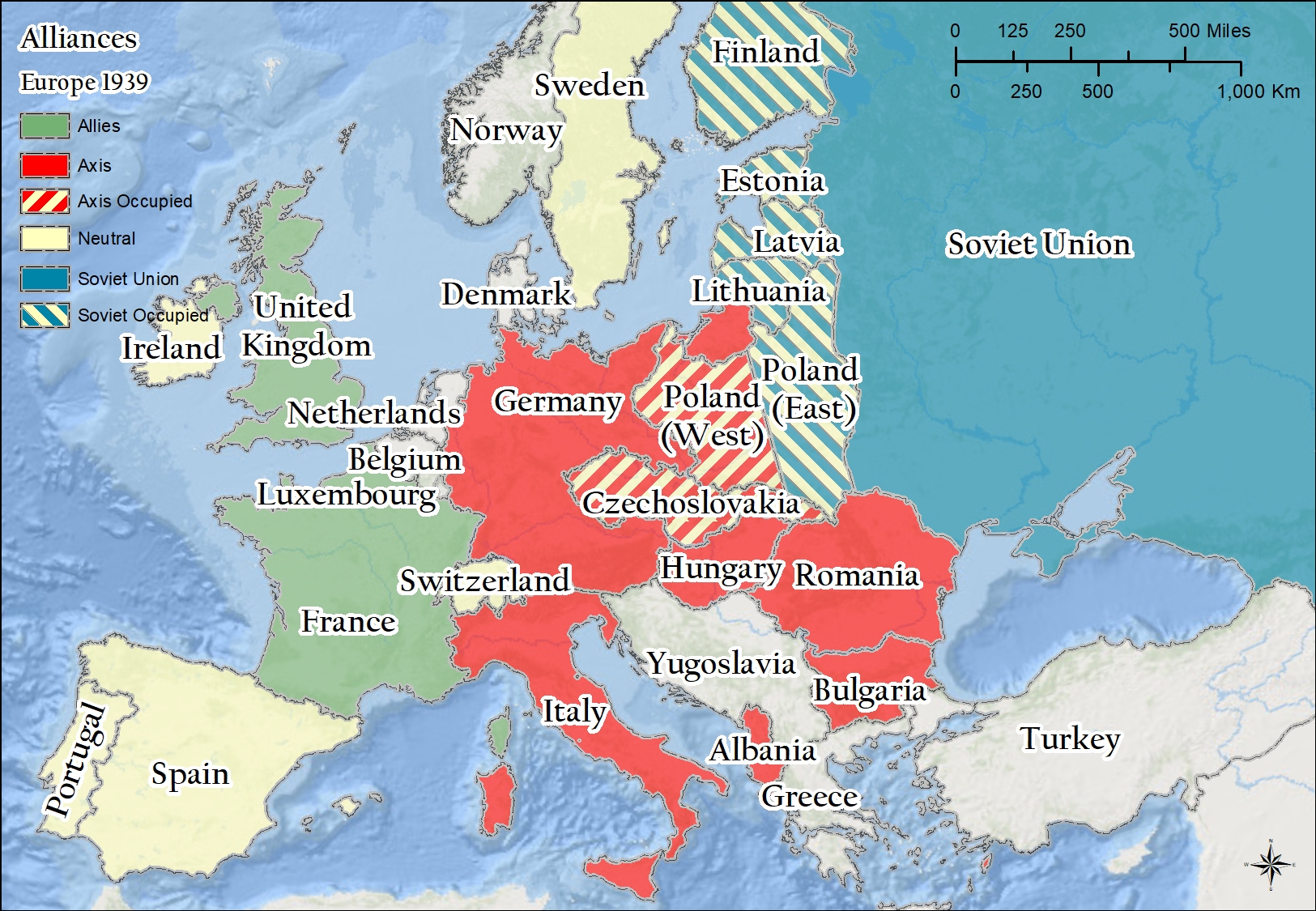
World War II, a conflict that engulfed the globe from 1939 to 1945, fundamentally reshaped the political and geographical landscape of Europe. Understanding the map of Europe during this tumultuous period is essential for comprehending the war’s causes, consequences, and enduring impact.
The Axis Powers: A Shadow Cast Across Europe
The war’s outbreak was triggered by the aggressive expansionism of the Axis powers – Germany, Italy, and Japan. Germany, under the leadership of Adolf Hitler, spearheaded the invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939, marking the formal beginning of the conflict. This aggression quickly escalated, with Germany conquering Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France by June 1940.
The map of Europe during this period reflects the rapid spread of German control. The once-vibrant democracies of Western Europe were swallowed by the Nazi regime, their territories becoming battlegrounds and occupied zones. The map, now starkly divided, showcased the Axis’s dominance, with a vast swathe of continental Europe under German control.
The Allied Response: A Fight for Freedom
The Allied powers, initially comprised of Great Britain, France, and the Soviet Union, resisted the Axis advance. While France fell swiftly, Great Britain, under the leadership of Winston Churchill, stood defiant. The map of Europe, though dominated by the Axis, showcased pockets of resistance – the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, and a nascent resistance movement in occupied territories.
The war’s trajectory shifted dramatically in 1941 with Germany’s invasion of the Soviet Union. The Eastern Front, characterized by brutal fighting and immense casualties, became a central battleground. The map of Europe, now witnessing a protracted and bloody struggle, underscored the stakes involved. The Soviet Union, though initially overwhelmed, demonstrated incredible resilience, ultimately contributing significantly to the Allied victory.
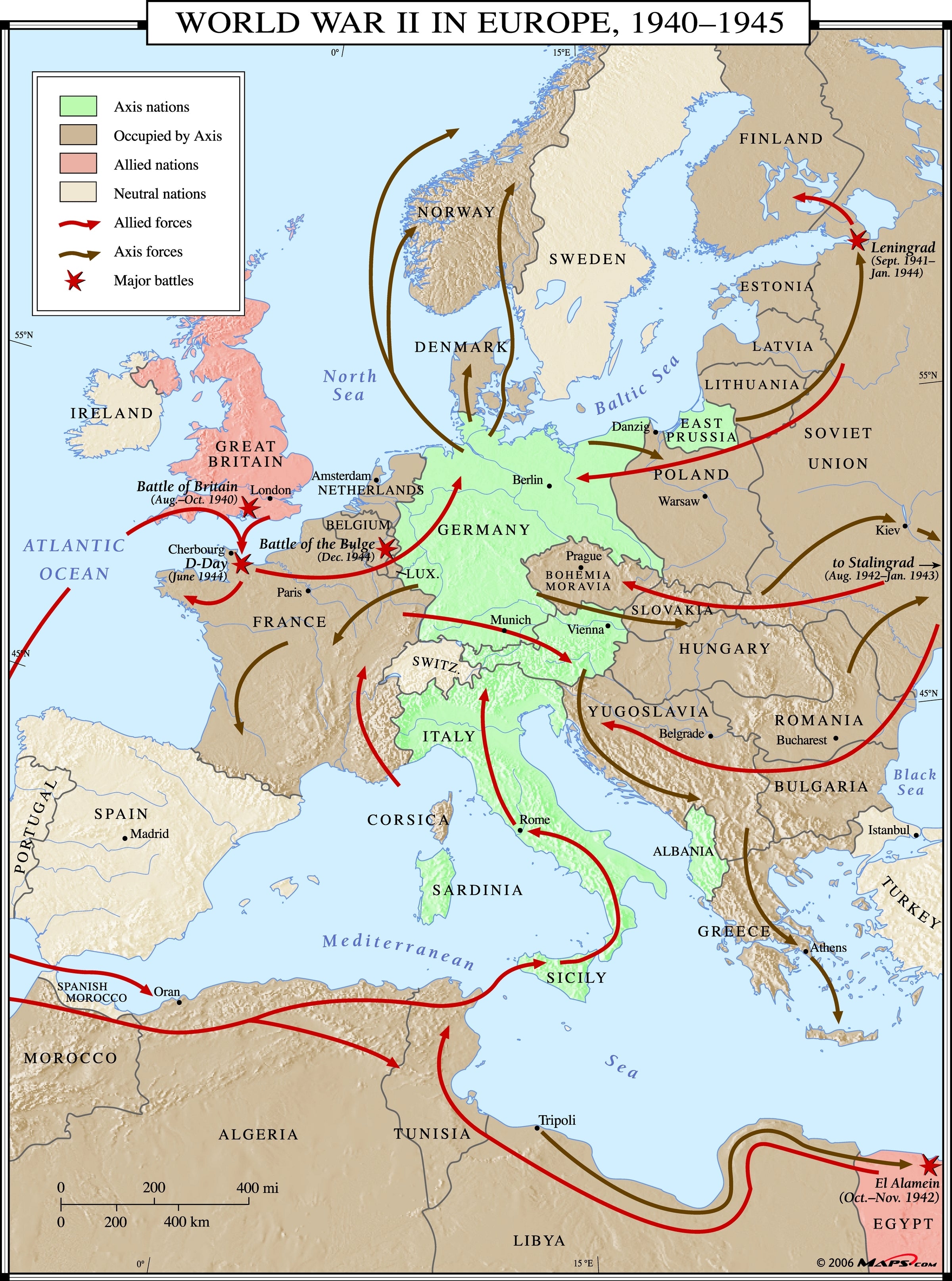
The Shifting Lines: A War of Attrition
The war’s progress saw the map of Europe constantly changing. The Axis, despite early victories, faced mounting resistance and internal divisions. The Allies, through strategic alliances and military advancements, gradually pushed back, liberating territories and reclaiming lost ground.
The map, in its constant state of flux, illustrated the war’s brutal reality – a war of attrition fought on multiple fronts. The liberation of France in 1944 marked a turning point, signifying the weakening of the Axis and the growing strength of the Allies.
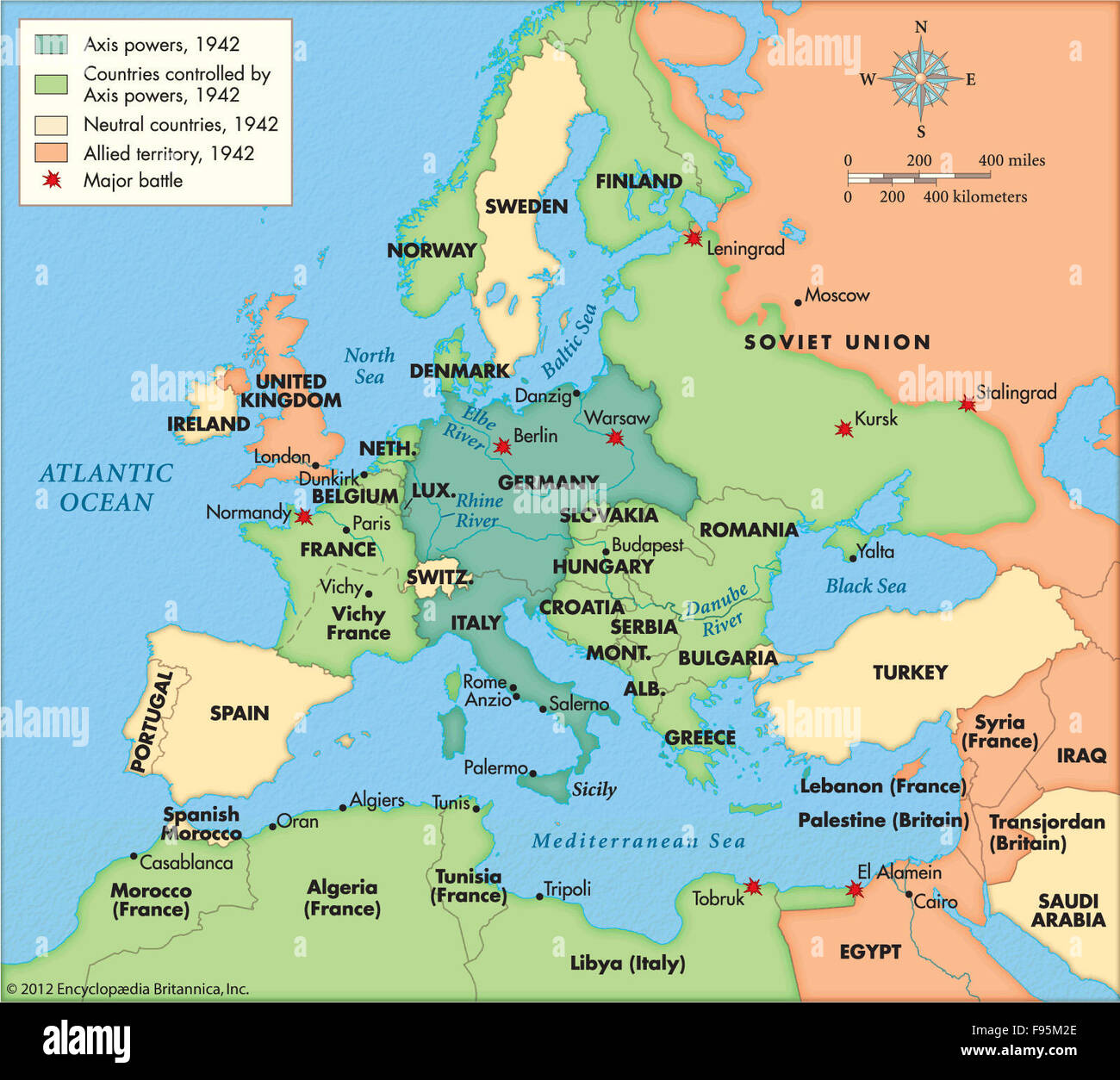
The Post-War Landscape: A New Europe Emerges
The Allied victory in 1945 brought an end to the war, but not without profound consequences. The map of Europe, once defined by the Axis’s dominance, was now fractured by the Cold War. The division of Germany into East and West, the emergence of the Iron Curtain, and the formation of NATO and the Warsaw Pact solidified the ideological divide that shaped the continent for decades.
The map of Europe after World War II reflected the war’s lasting impact. The boundaries of nations were redrawn, political ideologies clashed, and a new era of international relations emerged.
Understanding the Map: A Window into the Past
The map of Europe during World War II serves as a crucial historical document. It provides a visual representation of the war’s geographic scope, the shifting alliances, and the human cost of conflict. By studying the map, we can gain a deeper understanding of:
- The strategic importance of geographic locations: The map highlights the strategic importance of key locations like the English Channel, the Rhine River, and the Eastern Front, underscoring the impact of geography on military operations.
- The shifting power dynamics: The map illustrates the rise and fall of the Axis and Allied powers, revealing the ebb and flow of the war’s momentum.
- The impact of occupation and resistance: The map showcases the areas under Axis control, highlighting the struggles of occupied populations and the efforts of resistance movements.
FAQs
Q: What were the key territorial changes in Europe during World War II?
A: The war led to significant territorial changes. Germany annexed Austria and the Sudetenland, while the Soviet Union gained territories in Eastern Europe. France lost Alsace-Lorraine to Germany, while Italy gained control of Ethiopia and Albania.
Q: How did the map of Europe reflect the changing alliances during the war?
A: The map of Europe witnessed a shift in alliances as the war progressed. The initial alliance of Germany, Italy, and Japan expanded to include Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, and Slovakia. The Allies, initially composed of Britain, France, and the Soviet Union, later expanded to include the United States, Canada, and other countries.
Q: What was the impact of the war on the map of Europe after 1945?
A: The war led to the division of Germany, the formation of the Iron Curtain, and the establishment of new political blocs. The map of Europe became a reflection of the Cold War, with the continent divided into Eastern and Western blocs.
Tips
- Use maps with detailed annotations: Look for maps that include key cities, battlefronts, and political boundaries.
- Compare maps from different periods: Observe how the map of Europe changed throughout the war, highlighting the shifting power dynamics and territorial changes.
- Research individual countries: Explore the specific experiences of individual countries during the war, focusing on their roles in the conflict and the impact of occupation or liberation.
- Consider the human cost: Remember that the map represents real people and their experiences, both those who fought and those who were caught in the crossfire.
Conclusion
The map of Europe during World War II serves as a powerful reminder of the war’s devastating impact on the continent. It showcases the shifting tides of conflict, the human cost of war, and the enduring legacy of the war’s aftermath. By studying the map, we gain a deeper understanding of the war’s complexities and its lasting impact on the European landscape. It serves as a poignant reminder of the need for peace, cooperation, and understanding in the pursuit of a more stable and prosperous future.


:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/676262/postwar_europe.0.png)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Shifting Landscape: Europe Under the Shadow of World War II. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
