7, Sep 2023
Germany’s Position In The European Landscape: A Geographical And Historical Perspective
Germany’s Position in the European Landscape: A Geographical and Historical Perspective
Related Articles: Germany’s Position in the European Landscape: A Geographical and Historical Perspective
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Germany’s Position in the European Landscape: A Geographical and Historical Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Germany’s Position in the European Landscape: A Geographical and Historical Perspective
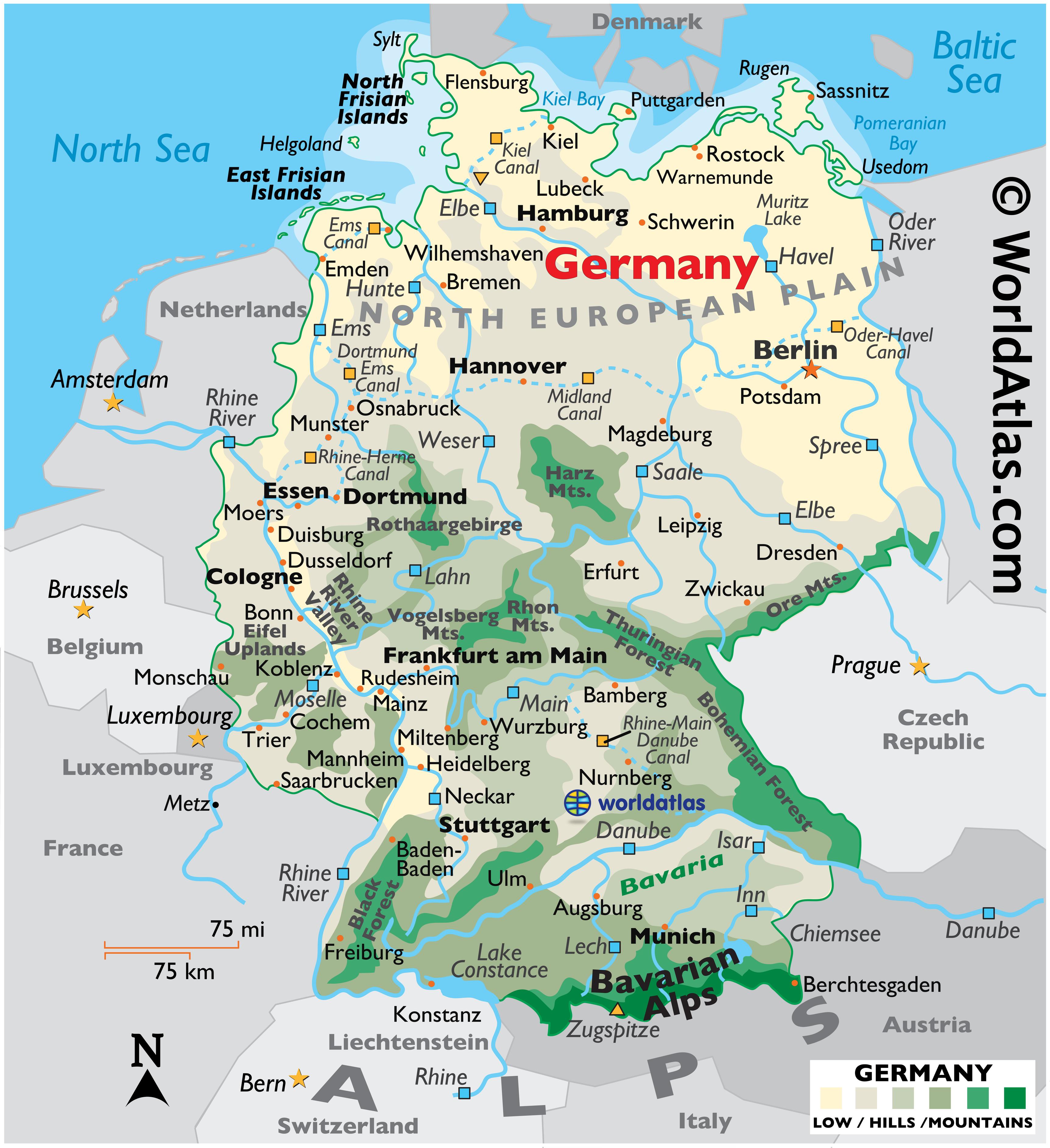
Germany, a nation located in the heart of Europe, holds a prominent position in the continent’s geopolitical and economic landscape. Its geographical location, spanning from the North Sea coast to the Alps, has shaped its history, culture, and influence. Understanding Germany’s position within the European map is crucial for appreciating its role in the continent’s political, economic, and social dynamics.
A Geographical Overview:
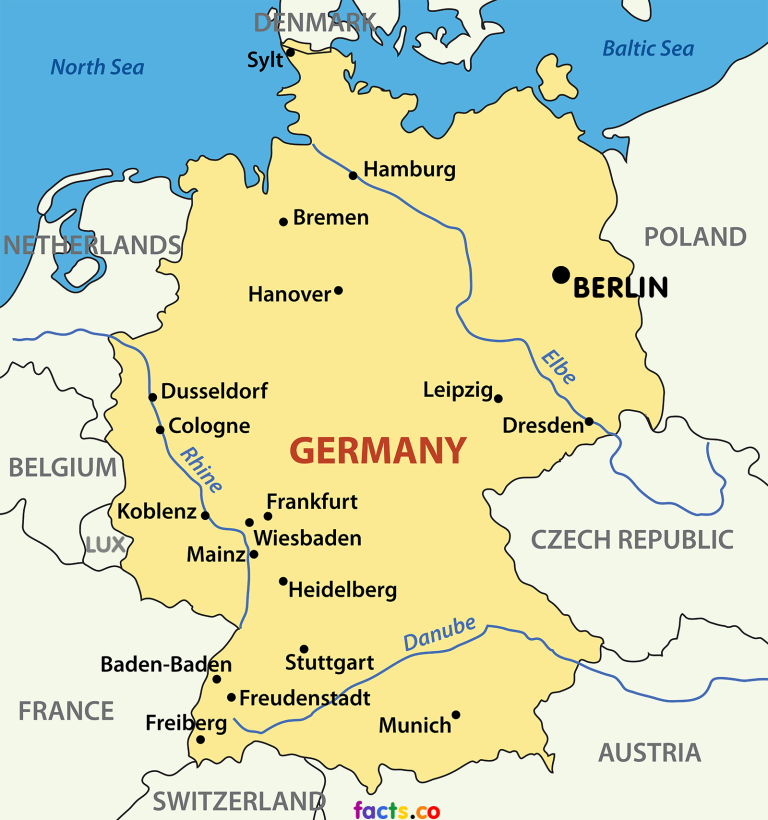
Germany is situated in Central Europe, bordered by nine countries: Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands to the west. This central location has historically made Germany a crossroads of trade, migration, and cultural exchange, influencing its development and fostering its interconnectedness with neighboring nations.
The Importance of Location:
Germany’s central position has contributed significantly to its economic success. The country’s proximity to major markets, including those in Western and Eastern Europe, has facilitated trade and investment. The well-developed infrastructure, including a robust road, rail, and air network, further enhances connectivity and economic integration.
Historical Context:
Germany’s history is deeply intertwined with the European map. As a major power in the continent, it has played a pivotal role in shaping Europe’s political and social landscape. The country’s unification in 1871 marked a significant shift in the European power balance, leading to periods of both conflict and cooperation. The 20th century witnessed Germany’s involvement in two devastating World Wars, leaving a lasting impact on the continent.
Post-War Reconstruction and European Integration:
Following World War II, Germany embarked on a path of reconstruction and reconciliation. Its integration into the European Union (EU) in 1957 marked a turning point, fostering economic growth and promoting peace and stability in the region. Germany’s commitment to the EU has been instrumental in shaping the bloc’s policies and driving its expansion.
Germany’s Role in the European Union:
As one of the founding members of the EU, Germany holds a prominent position within the bloc. It is the largest economy in Europe and a major contributor to the EU budget. Germany’s influence extends to various policy areas, including economic, social, and environmental issues. Its strong commitment to European integration is evident in its active participation in EU decision-making processes.
The Challenges of European Integration:
While Germany has played a significant role in promoting European integration, the EU faces numerous challenges. These include economic disparities between member states, migration pressures, and the rise of nationalism and populism. Germany’s leadership and commitment to European cooperation are crucial in addressing these challenges and ensuring the EU’s continued success.
Beyond the Map: The Impact of Globalization:
Germany’s geographical position has also been influenced by globalization. The country has become increasingly connected to the global economy, with its businesses operating in various international markets. This has led to increased trade and investment flows, fostering economic growth and creating new opportunities.
Conclusion:
Germany’s location in the heart of Europe has shaped its history, culture, and influence. Its central position has facilitated trade, migration, and cultural exchange, contributing to its economic success and political prominence. Germany’s commitment to European integration has been instrumental in shaping the EU’s policies and driving its expansion. As a major player in the European landscape, Germany’s future will continue to be intertwined with the continent’s destiny.
FAQs:
Q: What are the main geographical features of Germany?
A: Germany is characterized by its diverse landscape, ranging from the North Sea coast to the Alps. It includes the North German Plain, the Central Uplands, and the Bavarian Alps. The country also has numerous rivers, including the Rhine, Danube, and Elbe.
Q: How has Germany’s geographical location influenced its history?
A: Germany’s central location has made it a crossroads of trade, migration, and cultural exchange. It has also made it a target of invasion and conflict, shaping its history and political landscape.
Q: What are the main economic sectors in Germany?
A: Germany’s economy is characterized by a strong manufacturing sector, particularly in the automotive, engineering, and chemical industries. The country also has a significant service sector, including finance, tourism, and technology.
Q: What are the main challenges facing Germany today?
A: Germany faces challenges related to its aging population, the integration of refugees, and the rise of nationalism and populism. The country also faces pressure to maintain its economic competitiveness in a globalized world.
Tips:
- Use a map: A map of Europe is essential for understanding Germany’s location and its relationships with neighboring countries.
- Research German history: Understanding Germany’s historical context is crucial for appreciating its role in the European landscape.
- Explore German culture: Germany is known for its rich culture, including its music, literature, and art.
- Follow German news and politics: Staying informed about current events in Germany can provide insights into its role in the European Union.
Conclusion:
Germany’s position in the European map is more than just a geographical location. It represents a complex interplay of history, culture, and politics. Understanding Germany’s role in the European landscape is essential for appreciating the continent’s past, present, and future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Germany’s Position in the European Landscape: A Geographical and Historical Perspective. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
