12, Sep 2023
A Visual Guide To European Security: Understanding NATO Membership In 2000
A Visual Guide to European Security: Understanding NATO Membership in 2000
Related Articles: A Visual Guide to European Security: Understanding NATO Membership in 2000
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Visual Guide to European Security: Understanding NATO Membership in 2000. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Visual Guide to European Security: Understanding NATO Membership in 2000

The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is a cornerstone of European security, a collective defense alliance formed in 1949 to deter Soviet aggression and promote stability in the post-World War II era. Understanding the geographical distribution of NATO members is crucial for comprehending the alliance’s strategic posture and its role in shaping the security landscape of Europe.
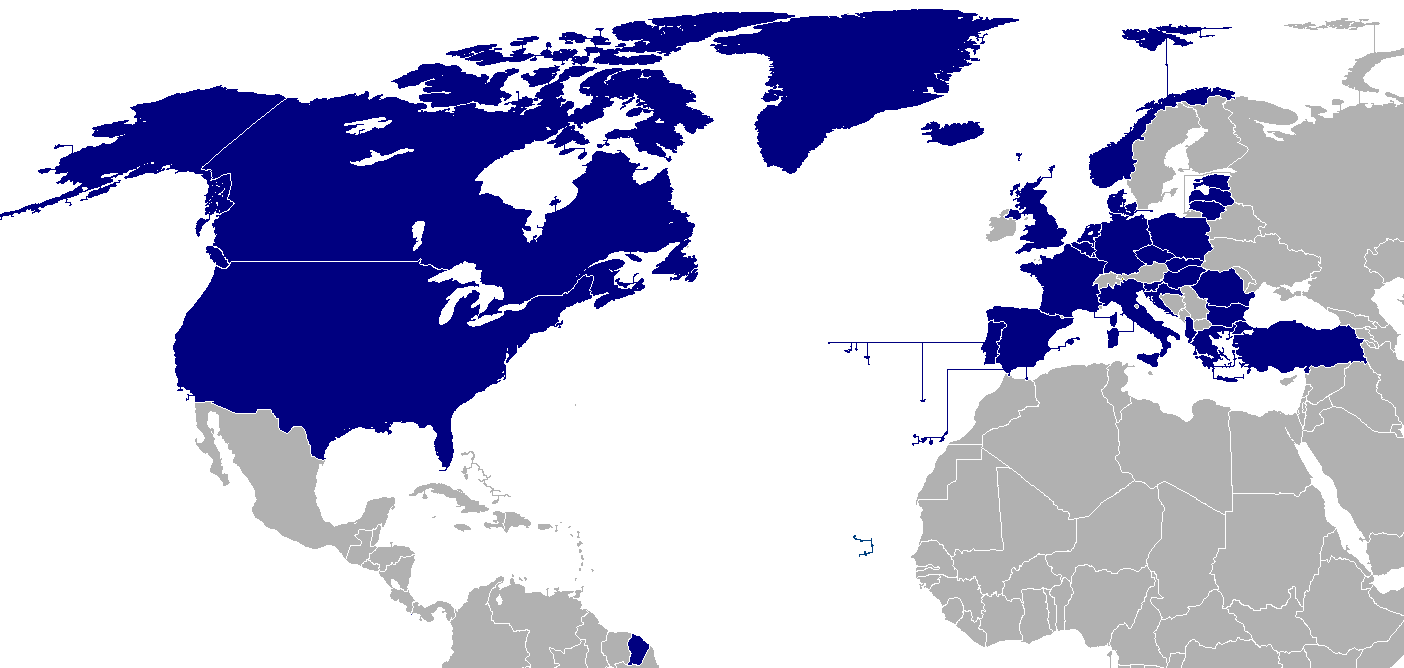
Visualizing the Alliance: A Map of NATO Members in Europe
A map depicting NATO members in Europe provides a clear visual representation of the alliance’s geographical reach. It showcases the interconnectedness of member states, highlighting their commitment to collective security. The map reveals that NATO’s presence extends across the continent, encompassing both Western and Eastern Europe.
Key Features of the Map:
- Core Members: The map prominently displays the original 12 founding members of NATO, including Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom, and the United States. These countries form the bedrock of the alliance, having played a crucial role in establishing its principles and shaping its early development.
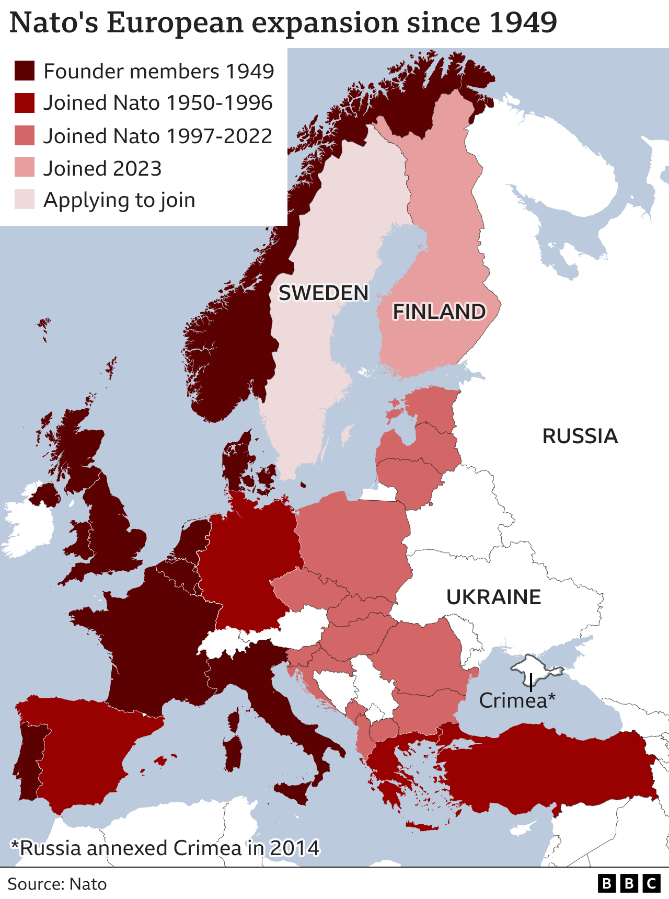
- Expansion to the East: The map showcases the significant expansion of NATO eastward since the end of the Cold War. The inclusion of Central and Eastern European countries such as Poland, Hungary, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Romania, Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania reflects the alliance’s commitment to bolstering security in the region and integrating former Soviet bloc states into the Western security framework.
- Mediterranean Presence: The map highlights the presence of NATO members in the Mediterranean region, including Greece, Turkey, and Spain. These countries contribute to the alliance’s maritime security efforts, particularly in the context of counter-terrorism and maritime security operations.
- Baltic Sea Security: The map underscores NATO’s focus on security in the Baltic Sea region, with members such as Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania sharing a maritime border with Russia. This strategic location has become increasingly important in the context of Russia’s annexation of Crimea and its ongoing military activities in the region.
The Importance of the Map:
The map of NATO members in Europe serves as a powerful tool for understanding the alliance’s strategic significance. It provides a visual representation of the following:
- Collective Defense: The geographical proximity of NATO members demonstrates the principle of collective defense, where an attack on one member is considered an attack on all. This shared commitment to security fosters a strong sense of solidarity and deterrence against potential aggressors.
- Strategic Depth: The map illustrates the strategic depth of NATO, stretching from the Atlantic Ocean to the Black Sea. This geographical reach enables the alliance to respond effectively to a range of security threats, from conventional warfare to terrorism and cyberattacks.
- Regional Stability: The map highlights NATO’s role in promoting regional stability. The integration of former Soviet bloc states into the alliance has contributed to the peaceful transition of these countries to democratic governance and market economies.
- Global Security: The map underscores the global security implications of NATO membership. The alliance’s presence in Europe contributes to a broader framework of international security, working with other organizations to address shared challenges such as terrorism, proliferation of weapons of mass destruction, and climate change.
Understanding the Map: Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the benefits of NATO membership for European countries?
A: NATO membership provides European countries with several benefits:
- Collective Security: NATO’s collective defense commitment offers members a strong deterrent against potential aggressors, assuring them of the support of other member states in the event of an attack.
- Military Cooperation: NATO membership fosters military cooperation and interoperability, allowing member states to share expertise, conduct joint exercises, and enhance their military capabilities.
- Political Influence: NATO membership provides European countries with a platform to influence international security policy and participate in decision-making processes at the global level.
- Economic Benefits: NATO membership can lead to increased economic cooperation, investment in defense industries, and access to advanced technologies.
Q: What are the challenges facing NATO in the 21st century?
A: NATO faces several challenges in the 21st century:
- Russia’s Assertiveness: Russia’s increasingly assertive foreign policy and military activities in Europe pose a significant challenge to NATO’s security framework.
- Terrorism and Extremism: The rise of terrorism and extremism, particularly in the Middle East and North Africa, presents a growing threat to NATO member states.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Cyberattacks and information warfare pose a new and evolving challenge to NATO’s security and stability.
- Resource Constraints: NATO member states face budgetary constraints and pressure to reduce defense spending, which can impact the alliance’s ability to maintain its military capabilities.
Q: What are the future prospects for NATO?
A: The future of NATO is uncertain, but the alliance is likely to remain a significant force in European security for the foreseeable future. NATO will need to adapt to the evolving security environment, including:
- Strengthening Deterrence: NATO will need to continue to strengthen its deterrent capabilities to counter Russia’s military activities and deter potential aggression.
- Adapting to New Threats: The alliance will need to adapt to new threats, including cyberattacks, terrorism, and hybrid warfare.
- Promoting Cooperation: NATO will need to foster closer cooperation with other international organizations and regional partners to address shared security challenges.
Tips for Understanding the Map:
- Focus on Geographical Context: Pay attention to the geographical location of NATO members and their proximity to potential threats.
- Consider Historical Context: Understand the historical context of NATO’s expansion and the motivations behind the inclusion of new members.
- Examine Strategic Partnerships: Explore NATO’s strategic partnerships with non-member countries, such as Ukraine and Georgia.
- Analyze Current Events: Stay informed about current events and developments that impact NATO’s security posture.
Conclusion
The map of NATO members in Europe provides a valuable visual representation of the alliance’s strategic significance. It showcases the interconnectedness of member states, their commitment to collective security, and the alliance’s role in shaping the security landscape of Europe. As the world continues to face new and evolving security challenges, NATO’s ability to adapt and respond effectively will be crucial to maintaining peace and stability in the region and beyond.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Visual Guide to European Security: Understanding NATO Membership in 2000. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin

