4, Apr 2024
A Shifting Landscape: Understanding The Eastern European Map In 2024
A Shifting Landscape: Understanding the Eastern European Map in 2024
Related Articles: A Shifting Landscape: Understanding the Eastern European Map in 2024
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Shifting Landscape: Understanding the Eastern European Map in 2024. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Shifting Landscape: Understanding the Eastern European Map in 2024

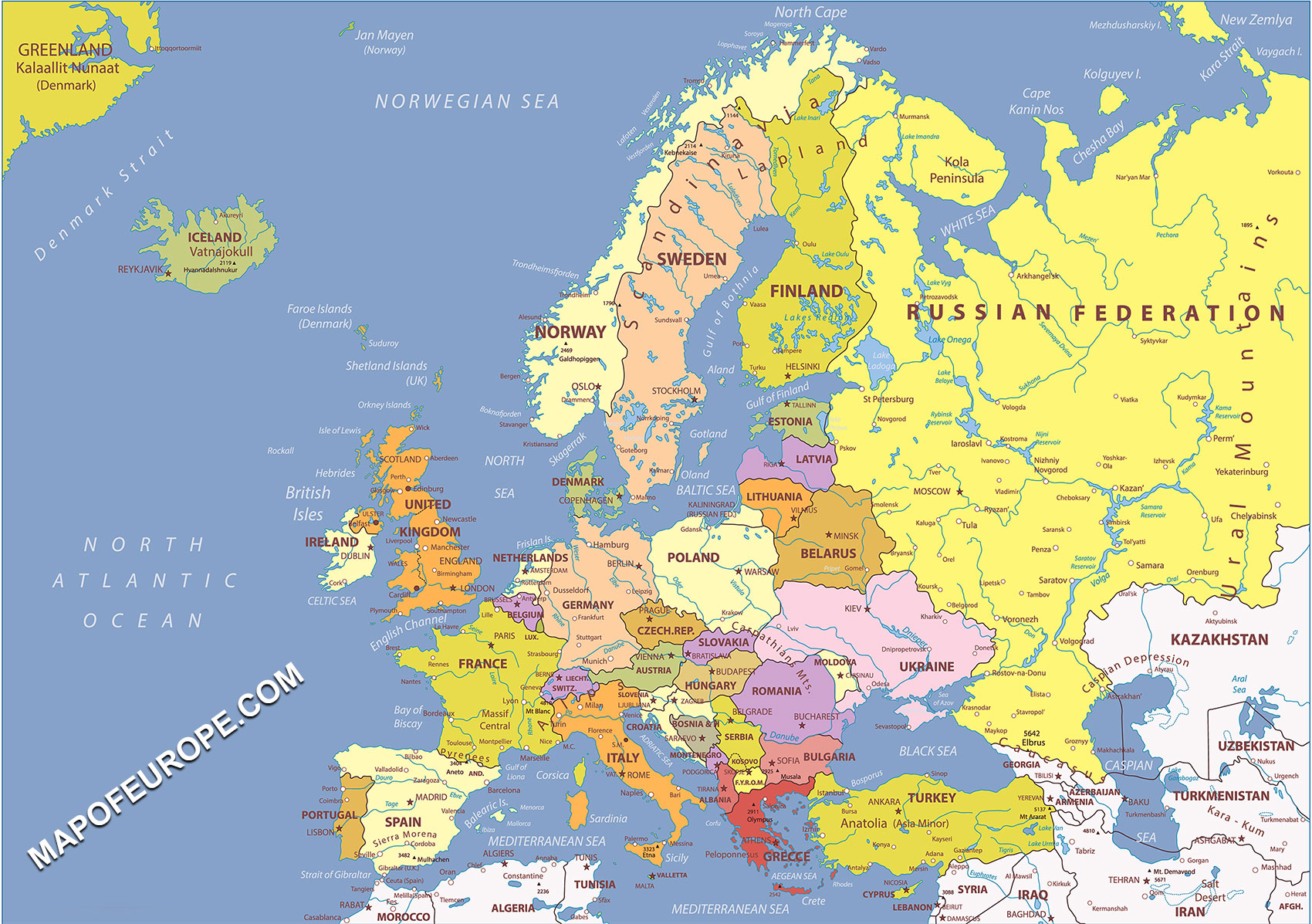
The Eastern European landscape, once defined by the Iron Curtain, has undergone significant transformations in the 21st century. While the political map remains largely unchanged, the region is experiencing dynamic shifts in demographics, economics, and geopolitical influence. Understanding these changes is crucial for comprehending the present and anticipating the future of this vital part of the world.
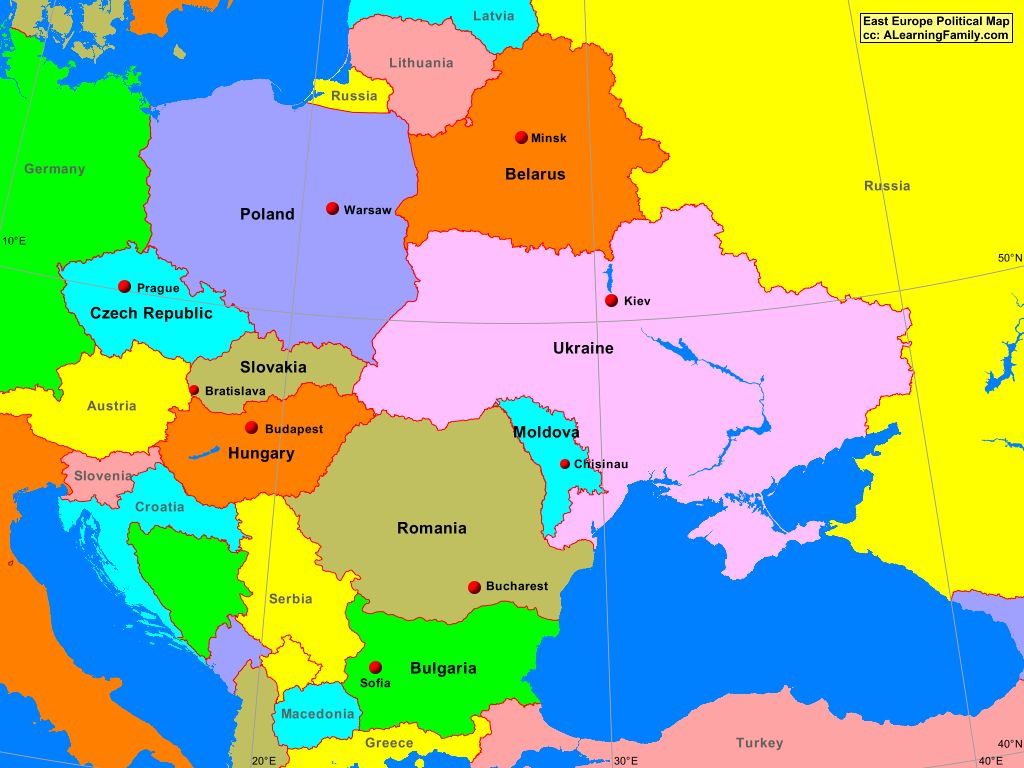
The Boundaries of Eastern Europe: A Matter of Definition
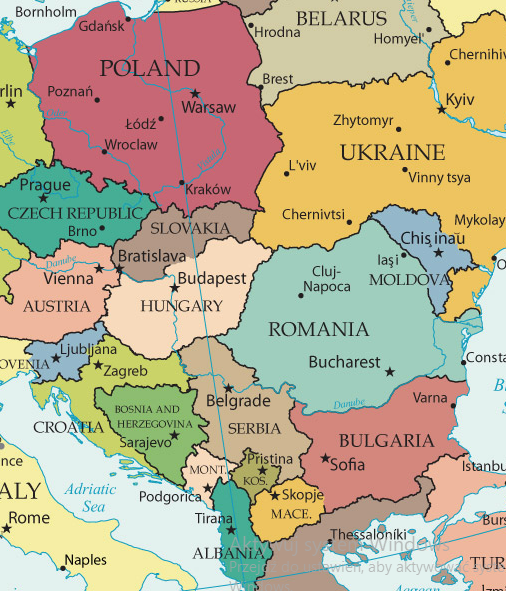
Defining the precise boundaries of Eastern Europe has always been a complex matter. Traditionally, the region encompasses countries located east of Germany and west of Russia, including the Baltic states, Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, and the former Yugoslav republics. However, this definition is contested, with some scholars including Ukraine, Belarus, and Moldova, while others consider them part of a separate "Post-Soviet" region.
For this analysis, we will focus on the core Eastern European countries listed above, recognizing that the inclusion or exclusion of specific territories can be debated. The geographical focus is important because it allows us to examine common trends and challenges faced by these nations, despite their individual nuances.
A Mosaic of Cultures and Identities
Eastern Europe is a melting pot of cultures and identities, shaped by centuries of historical interactions and influences. The region has been a crossroads of civilizations, with Slavic, Germanic, Turkic, and Byzantine elements contributing to its diverse heritage. This rich cultural tapestry is evident in the region’s languages, religions, traditions, and artistic expressions.
The region’s cultural diversity is further enriched by the presence of various ethnic minorities, adding another layer of complexity to its social fabric. Understanding these cultural nuances is essential for navigating the region’s political and social landscape.
The Economic Landscape: Opportunities and Challenges
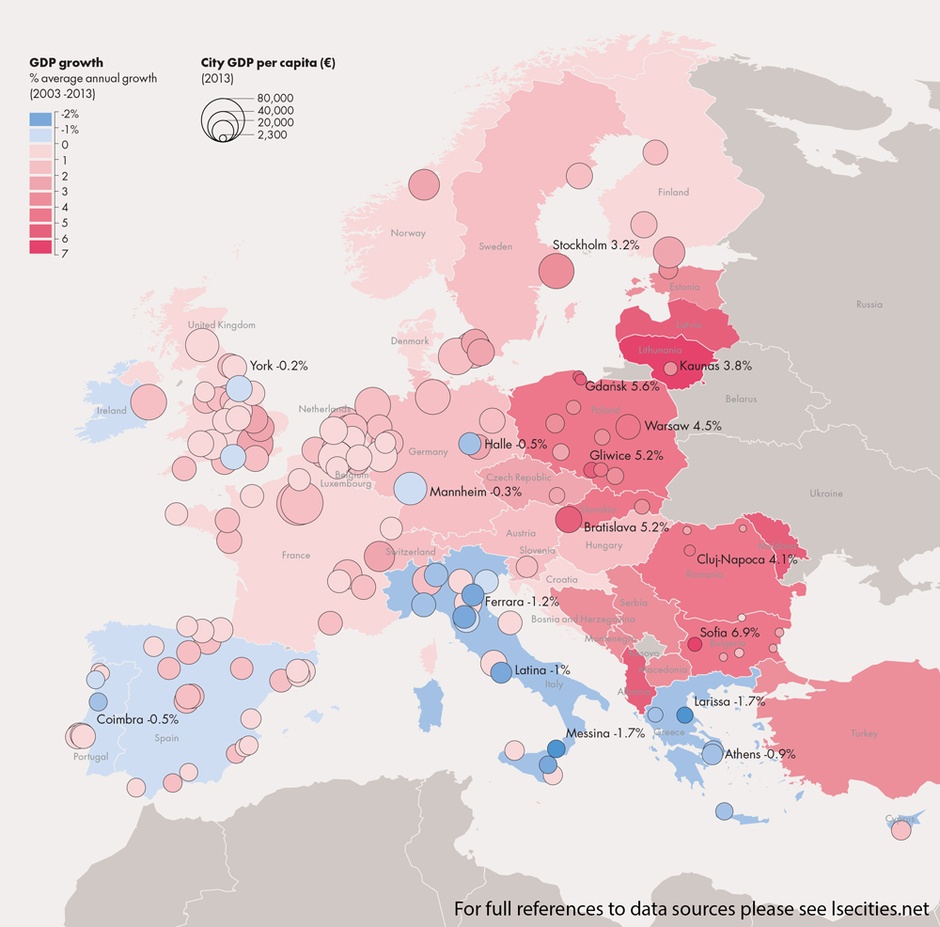
Economically, Eastern Europe has experienced a period of significant growth and transformation since the fall of the Soviet Union. Many countries have transitioned to market economies, attracting foreign investment and participating in global trade. However, the region still faces challenges related to income inequality, corruption, and limited access to resources.
The economic landscape is further complicated by the ongoing war in Ukraine, which has disrupted supply chains, increased energy prices, and raised concerns about regional security. Nevertheless, Eastern European countries are actively seeking to diversify their economies, develop new technologies, and enhance their competitiveness in the global marketplace.
Geopolitical Dynamics: Navigating a Complex Web of Relationships
Geopolitically, Eastern Europe finds itself at a crossroads, caught between the influence of Russia, the European Union, and the United States. The region’s strategic location has historically made it a battleground for competing powers, and this dynamic remains relevant today.
The ongoing war in Ukraine has significantly heightened geopolitical tensions, forcing Eastern European countries to reassess their security priorities and strengthen their alliances. While many countries are seeking closer integration with the European Union and NATO, they also face pressure from Russia to maintain neutrality or even align with its interests.
Navigating the Future: Challenges and Opportunities
The Eastern European map is constantly evolving, shaped by economic, social, and political forces. The region faces a number of challenges, including:
- Economic disparities: Income inequality remains a significant issue in many Eastern European countries, leading to social unrest and hindering economic development.
- Demographic decline: Many countries are experiencing declining populations, putting pressure on social welfare systems and workforce participation.
- Political instability: The rise of populism and nationalism has led to political instability in some countries, undermining democratic institutions and hindering regional cooperation.
- Security threats: The war in Ukraine has highlighted the vulnerability of Eastern Europe to external aggression and the need for strong security guarantees.
Despite these challenges, Eastern Europe also possesses a number of strengths and opportunities, including:
- A young and educated workforce: The region has a relatively young population with a high level of education, providing a skilled workforce for businesses and industries.
- A strategic location: Eastern Europe’s location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia provides access to key markets and transportation routes.
- A rich cultural heritage: The region’s diverse culture and history offer potential for tourism and cultural exchange.
Conclusion: A Region in Transition
The Eastern European map in 2024 reflects a region in transition, navigating a complex web of challenges and opportunities. While the future remains uncertain, the region’s resilience, its growing economic potential, and its strategic location suggest that it will continue to play a significant role in shaping the global landscape. Understanding the dynamics of the Eastern European map is crucial for navigating the complexities of the 21st century and fostering a more peaceful, prosperous, and interconnected world.
FAQs:
Q: What are the main political and economic challenges facing Eastern Europe in 2024?
A: The region faces a range of challenges, including political instability, economic disparities, demographic decline, and security threats. The ongoing war in Ukraine has exacerbated these issues, leading to heightened geopolitical tensions and economic uncertainty.
Q: How is the war in Ukraine impacting the Eastern European map?
A: The war has significantly reshaped the geopolitical landscape, forcing countries to reassess their security priorities and strengthen their alliances. It has also disrupted supply chains, increased energy prices, and raised concerns about regional security.
Q: What are the key economic opportunities for Eastern Europe in the future?
A: The region offers a number of economic opportunities, including a young and educated workforce, access to key markets and transportation routes, and a growing tourism industry. However, addressing issues like corruption, income inequality, and bureaucratic inefficiencies is essential for unlocking this potential.
Q: What are the main cultural and historical influences that have shaped Eastern Europe?
A: Eastern Europe is a melting pot of cultures and identities, shaped by centuries of historical interactions and influences. Slavic, Germanic, Turkic, and Byzantine elements have all contributed to the region’s diverse heritage, evident in its languages, religions, traditions, and artistic expressions.
Q: What are the implications of the changing demographics in Eastern Europe?
A: The declining populations in many Eastern European countries are putting pressure on social welfare systems, workforce participation, and economic growth. Addressing these challenges requires innovative solutions to attract and retain talent, promote economic development, and ensure long-term sustainability.
Tips for Understanding the Eastern European Map:
- Focus on historical context: Understanding the region’s history, including its experience under Soviet rule and the transition to democracy, is crucial for comprehending current events and challenges.
- Pay attention to regional dynamics: Eastern Europe is not a monolithic entity. Each country has its own unique history, culture, and political system, which influence its relationships with neighboring states and international organizations.
- Stay informed about geopolitical developments: The region’s geopolitical landscape is constantly evolving, and it is important to stay informed about key events and developments, particularly regarding the war in Ukraine and its impact on regional security.
- Consider economic indicators: Economic data can provide insights into the region’s growth potential, challenges, and opportunities. Pay attention to GDP growth, foreign investment, and unemployment rates.
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out different perspectives on Eastern Europe, including those from academics, journalists, and policy experts. This will provide a more nuanced understanding of the region’s complexities.
Conclusion:
The Eastern European map is a dynamic and evolving landscape, shaped by a complex interplay of historical, cultural, economic, and geopolitical factors. Understanding the region’s challenges and opportunities is essential for navigating the complexities of the 21st century and fostering a more peaceful, prosperous, and interconnected world.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Shifting Landscape: Understanding the Eastern European Map in 2024. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
