26, Jan 2024
Europe On The World Map: A Continent Of History, Culture, And Innovation
Europe on the World Map: A Continent of History, Culture, and Innovation
Related Articles: Europe on the World Map: A Continent of History, Culture, and Innovation
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Europe on the World Map: A Continent of History, Culture, and Innovation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Europe on the World Map: A Continent of History, Culture, and Innovation
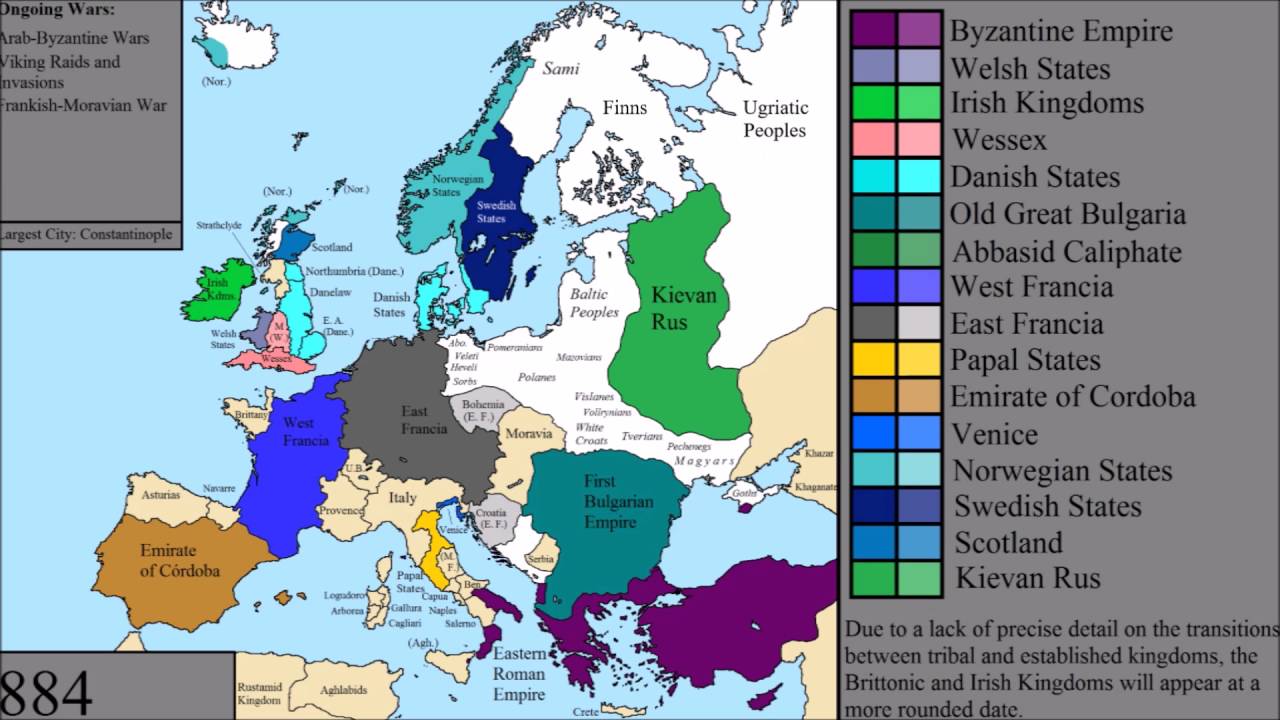
Europe, a continent shaped by millennia of history, culture, and innovation, occupies a prominent position on the world map. Its strategic location, diverse landscapes, and rich tapestry of civilizations have profoundly influenced global affairs, leaving an indelible mark on the world’s cultural, political, and economic landscape.
Geographic Location and Physical Features:
Europe, the second-smallest continent by land area, extends westward from the Ural Mountains in Russia to the Atlantic Ocean, and from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Mediterranean Sea in the south. The continent encompasses a diverse range of physical features, from the snow-capped peaks of the Alps and Pyrenees to the rolling plains of the European Lowlands. Its coastline is characterized by numerous peninsulas, islands, and inlets, creating a complex and varied geography.
Historical Significance and Cultural Heritage:
Europe’s history is a vibrant tapestry woven from the threads of ancient civilizations, empires, and revolutions. From the cradle of Western civilization in Greece and Rome to the rise of powerful medieval kingdoms and the transformative forces of the Renaissance and Enlightenment, Europe has been a crucible of ideas, art, and societal progress. This rich history has left behind an extraordinary legacy of architectural marvels, artistic masterpieces, and cultural traditions that continue to inspire and captivate the world.
Political and Economic Landscape:
Europe is a complex mosaic of nations, each with its own unique history, culture, and political system. The European Union (EU), a political and economic union of 27 member states, represents a significant force in global affairs. Its single market and common currency, the Euro, have fostered economic integration and cooperation within the continent. Despite the challenges of integration, the EU has become a powerful advocate for peace, democracy, and human rights on the global stage.
Cultural Diversity and Heritage:
Europe is renowned for its rich tapestry of cultures and languages. From the Romance languages of the south to the Germanic languages of the north, Europe is home to a diverse array of linguistic traditions. Its cultural heritage is equally diverse, encompassing everything from the classical music of Vienna and the romanticism of Paris to the vibrant street art of Berlin and the ancient traditions of the Basque Country.
Scientific and Technological Advancements:
Europe has been at the forefront of scientific and technological advancements for centuries. From the scientific revolution of the 17th century to the technological innovations of the 20th and 21st centuries, Europe has played a crucial role in shaping the modern world. The continent is home to some of the world’s leading universities, research institutions, and technology companies, driving innovation in fields ranging from medicine and engineering to artificial intelligence and renewable energy.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite its remarkable achievements, Europe faces a number of challenges in the 21st century. These include the rise of populism and nationalism, the increasing threat of terrorism, the challenges of climate change, and the need to address social and economic inequalities. However, these challenges also present opportunities for Europe to strengthen its unity, promote inclusivity, and build a more sustainable and prosperous future.
Europe on the World Map: A Continent of Influence and Impact
Europe’s position on the world map is not merely geographical. It is a testament to the continent’s enduring influence and impact on global affairs. Its history, culture, and innovation have shaped the course of human civilization, leaving an indelible mark on the world. As Europe navigates the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, its role on the world stage remains crucial, shaping the future of the global community.
FAQs
Q1: What are the major geographic features of Europe?
A: Europe’s geography is diverse, encompassing a range of physical features:
- Peninsulas: The Iberian Peninsula, Italian Peninsula, and Balkan Peninsula are prominent features.
- Islands: The British Isles, Iceland, and the numerous islands in the Mediterranean Sea.
- Mountains: The Alps, Pyrenees, Carpathians, and Scandinavian Mountains.
- Plains: The European Lowlands, extending from France to Russia.
- Rivers: The Danube, Rhine, Volga, and Thames are major waterways.
- Coastline: Europe has a long and complex coastline, with numerous inlets, bays, and estuaries.
Q2: What are some of the major cultural and historical influences on Europe?
A: Europe’s cultural heritage is a rich tapestry woven from numerous influences:
- Ancient Greece and Rome: Their contributions to philosophy, art, architecture, and law continue to resonate today.
- Medieval Kingdoms: The rise of powerful kingdoms, like the Holy Roman Empire and the British Empire, shaped Europe’s political and social landscape.
- Renaissance and Enlightenment: These periods ushered in a new era of intellectual and artistic flourishing, influencing scientific thought and societal values.
- Industrial Revolution: This period transformed European economies and societies, leading to urbanization and technological advancements.
Q3: What are the major challenges facing Europe today?
A: Europe faces a number of challenges in the 21st century:
- Populism and Nationalism: The rise of these movements has led to political instability and social divisions.
- Terrorism: The threat of terrorism remains a significant concern, requiring robust security measures.
- Climate Change: Europe is facing the consequences of climate change, including rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and environmental degradation.
- Social and Economic Inequalities: The gap between the rich and the poor continues to widen, leading to social unrest and economic instability.
Q4: What are some of the opportunities for Europe in the future?
A: Despite the challenges, Europe has numerous opportunities for growth and development:
- Technological Innovation: Europe is a leader in technology, with a strong research and development sector.
- Green Transition: The EU has committed to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, creating opportunities for investment in renewable energy and sustainable technologies.
- Global Cooperation: Europe can play a crucial role in promoting international cooperation on issues like climate change and global health.
- Cultural Diplomacy: Europe’s rich cultural heritage can be used to foster understanding and dialogue between different cultures.
Tips for Studying Europe on a World Map
- Use a detailed map: Choose a map that clearly shows the boundaries of European countries, major cities, and physical features.
- Focus on key regions: Identify the major geographic regions of Europe, such as the Iberian Peninsula, the British Isles, and the Balkan Peninsula.
- Explore historical connections: Trace the historical development of European empires and kingdoms on the map.
- Connect with current events: Relate current events in Europe to the geographic context, understanding how location influences political and economic dynamics.
- Use online resources: Utilize interactive maps and online resources to gain deeper insights into European geography, history, and culture.
Conclusion
Europe, a continent rich in history, culture, and innovation, occupies a significant position on the world map. Its strategic location, diverse landscapes, and complex political landscape have shaped the course of human civilization. While facing challenges in the 21st century, Europe remains a powerful force in global affairs, with the potential to drive positive change and build a more sustainable and prosperous future for all.


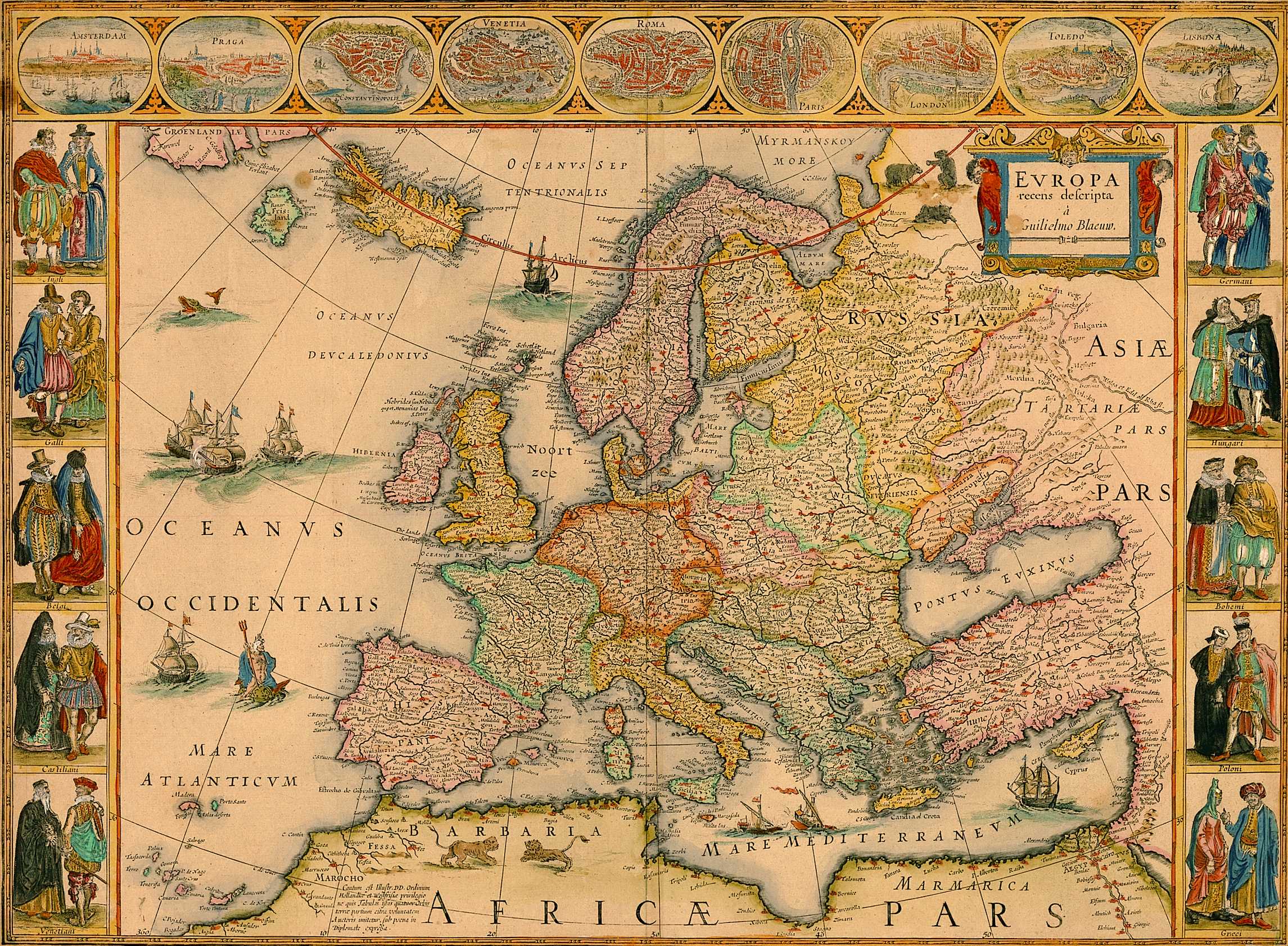

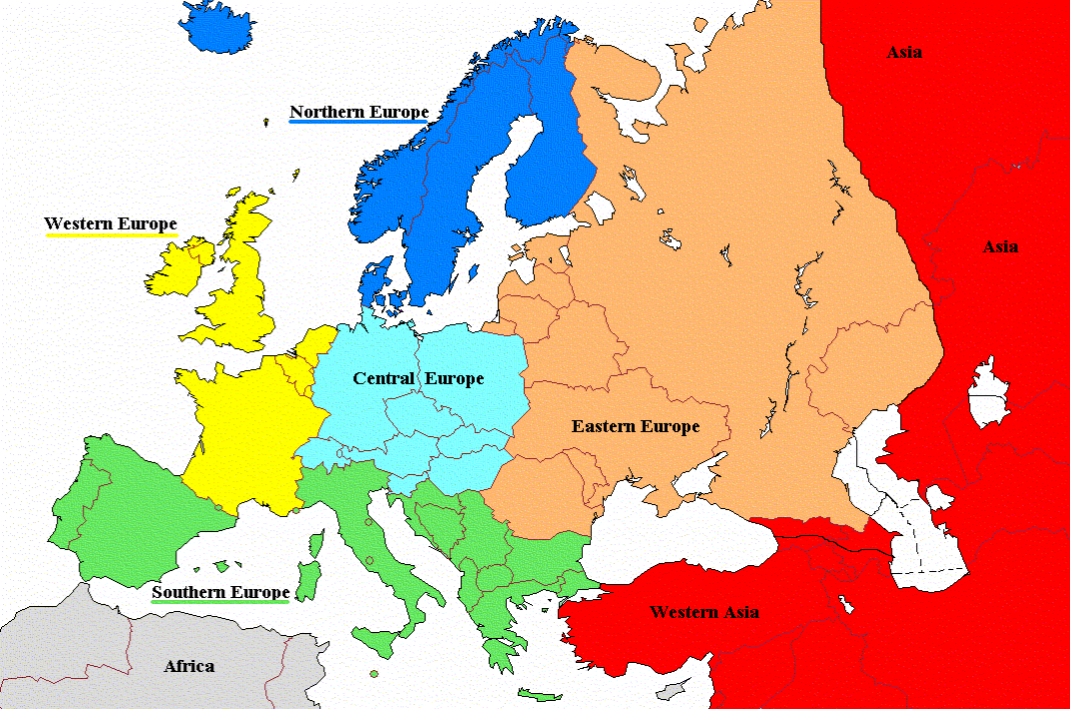

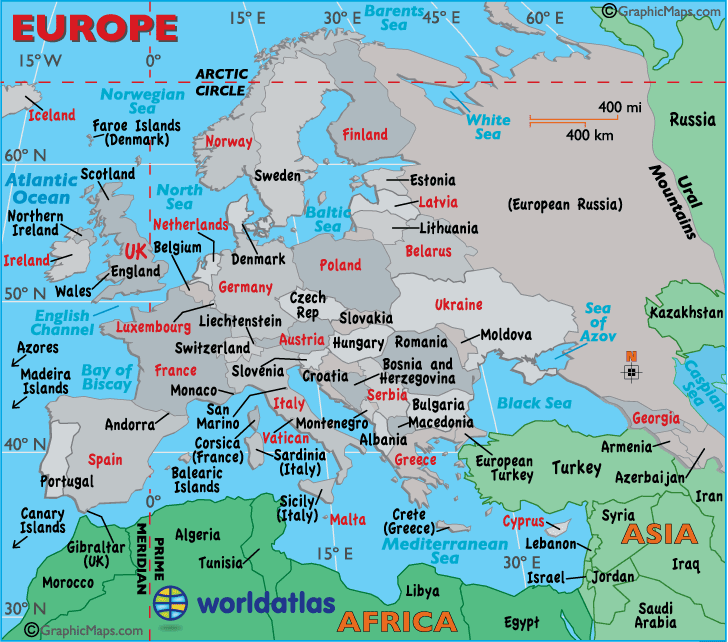
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Europe on the World Map: A Continent of History, Culture, and Innovation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
