26, Feb 2024
Navigating The European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To The Continent’s Political Geography
Navigating the European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Continent’s Political Geography
Related Articles: Navigating the European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Continent’s Political Geography
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Continent’s Political Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Continent’s Political Geography
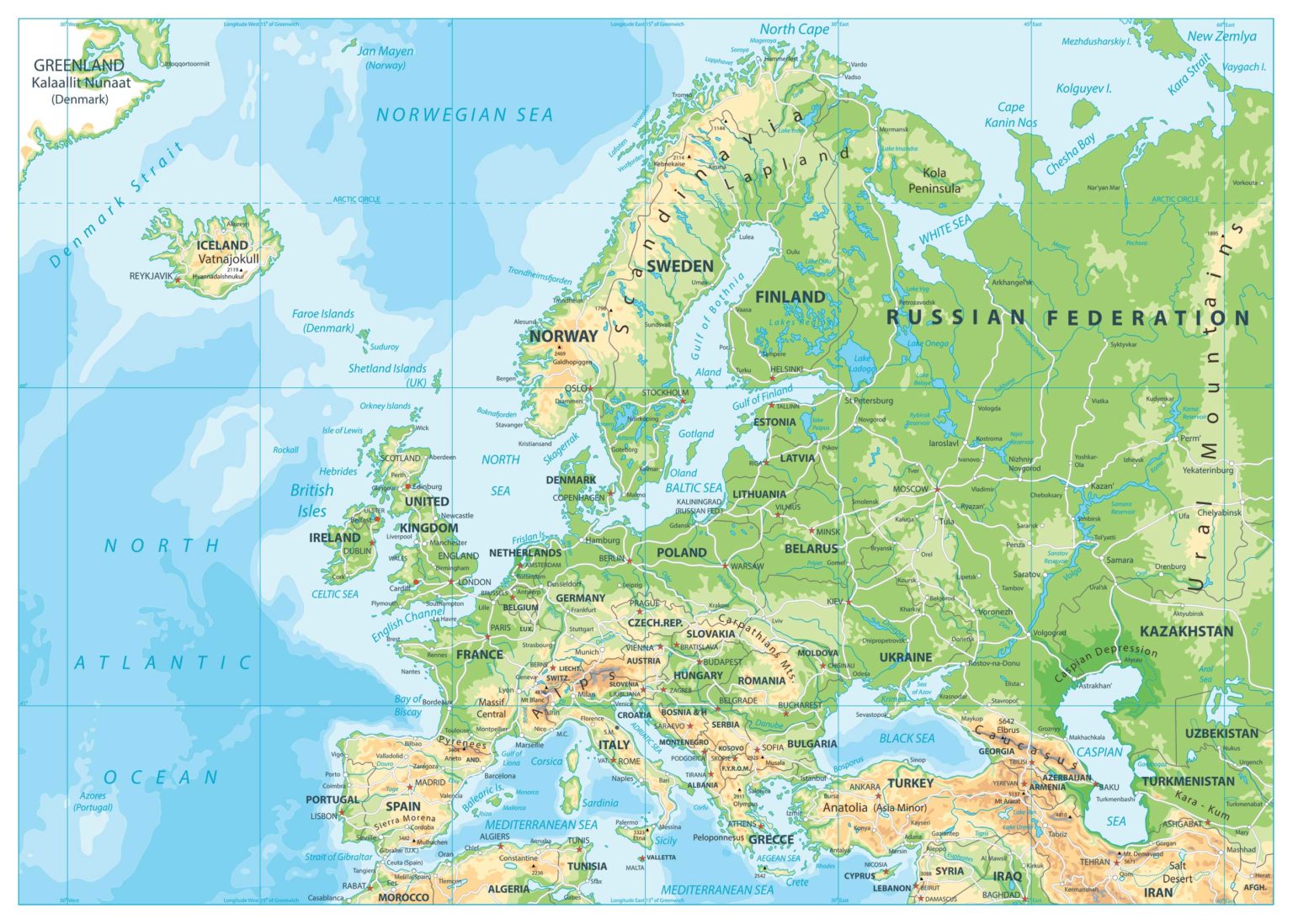
The European continent, a tapestry of diverse cultures, languages, and histories, is a fascinating study in political geography. Understanding the intricate network of European countries and their borders is essential for appreciating the continent’s rich past, present, and future. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of the European map, delving into its historical context, present-day configuration, and the significant role it plays in global affairs.
A Shifting Landscape: From Empires to Nation-States
The map of Europe has undergone dramatic transformations over the centuries, reflecting the rise and fall of empires, the emergence of nation-states, and the ongoing process of political and social change. The Roman Empire, at its zenith, encompassed a vast territory spanning much of modern-day Europe, leaving a lasting legacy in language, law, and infrastructure. Its collapse, however, ushered in a period of fragmentation and the rise of numerous kingdoms and principalities.
The Middle Ages saw the emergence of powerful kingdoms like France, England, and Spain, while the Holy Roman Empire, a complex patchwork of territories, exerted significant influence in Central Europe. The Renaissance and the Age of Enlightenment spurred intellectual and scientific progress, leading to the rise of modern nation-states and the concept of national sovereignty.
The 19th and 20th centuries witnessed significant shifts in the European map. The Industrial Revolution fueled economic growth and spurred territorial expansion, leading to the formation of empires like the British Empire and the Austro-Hungarian Empire. The two World Wars, however, brought about dramatic changes, dismantling empires and redrawing borders. The Cold War further divided Europe into two blocs, with the Soviet Union and its allies in the East, and Western Europe under the influence of the United States.
The European Union: A New Era of Integration
The end of the Cold War and the fall of the Soviet Union marked a new chapter in European history. The European Union (EU), established in 1993, emerged as a powerful force for economic and political integration, promoting cooperation and fostering closer ties between its member states. The EU has expanded significantly since its inception, encompassing a diverse group of countries with distinct histories, languages, and cultures.
The EU’s influence extends far beyond its borders, playing a significant role in global trade, diplomacy, and security. The Eurozone, consisting of countries that have adopted the euro as their common currency, further strengthens the EU’s economic power.
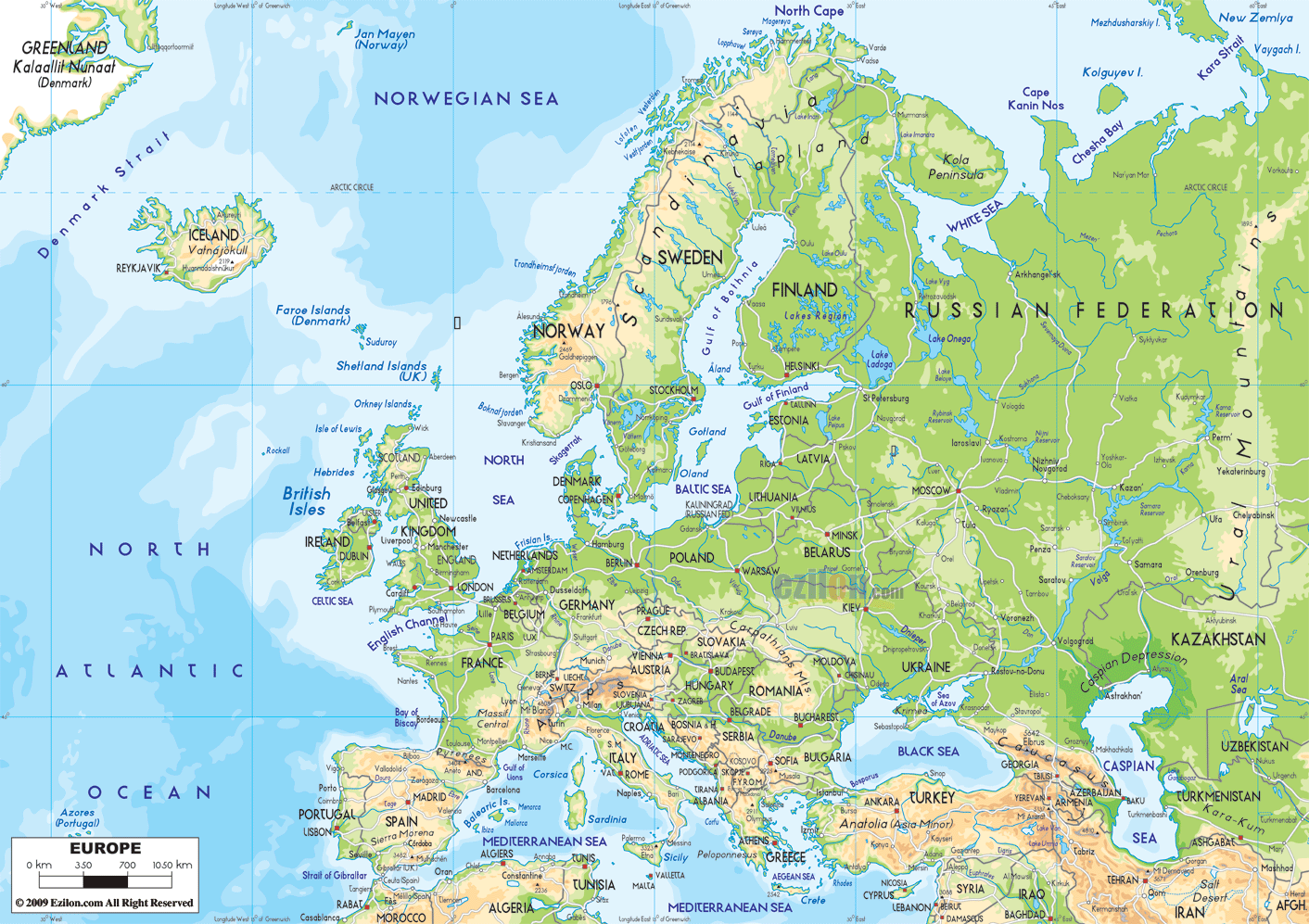
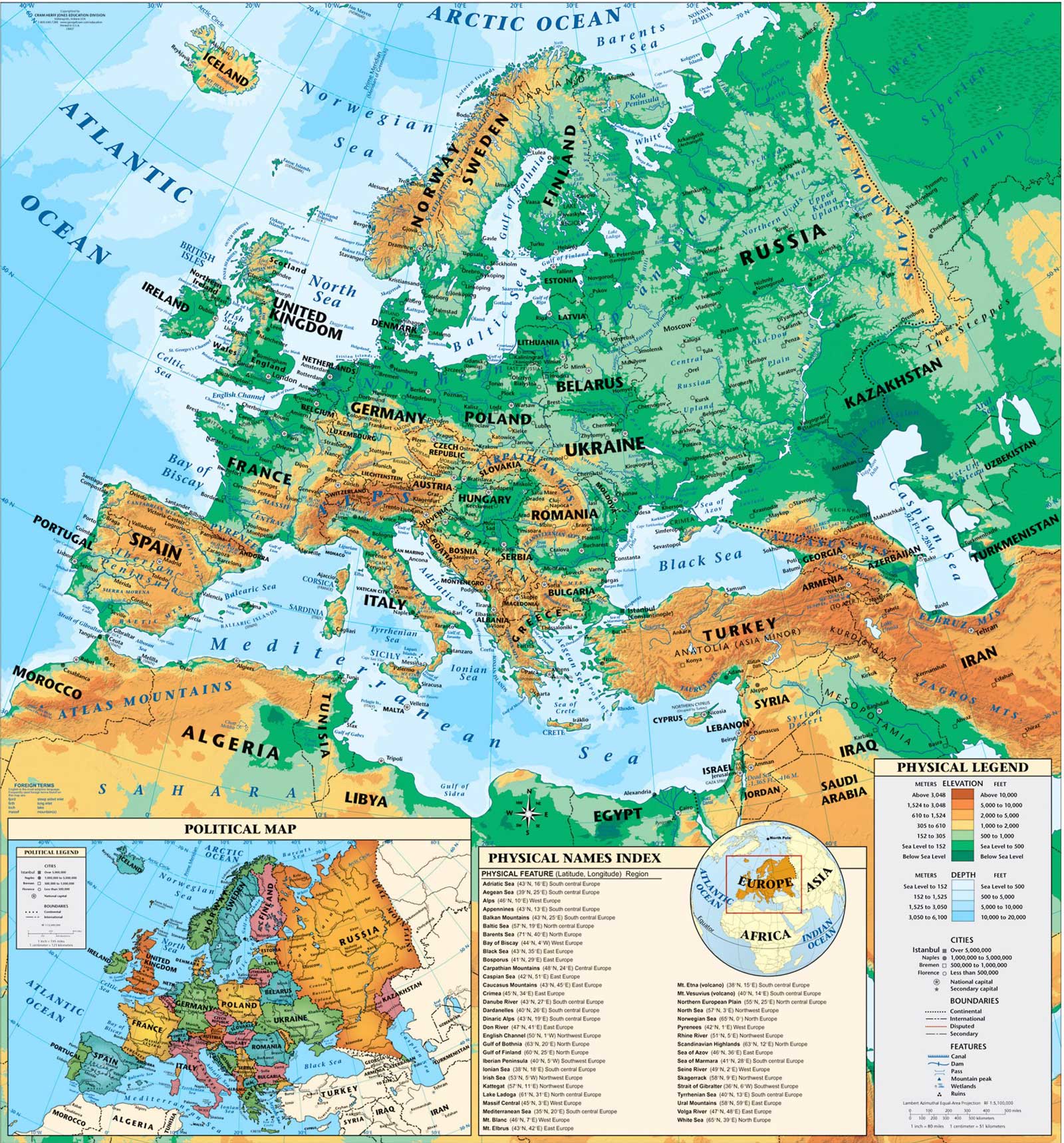
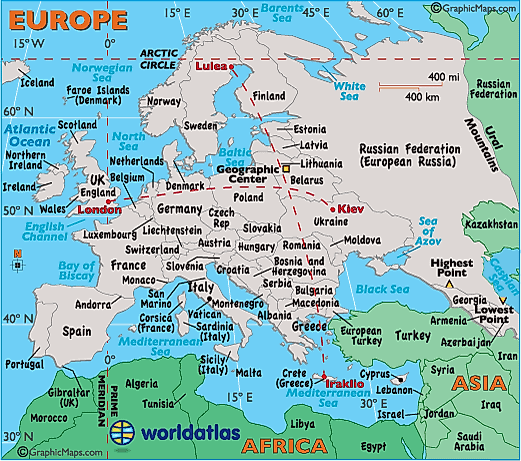
Understanding the European Map: Key Features and Regions
The European map is a complex and dynamic entity, characterized by its diverse geography, varied cultures, and intricate political landscape. It is helpful to divide the continent into distinct regions for a better understanding of its different characteristics:
- Western Europe: This region encompasses countries like France, Germany, the United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, and Portugal. It is home to major economic centers, significant cultural heritage, and a strong tradition of democracy.
- Central Europe: This region includes countries like Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Austria, and Slovenia. It is characterized by a rich history, diverse cultures, and a growing economic influence.
- Eastern Europe: This region includes countries like Ukraine, Belarus, Moldova, Romania, Bulgaria, and the Baltic states (Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania). It is marked by a transition from communist rule to democratic systems, with varying degrees of economic development.
- Northern Europe: This region encompasses countries like Sweden, Norway, Denmark, Finland, and Iceland. It is known for its high standard of living, social welfare systems, and strong environmental consciousness.
- Southern Europe: This region includes countries like Greece, Cyprus, Malta, Italy, and Spain. It is characterized by a warm climate, ancient history, and a strong emphasis on culture and tourism.
The Importance of Understanding the European Map
Understanding the European map is crucial for a variety of reasons:
- Historical Context: The European map provides insights into the continent’s rich history, from ancient empires to modern nation-states, helping us understand the complex tapestry of cultures and identities that have shaped the region.
- Political Landscape: The map reveals the intricate web of political relationships and alliances that define the continent, highlighting the role of international organizations like the EU in shaping European politics.
- Economic Dynamics: The map reveals the geographical distribution of economic activity and trade patterns, highlighting the importance of major economic centers and the interconnectedness of European economies.
- Cultural Diversity: The map highlights the vast cultural diversity of Europe, showcasing the unique traditions, languages, and artistic expressions that enrich the continent’s identity.
- Global Significance: Europe’s strategic location, its economic power, and its influence in global affairs make understanding the European map essential for comprehending international relations and global trends.
FAQs about the European Map
Q: What is the largest country in Europe by land area?
A: Russia, although a significant portion of its territory lies in Asia, is the largest country in Europe by land area.
Q: What is the smallest country in Europe?
A: Vatican City, an independent city-state located within Rome, Italy, is the smallest country in Europe by land area.
Q: What are some of the most important geographical features of Europe?
A: Europe’s geography is diverse, featuring the Alps mountain range, the Danube River, the Mediterranean Sea, the North Sea, and numerous other prominent features.
Q: How has the European map changed over time?
A: The European map has undergone significant changes over centuries, reflecting the rise and fall of empires, the emergence of nation-states, and the ongoing process of political and social change.
Q: What are the main challenges facing the European Union?
A: The EU faces various challenges, including economic disparities, immigration, political fragmentation, and the rise of nationalism.
Tips for Navigating the European Map
- Use Online Resources: Utilize interactive maps and online atlases to explore the European continent in detail.
- Focus on Key Regions: Divide the continent into distinct regions to understand the unique characteristics of each area.
- Explore Historical Context: Research the historical events that have shaped the European map and the political boundaries we see today.
- Engage with Current Events: Stay informed about current events in Europe to understand the evolving political landscape.
Conclusion
The European map is a dynamic and ever-evolving representation of the continent’s rich history, diverse cultures, and complex political landscape. Understanding its intricate details provides valuable insights into the continent’s past, present, and future. By exploring the historical context, the present-day configuration, and the significant role of the EU, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities and dynamism of the European landscape. As we navigate the 21st century, understanding the European map remains essential for comprehending the global interconnectedness and the evolving forces that shape our world.
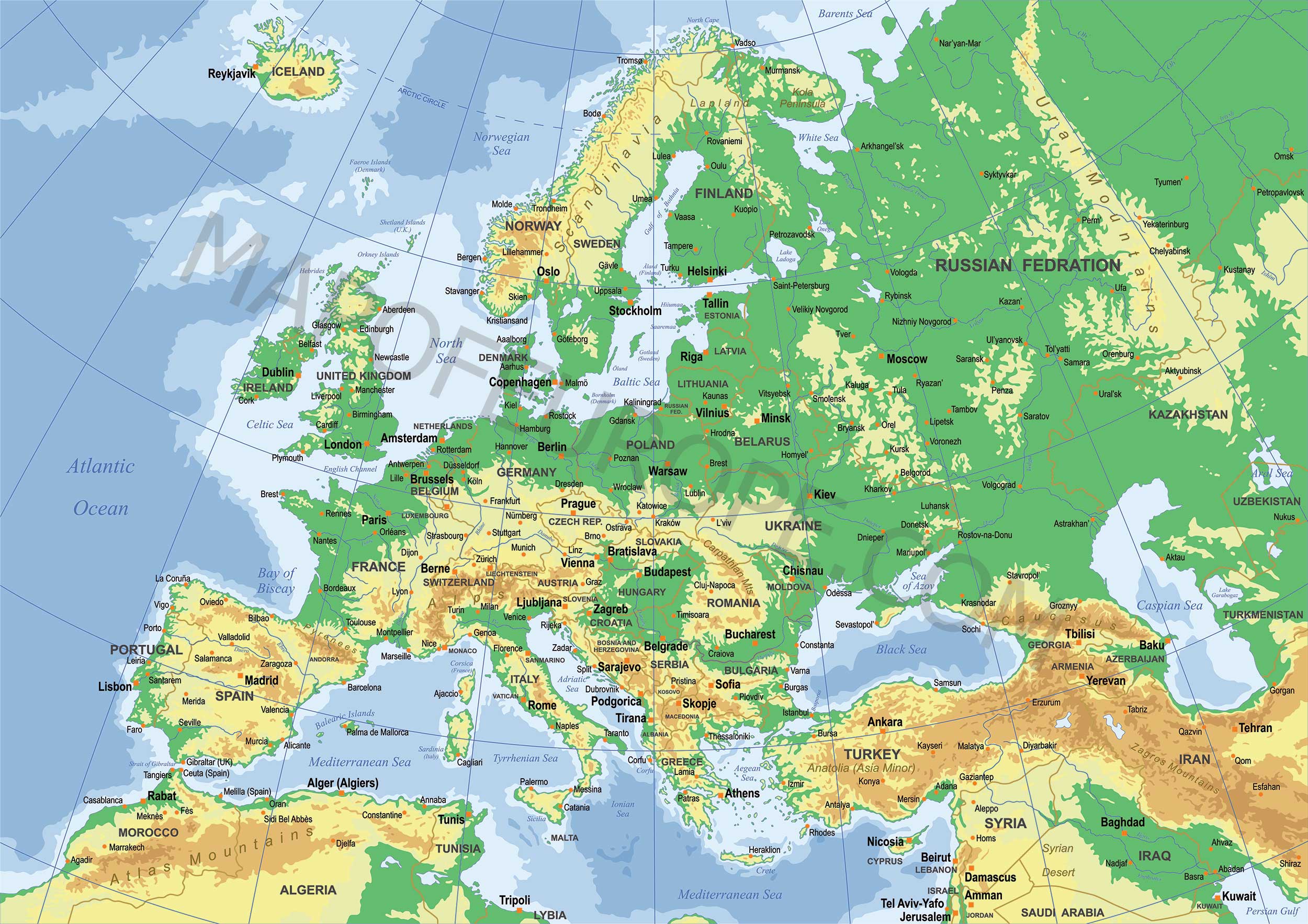

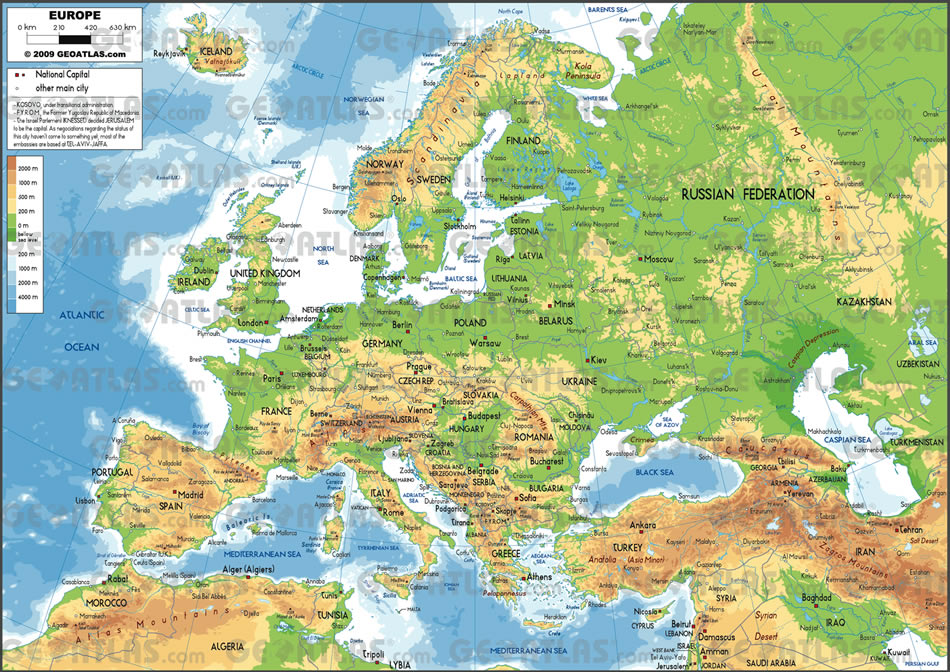

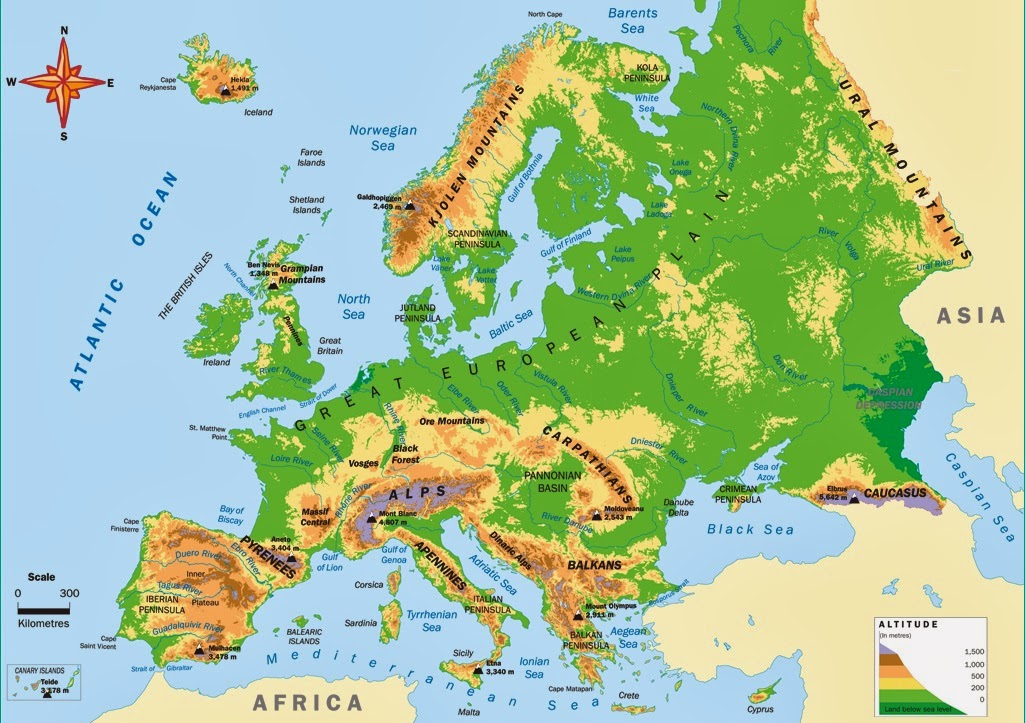
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Continent’s Political Geography. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
