6, Jun 2024
Leveraging NWEA MAP Data For Effective Instruction: A Comprehensive Guide
Leveraging NWEA MAP Data for Effective Instruction: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Leveraging NWEA MAP Data for Effective Instruction: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Leveraging NWEA MAP Data for Effective Instruction: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Leveraging NWEA MAP Data for Effective Instruction: A Comprehensive Guide
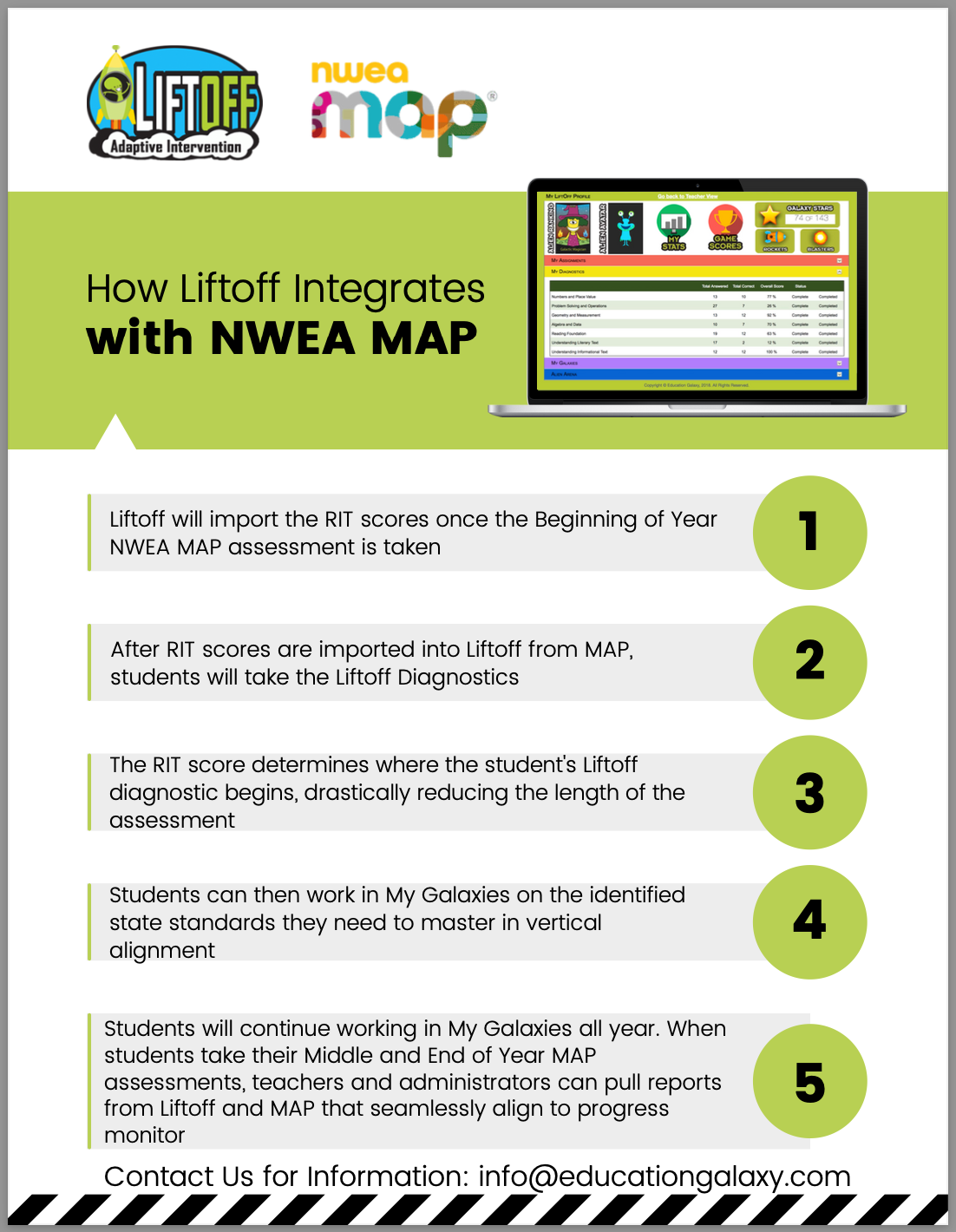
The NWEA Measures of Academic Progress (MAP) assessments provide valuable data that can be harnessed to personalize instruction and enhance student learning. This comprehensive guide explores the multifaceted ways in which MAP data can inform pedagogical decisions, fostering a data-driven approach to education.
Understanding the Power of MAP Data
NWEA MAP assessments measure student growth and achievement in key academic areas, offering a standardized, reliable measure of individual student progress. This data transcends simple test scores, providing a nuanced understanding of each student’s strengths and areas for improvement. MAP data can be utilized to:
- Identify Learning Gaps: By analyzing student performance across various subjects and skill levels, teachers can pinpoint specific areas where students struggle. This allows for targeted interventions and differentiated instruction to address individual needs.
- Track Student Growth: MAP assessments are designed to measure growth over time, allowing teachers to monitor individual student progress and identify trends. This longitudinal data provides a clear picture of student development and informs instructional adjustments.
- Compare Student Performance: Comparing student performance against national norms and within the school context helps identify areas where the school as a whole may require additional support or resources. This data can be used to inform school-wide initiatives and professional development opportunities.
- Inform Curriculum and Instruction: MAP data can be used to inform curriculum decisions, ensuring that instruction is aligned with student needs and standards. It can also guide the selection of appropriate instructional materials and strategies.
Strategies for Utilizing MAP Data to Drive Instruction
1. Analyze Student Performance:
- Individual Student Profiles: Teachers should carefully review individual student performance reports, focusing on areas of strength and weakness. This data can be used to create personalized learning plans and differentiate instruction.
- Growth Over Time: Examining student growth trajectories over multiple administrations can reveal patterns and identify students who are excelling, plateauing, or falling behind. This data can inform interventions and adjustments to instruction.
- Benchmarking: Comparing student performance to national norms and school-wide averages helps identify areas where the curriculum or instruction may need to be adjusted.
2. Develop Targeted Interventions:
- Small Group Instruction: MAP data can be used to create small groups of students with similar learning needs. This allows for targeted instruction and support, ensuring that students receive the appropriate level of assistance.
- Differentiated Instruction: By analyzing student performance, teachers can tailor instruction to meet individual needs. This can include providing additional support for struggling students, accelerating learning for advanced students, or focusing on specific skills for all students.
- Technology Integration: MAP data can inform the selection of technology-based interventions and learning resources, ensuring that students have access to appropriate tools and support.
3. Foster Collaboration and Communication:
- Teacher Collaboration: Sharing MAP data among teachers can facilitate collaboration and the development of shared strategies for supporting student learning. This can involve creating common assessments, designing shared interventions, and coordinating instruction across grade levels.
- Parent Communication: Regular communication with parents about student performance and progress is essential. This can involve sharing MAP data, discussing individual student needs, and collaborating on strategies for supporting student learning at home.
- School-Wide Initiatives: Analyzing school-wide MAP data can inform school-wide initiatives to improve student achievement. This can involve implementing new curriculum, providing professional development opportunities for teachers, or investing in additional resources.
FAQs on Utilizing NWEA MAP Data
Q: What are some common misconceptions about MAP data?
A: A common misconception is that MAP data should be used solely for accountability purposes. While it is valuable for evaluating student progress and school performance, its primary purpose is to inform instructional decisions and improve student learning.
Q: How often should MAP assessments be administered?
A: The frequency of MAP assessments varies depending on the grade level and specific needs of the school. Generally, it is recommended to administer MAP assessments three times a year: fall, winter, and spring.
Q: How can MAP data be used to support students with disabilities?
A: MAP data can be used to identify students with disabilities who may require additional support or accommodations. It can also inform the development of individualized education programs (IEPs) and ensure that students with disabilities receive appropriate instruction and services.
Q: What are some tips for using MAP data effectively?
A:
- Focus on individual student growth: Focus on tracking student progress over time rather than just comparing scores to national norms.
- Use data to inform instructional decisions: Don’t just collect data; use it to make informed decisions about curriculum, instruction, and interventions.
- Involve all stakeholders: Share data with teachers, parents, and administrators to foster collaboration and ensure that everyone is working together to support student learning.
- Be flexible and adapt: Don’t be afraid to adjust your approach based on student data and feedback.
Conclusion
By effectively utilizing NWEA MAP data, educators can gain a deeper understanding of student learning, identify areas for improvement, and implement targeted interventions to enhance student achievement. This data-driven approach to instruction empowers teachers to personalize learning experiences, foster student growth, and create a more equitable and effective learning environment. By embracing the power of MAP data, educators can move beyond traditional assessments and embrace a dynamic, data-informed approach to education.
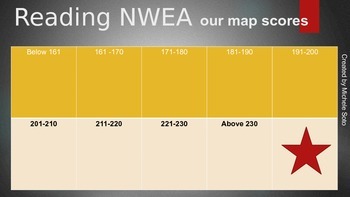
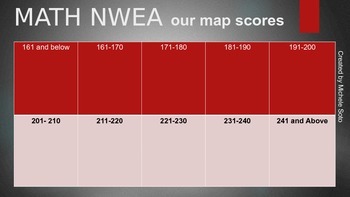
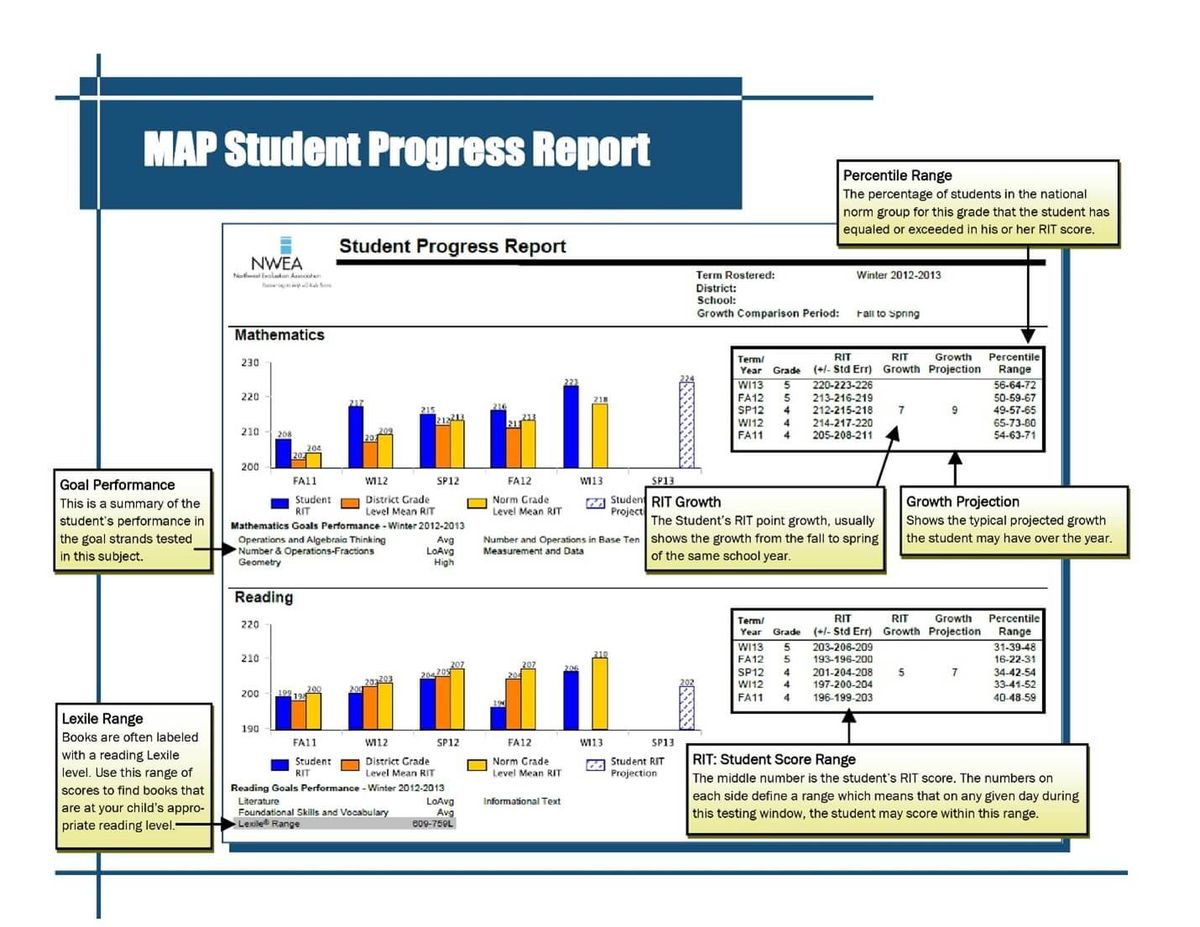

![]()



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Leveraging NWEA MAP Data for Effective Instruction: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
