24, Jan 2024
Deciphering The MAP NWEA Score Chart: A Guide To Understanding Student Growth
Deciphering the MAP NWEA Score Chart: A Guide to Understanding Student Growth
Related Articles: Deciphering the MAP NWEA Score Chart: A Guide to Understanding Student Growth
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the MAP NWEA Score Chart: A Guide to Understanding Student Growth. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the MAP NWEA Score Chart: A Guide to Understanding Student Growth
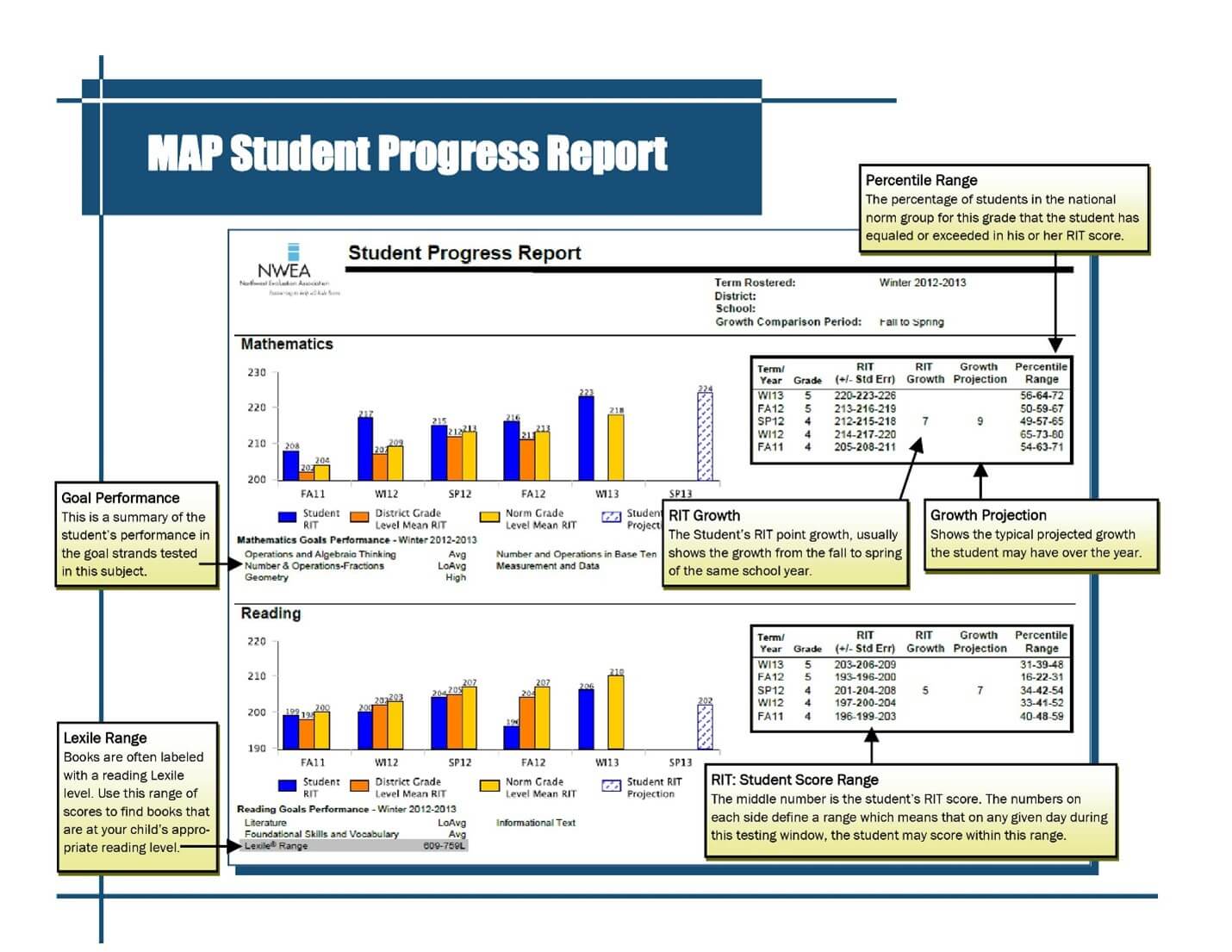
The MAP (Measures of Academic Progress) NWEA score chart, a vital tool in educational assessment, provides a standardized framework for understanding student performance across various academic subjects. This chart, developed by the Northwest Evaluation Association (NWEA), offers a comprehensive picture of a student’s academic standing, revealing strengths, weaknesses, and areas for growth.
Understanding the Basics
The MAP NWEA score chart utilizes a standardized scale known as the RIT scale (Rasch Item Difficulty). The RIT scale is a continuous scale, meaning it allows for precise measurement of student growth over time. Each RIT score represents a specific level of academic proficiency in a particular subject, such as reading, math, or language usage.
Key Components of the MAP NWEA Score Chart:
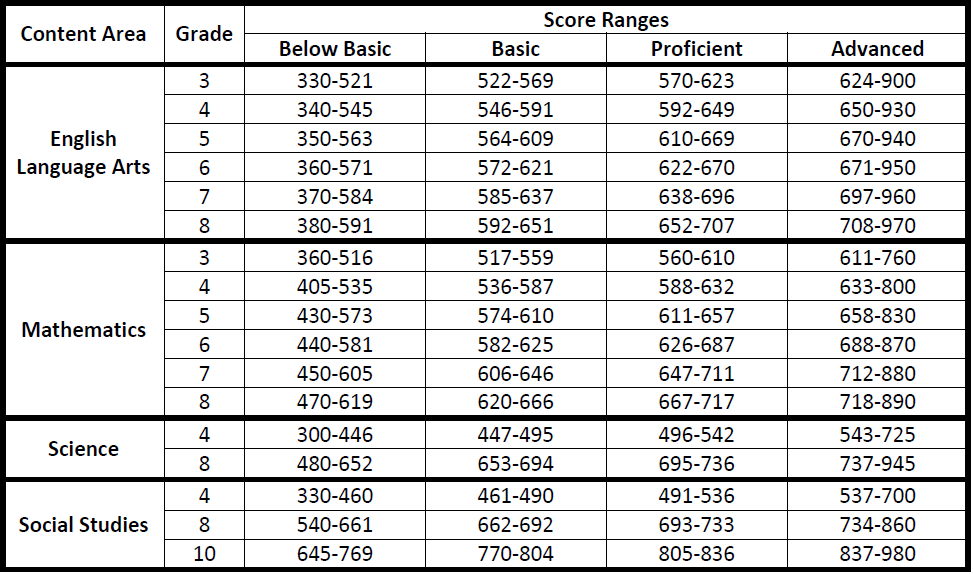
- RIT Score: This numerical score reflects a student’s current academic performance in a given subject. Higher RIT scores indicate stronger proficiency.
- Percentile Rank: This metric indicates the percentage of students in the same grade and time of year who scored at or below a particular student’s RIT score. For example, a percentile rank of 75 means the student scored higher than 75% of their peers.
- Growth Percentile: This metric measures a student’s academic progress over time. It indicates the percentage of students who achieved the same or greater growth in their RIT score over a specific period. A higher growth percentile signifies more significant academic progress.
- Growth Z-Score: This metric provides a standardized measure of a student’s growth compared to their peers. A positive z-score indicates above-average growth, while a negative z-score suggests below-average growth.
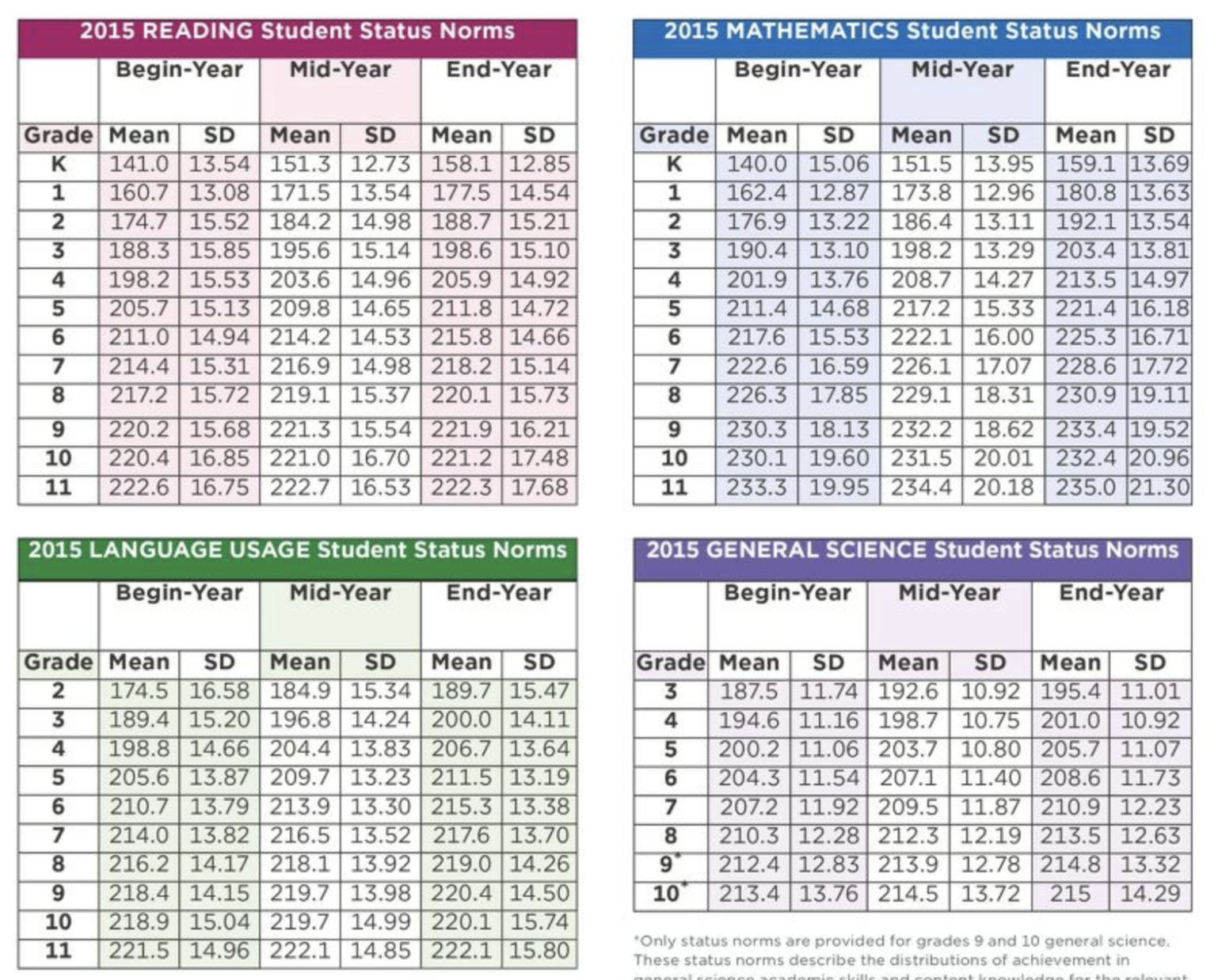
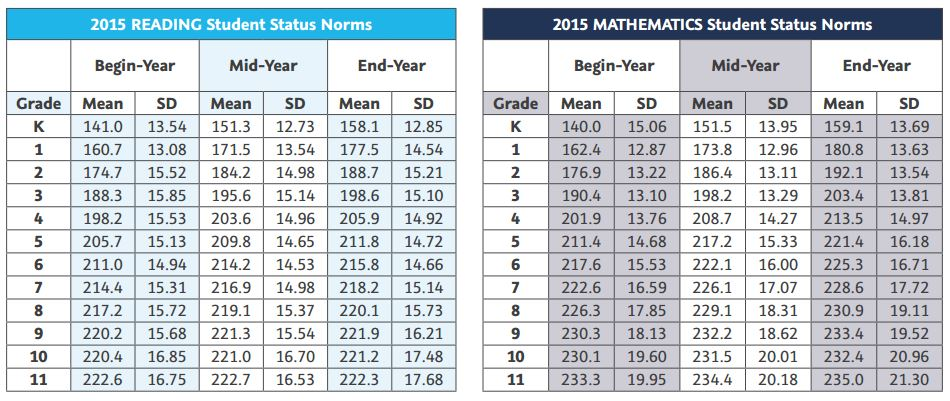
- National Norms: The MAP NWEA score chart includes national norms for each grade level and subject. These norms provide a benchmark for comparing individual student performance to the broader population.
Interpreting the MAP NWEA Score Chart: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Identify the Subject and Grade Level: Begin by locating the specific subject and grade level on the chart.
- Locate the Student’s RIT Score: Find the student’s RIT score on the corresponding subject and grade level section of the chart.
- Determine the Percentile Rank: Observe the percentile rank associated with the student’s RIT score. This indicates their relative performance compared to their peers.
- Analyze Growth Metrics: Examine the student’s growth percentile and z-score. These metrics provide insight into their academic progress over time.
- Compare to National Norms: Compare the student’s RIT score and percentile rank to the national norms for their grade level. This helps gauge their performance relative to the broader student population.
The Importance of the MAP NWEA Score Chart:
- Personalized Learning: The MAP NWEA score chart allows educators to tailor instruction to individual student needs. By identifying areas of strength and weakness, teachers can provide targeted support and enrichment opportunities.
- Monitoring Student Progress: The chart helps track student growth over time, enabling educators to identify areas where students are excelling and areas where they require additional support. This ongoing monitoring allows for timely intervention and adjustments to instruction.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: The MAP NWEA score chart provides valuable data that informs instructional decisions. Educators can use this data to adjust curriculum, differentiate instruction, and allocate resources effectively.
- Communication with Parents: The chart serves as a valuable tool for communicating student performance to parents. It provides a clear and concise overview of their child’s academic strengths and areas for improvement.
- School Accountability: The MAP NWEA score chart plays a role in school accountability measures. By tracking student performance over time, it provides insights into the effectiveness of school-wide programs and interventions.
FAQs about the MAP NWEA Score Chart:
Q: What is the difference between a RIT score and a percentile rank?
A: A RIT score represents a student’s actual performance level on the MAP assessment, while a percentile rank indicates their relative standing compared to other students in the same grade and time of year.
Q: How often should students take the MAP assessment?
A: The frequency of MAP testing varies depending on individual school policies and student needs. Typically, students take the assessment two to three times per year, allowing for regular monitoring of academic progress.
Q: What should parents do if their child’s MAP scores are below average?
A: Parents should discuss their child’s scores with their teacher or school counselor. They can collaborate to develop a plan for addressing any academic challenges and supporting their child’s growth.
Q: Can MAP scores be used to compare students across different schools?
A: While MAP scores provide a standardized measure of student performance, it is not recommended to compare students across different schools. This is because schools may have different student demographics, resources, and instructional approaches, which can influence student performance.
Tips for Utilizing the MAP NWEA Score Chart:
- Regular Review: Review student MAP scores regularly to track progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Focus on Growth: Emphasize student growth over time, rather than focusing solely on absolute scores.
- Collaboration: Collaborate with parents, teachers, and school administrators to develop strategies for supporting student growth.
- Utilize Data for Instruction: Use MAP data to inform instructional decisions, such as differentiating instruction, providing targeted interventions, and allocating resources effectively.
- Celebrate Success: Acknowledge and celebrate student growth and achievements, fostering a positive learning environment.
Conclusion:
The MAP NWEA score chart is an invaluable tool for educators, parents, and students. It provides a clear and comprehensive picture of student performance, enabling individualized instruction, personalized learning, and informed decision-making. By understanding the components of the score chart and utilizing its insights effectively, educators and parents can play a crucial role in supporting student growth and academic success.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the MAP NWEA Score Chart: A Guide to Understanding Student Growth. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
