4, Feb 2024
Navigating The European Landscape: A Comprehensive Look At The Map Of Europe In 2024
Navigating the European Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Europe in 2024
Related Articles: Navigating the European Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Europe in 2024
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the European Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Europe in 2024. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the European Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Europe in 2024
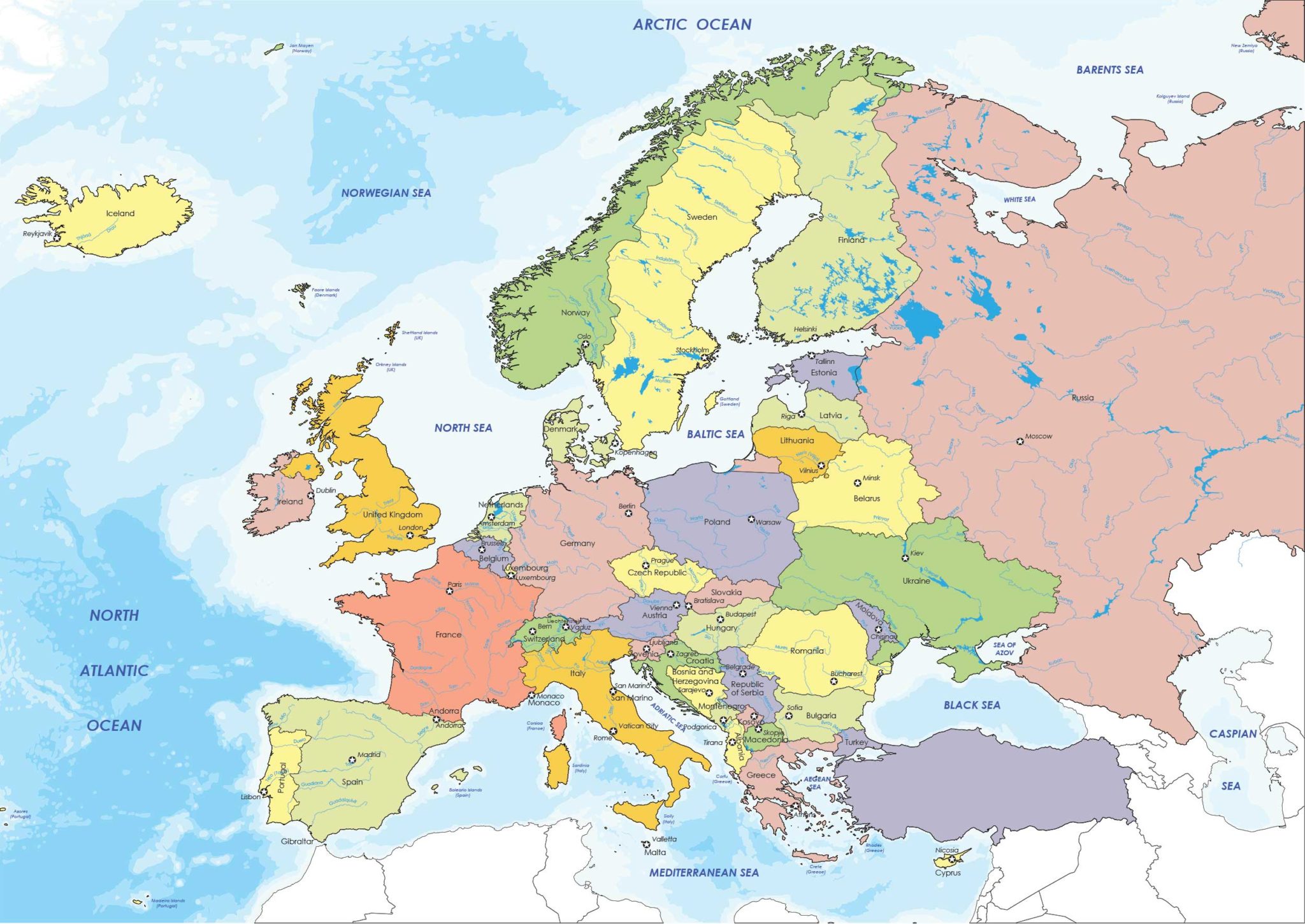
The European continent, a tapestry of diverse cultures, languages, and histories, continues to evolve. Understanding the geopolitical landscape of Europe in 2024 requires a nuanced perspective, one that encompasses both the enduring features of its map and the dynamic forces that shape its future. This article delves into the intricacies of the European map, exploring its significance in the context of contemporary political, economic, and social realities.
The Enduring Features: A Foundation of Borders and Identities
The map of Europe in 2024 largely reflects the established borders of its 44 sovereign nations. These borders, often shaped by historical events, wars, and treaties, represent a complex web of identities, languages, and cultural legacies. While the map may appear static, the very act of drawing and interpreting borders is a dynamic process, constantly influenced by internal and external pressures.
The Baltic States: A Bridge Between East and West
The Baltic States – Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania – occupy a unique position on the map. Having emerged from the collapse of the Soviet Union, they stand as a bridge between Eastern and Western Europe. Their membership in NATO and the European Union underscores their commitment to Western values and institutions, while their proximity to Russia highlights the ongoing geopolitical tensions in the region.
The Balkans: A Region of Transition
The Balkan Peninsula, often characterized by historical and ethnic complexities, continues to navigate a path toward stability and integration. The region’s diverse cultural tapestry, encompassing Orthodox Christianity, Islam, and Catholicism, has contributed to its unique identity. The ongoing process of EU accession for some Balkan nations, such as Serbia and Montenegro, signifies a commitment to European integration and a desire for greater economic and political stability.
The Mediterranean: A Crossroads of Cultures and Challenges
The Mediterranean region, a cradle of civilization and a nexus of trade routes, faces a multitude of challenges. The ongoing refugee crisis, fueled by conflict and instability in the Middle East and North Africa, has placed significant pressure on coastal nations. Moreover, the region’s diverse political and economic systems, coupled with the impacts of climate change, contribute to a complex and evolving landscape.
The North: A Hub of Innovation and Prosperity
The Nordic countries – Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden – are renowned for their high levels of social welfare, economic prosperity, and commitment to environmental sustainability. Their geographical location, with access to both the North Sea and the Baltic Sea, has facilitated trade and economic development. The region’s emphasis on innovation and technological advancements further reinforces its position as a leading force in Europe.
The West: A Powerhouse of Democracy and Economics
Western Europe, encompassing nations like France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the United Kingdom, remains a powerhouse of economic and political influence. The region’s robust economies, strong democratic institutions, and cultural heritage continue to shape global affairs. However, challenges such as economic inequality, political polarization, and the rise of populism pose challenges to the region’s stability and future direction.
The East: A Region in Transition
Eastern Europe, including Poland, Hungary, the Czech Republic, and Slovakia, has experienced significant transformations since the fall of the Soviet Union. The region’s membership in the EU has fostered economic growth and political stability. However, concerns regarding democratic backsliding in some countries, coupled with ongoing tensions with Russia, highlight the complexities of the region’s trajectory.
The Map as a Tool for Understanding: Beyond Borders
The map of Europe in 2024 serves as a valuable tool for understanding the continent’s geopolitical dynamics. However, it is crucial to recognize that the map represents more than just borders. It encapsulates the complex interplay of history, culture, economics, and politics that shape the European landscape.
Beyond the Borders: A Focus on the People and Their Stories
While the map provides a static representation of countries and their boundaries, it is the people who inhabit this space who truly bring it to life. Their stories, experiences, and struggles contribute to the rich tapestry of European culture and history. Understanding the diverse voices and perspectives within each nation is essential for comprehending the complexities of the European map.
The Future of the Map: A Constant State of Flux
The map of Europe is not a static entity. It is a dynamic landscape, constantly evolving in response to political, economic, and social forces. The ongoing integration process within the EU, coupled with the emergence of new geopolitical realities, will undoubtedly continue to shape the map in the years to come.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries about the European Map
1. What is the significance of the European Union (EU) in the context of the European map?
The EU, comprising 27 member states, represents a significant force in shaping the political, economic, and social landscape of Europe. It promotes economic integration, fosters cooperation on a range of issues, and serves as a forum for dialogue and consensus-building. The EU’s influence extends beyond its member states, impacting global affairs and international relations.
2. How has the map of Europe changed in recent years?
The map of Europe has undergone significant changes in recent decades, particularly with the collapse of the Soviet Union and the subsequent expansion of the EU. The addition of new member states, such as Croatia and Bulgaria, has reshaped the geographical and political landscape of the continent.
3. What are the key challenges facing Europe in 2024?
Europe faces a multitude of challenges, including:
- Economic inequality: The widening gap between rich and poor within many European nations poses a significant challenge to social cohesion and stability.
- Political polarization: The rise of populism and nationalist sentiments has led to increased political division and instability in several European countries.
- Climate change: The impacts of climate change, such as extreme weather events and rising sea levels, pose a significant threat to European economies and societies.
- Migration: The ongoing refugee crisis and the movement of people within Europe continue to be complex and challenging issues.
- Geopolitical tensions: The ongoing conflict in Ukraine, coupled with Russia’s assertive foreign policy, has heightened geopolitical tensions in Europe.
4. What are the opportunities for Europe in 2024?
Despite the challenges, Europe also presents significant opportunities for growth and development:
- Technological innovation: Europe is a hub of technological innovation, particularly in fields such as renewable energy, artificial intelligence, and biotechnology.
- Economic integration: The EU’s single market provides a platform for economic growth and prosperity, facilitating trade and investment within the region.
- Cultural diversity: Europe’s rich cultural heritage and diverse societies offer a unique source of creativity and innovation.
- Global leadership: Europe continues to play a significant role in global affairs, promoting diplomacy, peace, and human rights.
Tips for Understanding and Navigating the European Map:
- Utilize online resources: Numerous websites and interactive maps provide detailed information about the countries of Europe, their borders, and their historical context.
- Engage with news and media: Stay informed about current events in Europe through reputable news sources and media outlets.
- Explore cultural and historical perspectives: Delve into the rich cultural and historical tapestry of Europe through books, documentaries, and travel experiences.
- Engage in dialogue and discussion: Participate in discussions and debates about European issues to gain diverse perspectives and foster understanding.
Conclusion: A Dynamic Landscape of Interconnectedness
The map of Europe in 2024 serves as a visual representation of a complex and dynamic continent. It reflects the historical, political, and social forces that have shaped its landscape, while simultaneously highlighting the ongoing challenges and opportunities that define its future. Understanding the map, its nuances, and its evolving nature is crucial for navigating the complexities of the European landscape and engaging with its diverse voices and perspectives.

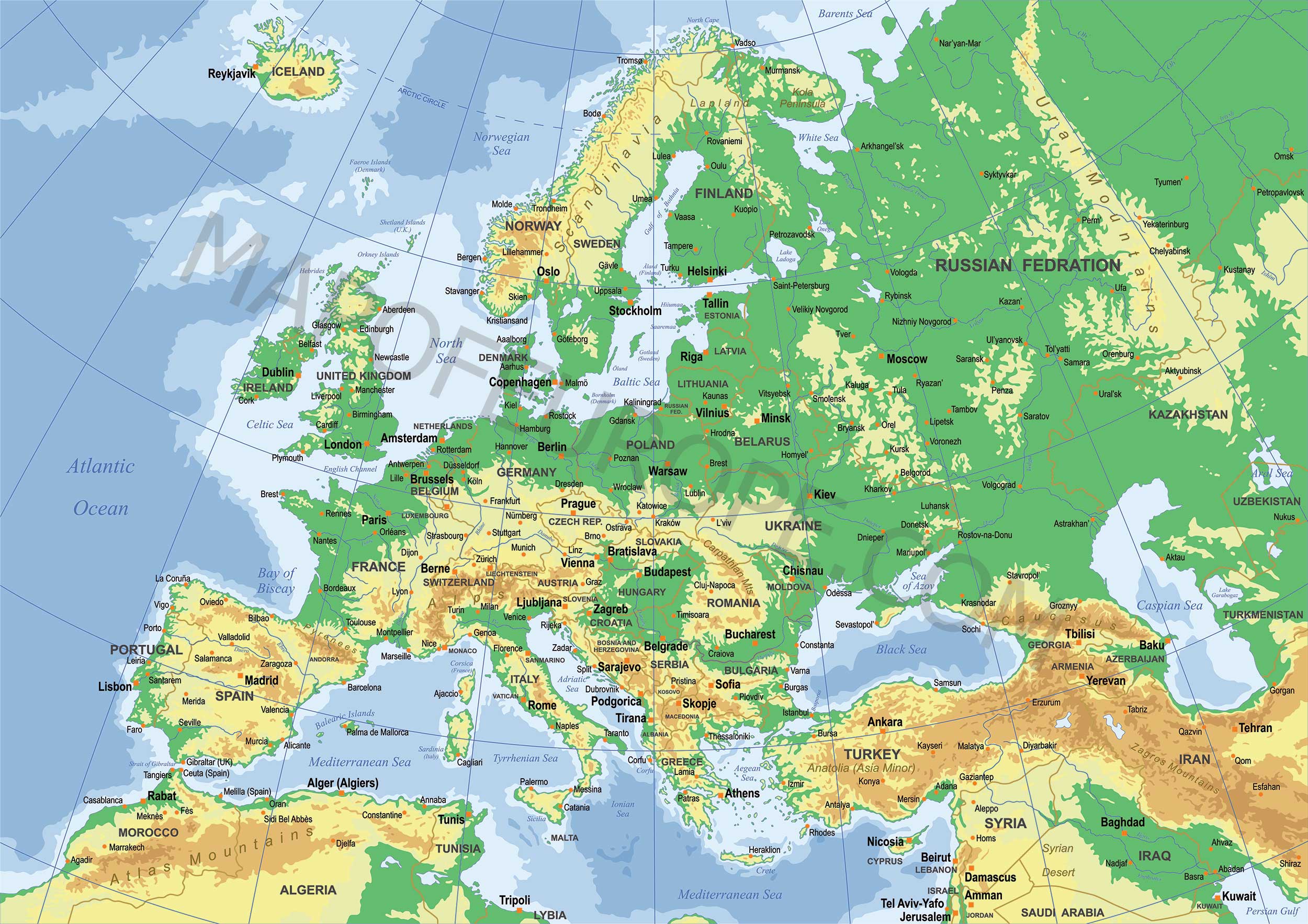



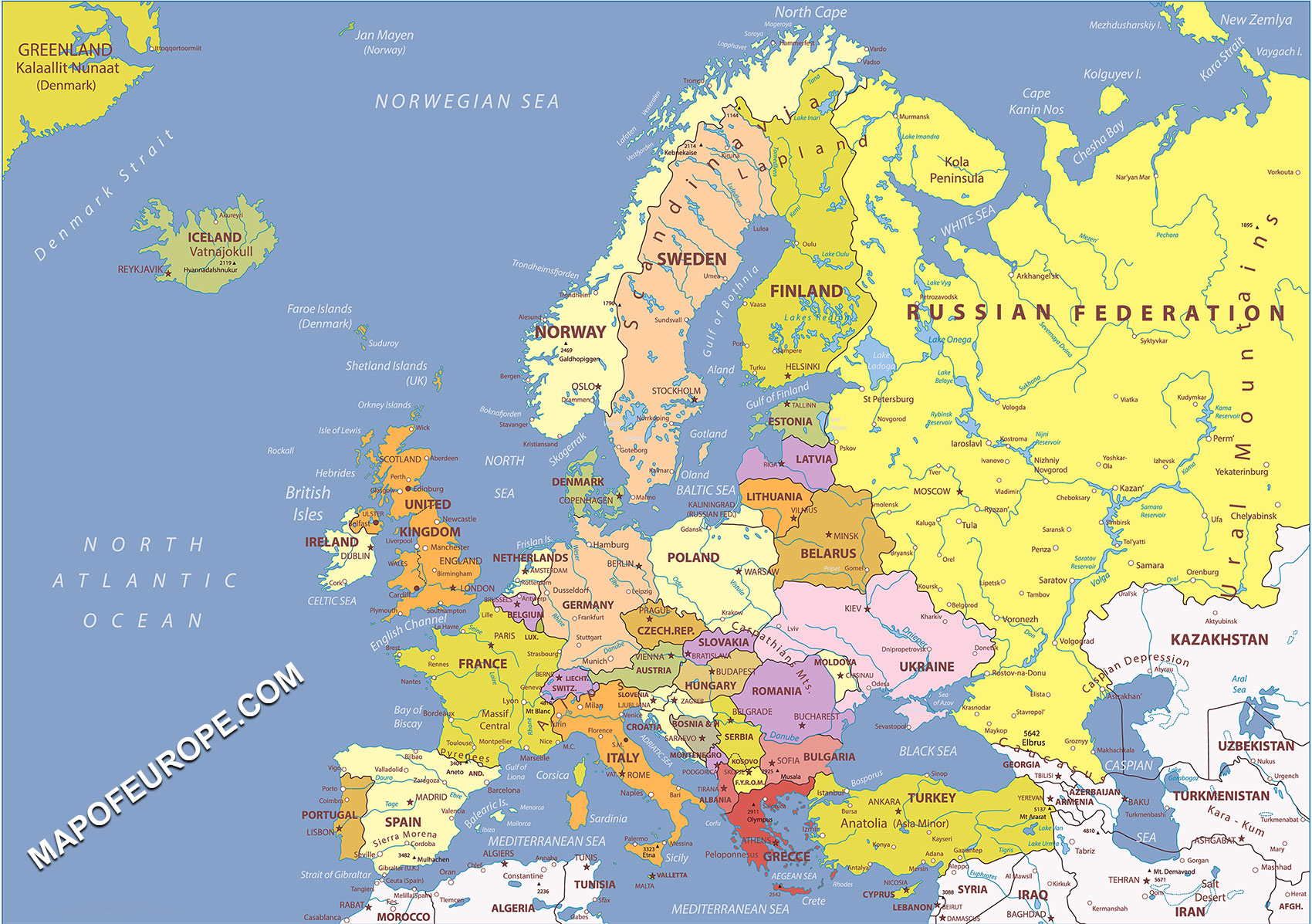

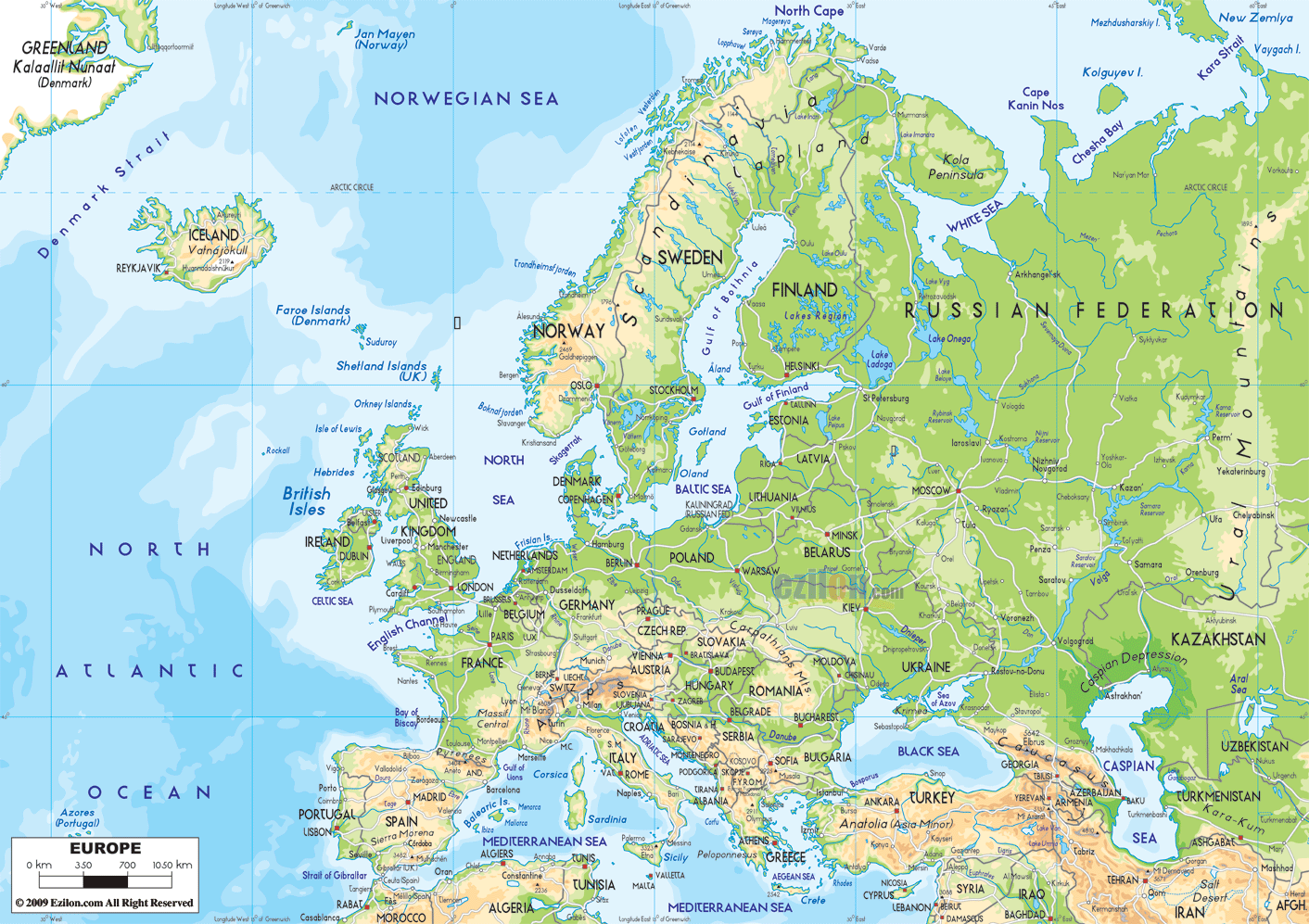
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the European Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Europe in 2024. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
