20, Nov 2023
Mapping The Ponderosa Pine In Nevada: A Landscape Of Resilience And Adaptation
Mapping the Ponderosa Pine in Nevada: A Landscape of Resilience and Adaptation
Related Articles: Mapping the Ponderosa Pine in Nevada: A Landscape of Resilience and Adaptation
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Ponderosa Pine in Nevada: A Landscape of Resilience and Adaptation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Ponderosa Pine in Nevada: A Landscape of Resilience and Adaptation

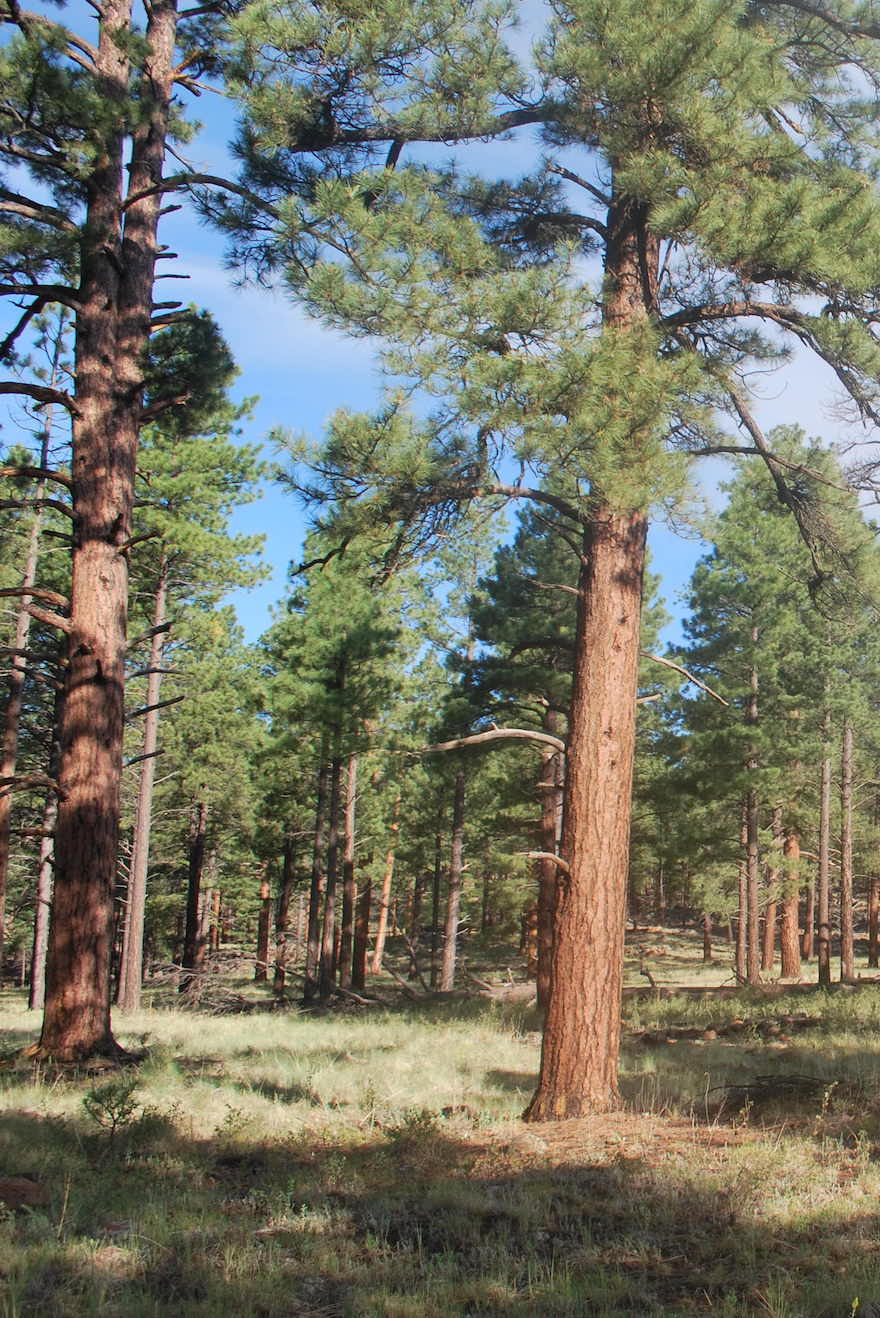
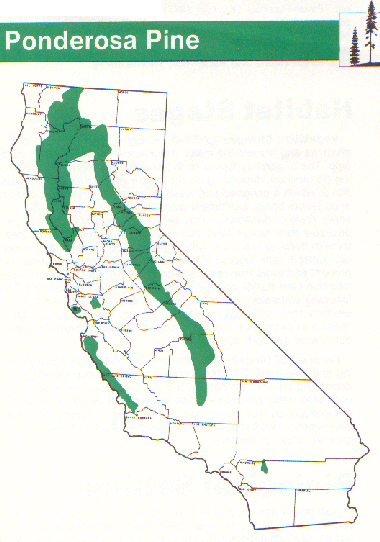
The ponderosa pine (Pinus ponderosa), a towering conifer known for its golden bark and resilience, holds a significant place in Nevada’s ecological tapestry. Its presence across the state’s diverse landscapes reflects a remarkable ability to thrive in challenging environments, shaping both the physical and biological characteristics of the region. Understanding the distribution and ecological role of the ponderosa pine requires a comprehensive approach, one that utilizes maps as powerful tools to illuminate its intricate relationship with the Nevada landscape.
A Visual Journey Through Nevada’s Ponderosa Pine Forests:
Maps serve as essential guides for navigating the complex world of the ponderosa pine in Nevada. By visually representing the species’ distribution, these maps provide invaluable insights into its habitat preferences, ecological interactions, and vulnerability to environmental change.
1. Distribution and Elevation:
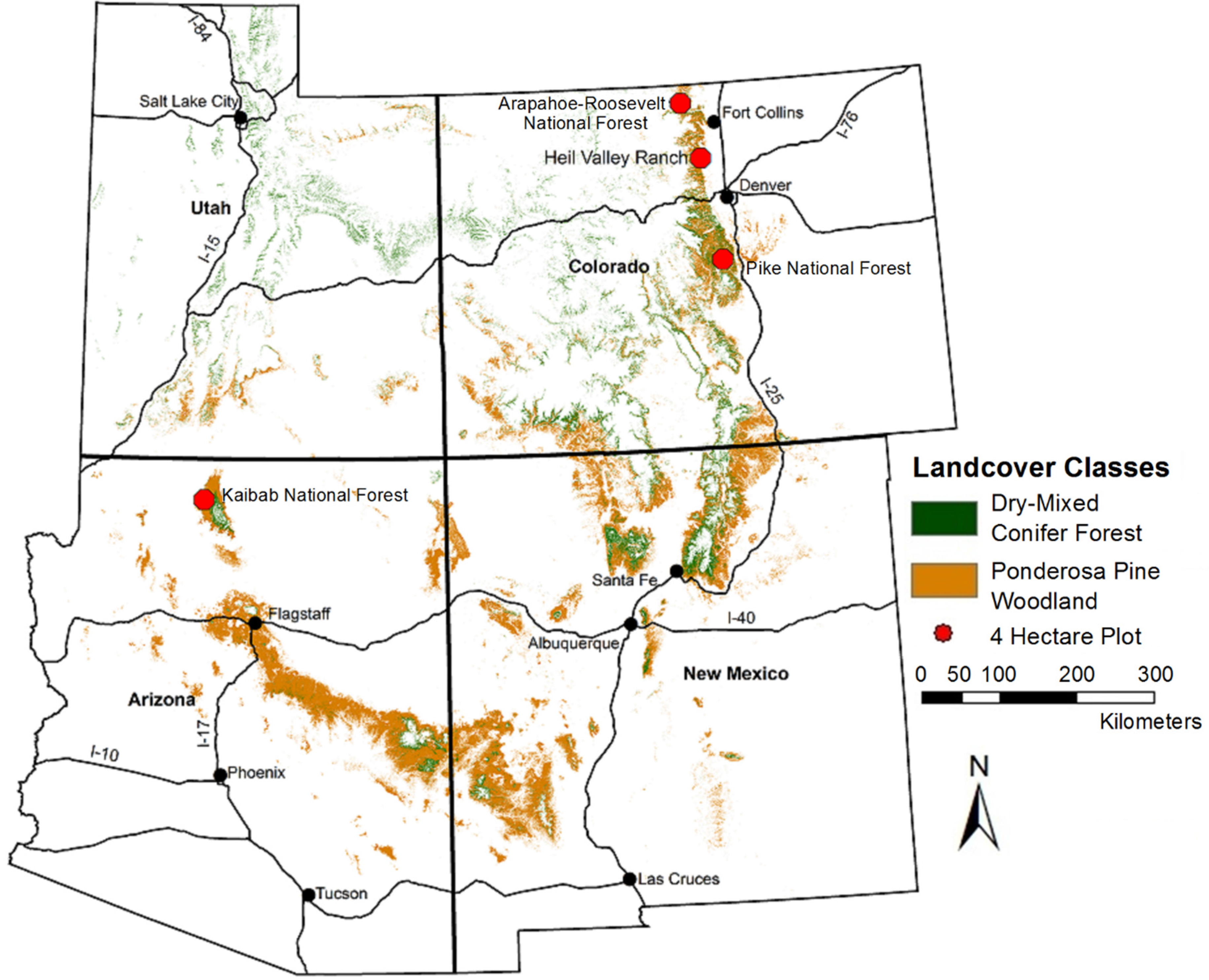
A map showcasing the distribution of ponderosa pine across Nevada reveals a fascinating pattern. The species thrives in the mountainous regions, particularly along the Sierra Nevada, the Spring Mountains, and the Humboldt Range. The map clearly depicts the species’ preference for higher elevations, ranging from approximately 5,000 to 9,000 feet above sea level. This elevation range is characterized by cooler temperatures, sufficient precipitation, and well-drained soils, all factors crucial for the ponderosa pine’s survival.
2. Climate and Precipitation:
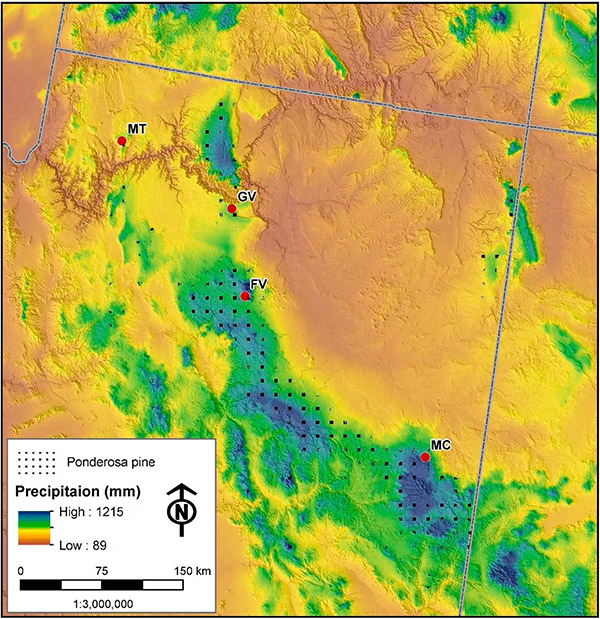
Superimposing climate data onto the distribution map highlights the relationship between the ponderosa pine and precipitation patterns. The species thrives in regions receiving an average annual precipitation of 15 to 30 inches, with a distinct dry season. The map emphasizes the importance of snowpack for the ponderosa pine, as it serves as a critical source of moisture during the dry summer months. This interplay between climate and distribution emphasizes the species’ adaptation to semi-arid conditions.
3. Soil Type and Topography:
A detailed map incorporating soil type and topography reveals the ponderosa pine’s preference for specific geological conditions. The species thrives on well-drained soils, often associated with granitic bedrock, volcanic ash, or sandy loam. The map demonstrates the species’ ability to colonize slopes, ridges, and canyons, showcasing its adaptability to diverse terrain. This connection between soil and topography underscores the importance of understanding the geological context for effective conservation and management efforts.
4. Wildlife Habitat and Ecological Interactions:
Beyond its physical distribution, maps can illuminate the ecological significance of the ponderosa pine. By integrating information on wildlife habitat, the map illustrates how the species provides shelter and sustenance for a wide array of animals. The ponderosa pine serves as a vital habitat for numerous bird species, including the Western Tanager, the American Robin, and the Clark’s Nutcracker. Additionally, the map highlights the species’ role in supporting populations of small mammals, such as squirrels, chipmunks, and deer, which rely on its seeds and needles for food.
5. Forest Health and Fire Ecology:
Maps can also be used to assess the health of ponderosa pine forests and their susceptibility to wildfire. By incorporating data on tree density, age structure, and past fire events, the map reveals areas prone to high-severity wildfires. This information is crucial for developing effective forest management strategies, such as controlled burns, that can reduce the risk of catastrophic wildfires and promote healthy forest ecosystems.
6. Climate Change Impacts:
In the face of a changing climate, maps become essential tools for understanding the potential impacts on ponderosa pine forests. By overlaying climate projections onto the distribution map, researchers can identify areas that may experience increased temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and more frequent wildfires. This information is crucial for developing adaptation strategies that mitigate the effects of climate change on the species’ survival.
Benefits of Mapping the Ponderosa Pine in Nevada:
The use of maps to illustrate the ponderosa pine in Nevada provides numerous benefits, ranging from scientific research to conservation efforts:
- Enhanced Understanding: Maps offer a visual representation of the species’ distribution, habitat preferences, and ecological interactions, fostering a deeper understanding of its role in the Nevada ecosystem.
- Effective Management: Maps provide valuable information for managing ponderosa pine forests, including identifying areas prone to wildfire, optimizing timber harvesting practices, and implementing effective conservation measures.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Maps facilitate the assessment of climate change impacts on ponderosa pine forests, enabling the development of adaptation strategies to mitigate negative consequences.
- Public Engagement: Maps can be used to educate the public about the importance of ponderosa pine forests and the challenges they face, fostering greater awareness and support for conservation efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What are the key threats facing ponderosa pine forests in Nevada?
A: Ponderosa pine forests in Nevada face numerous threats, including:
- Wildfire: Climate change is increasing the frequency and severity of wildfires, posing a significant threat to ponderosa pine forests.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species, such as cheatgrass, compete with ponderosa pine seedlings for resources and can exacerbate wildfire risk.
- Drought: Prolonged drought periods can weaken ponderosa pines, making them more susceptible to pests, diseases, and wildfires.
- Insect Outbreaks: Bark beetles and other insects can infest and kill ponderosa pines, particularly during periods of drought or stress.
Q: What are some strategies for managing ponderosa pine forests in Nevada?
A: Effective management strategies for ponderosa pine forests in Nevada include:
- Prescribed Fire: Controlled burns can mimic natural fire regimes, reducing fuel loads and promoting healthy forest ecosystems.
- Thinning: Removing overcrowded trees can improve forest health, reduce wildfire risk, and promote the growth of larger, healthier trees.
- Restoration: Restoring degraded areas through planting seedlings or using other methods can help to re-establish healthy ponderosa pine forests.
- Early Detection and Control: Monitoring for invasive species and pests allows for early detection and control efforts, minimizing their impact on ponderosa pine forests.
Tips for Understanding and Appreciating Ponderosa Pine Forests:
- Explore Local Forests: Visit ponderosa pine forests in Nevada to observe the species’ unique characteristics and appreciate its ecological importance.
- Engage with Local Experts: Connect with foresters, scientists, or conservation organizations to learn more about ponderosa pine management and conservation efforts.
- Support Conservation Efforts: Donate to or volunteer with organizations dedicated to protecting ponderosa pine forests and their associated ecosystems.
- Promote Awareness: Share information about the importance of ponderosa pine forests with friends, family, and community members, raising awareness about the challenges they face.
Conclusion:
Maps provide a powerful tool for understanding the distribution, ecology, and management of ponderosa pine forests in Nevada. By visually representing the species’ relationship with the landscape, these maps illuminate its crucial role in the region’s biodiversity, resilience, and ecological integrity. As climate change continues to impact Nevada’s ecosystems, the use of maps will be essential for developing effective conservation and adaptation strategies to ensure the long-term survival of the ponderosa pine, a symbol of Nevada’s unique and resilient landscapes.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Ponderosa Pine in Nevada: A Landscape of Resilience and Adaptation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
