19, Apr 2024
Navigating The Shifting Sands: Understanding Europe’s Gas Price Landscape
Navigating the Shifting Sands: Understanding Europe’s Gas Price Landscape
Related Articles: Navigating the Shifting Sands: Understanding Europe’s Gas Price Landscape
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Shifting Sands: Understanding Europe’s Gas Price Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Shifting Sands: Understanding Europe’s Gas Price Landscape

The price of natural gas in Europe is a complex and constantly evolving phenomenon, influenced by a multitude of factors ranging from global supply and demand dynamics to geopolitical tensions. A comprehensive understanding of this landscape is crucial for businesses, policymakers, and individuals alike, as it impacts energy security, economic stability, and the everyday lives of European citizens.
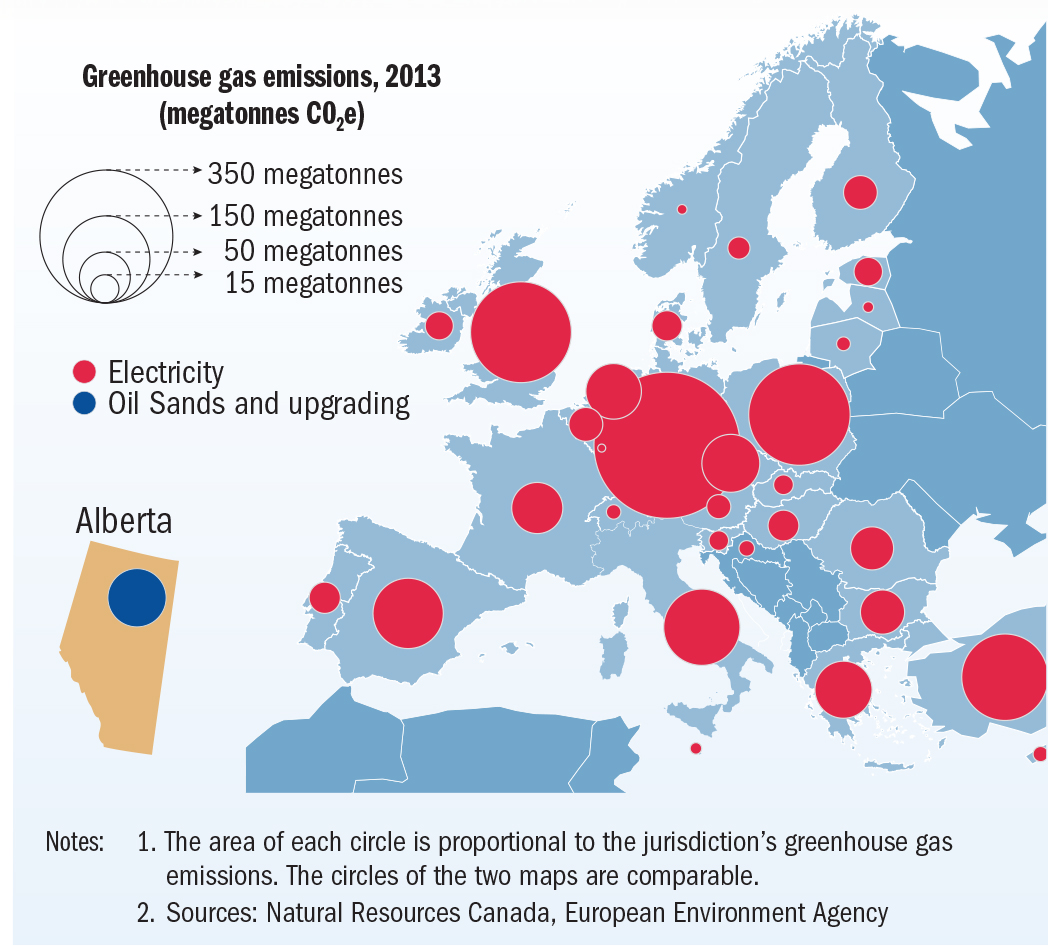
A Visual Representation of Volatility: The Gas Price Map of Europe
A gas price map of Europe provides a visual representation of the fluctuating prices across different regions and countries. This map serves as a valuable tool for understanding:
- Regional Variations: Gas prices can differ significantly between countries, reflecting factors such as proximity to production sources, pipeline infrastructure, and national policies. For instance, countries bordering Russia generally enjoy lower prices due to their direct access to Russian gas.
- Price Trends: The map allows for the visualization of price trends over time, highlighting periods of price spikes or dips. This information is essential for identifying potential market shifts and anticipating future price movements.
- Market Volatility: The map reveals the dynamic nature of the gas market, showcasing how prices can fluctuate rapidly in response to events such as geopolitical crises, supply disruptions, or changes in demand.
Factors Shaping the Gas Price Map
The gas price map of Europe is a product of a complex interplay of factors, including:
1. Global Supply and Demand:
- Global Production: The availability of natural gas reserves and production capacity globally plays a significant role in shaping prices. A decrease in global production or an increase in demand can lead to price increases.
- Global Demand: Factors such as economic growth, population increase, and industrial activity drive global demand for natural gas. As demand rises, prices tend to increase.
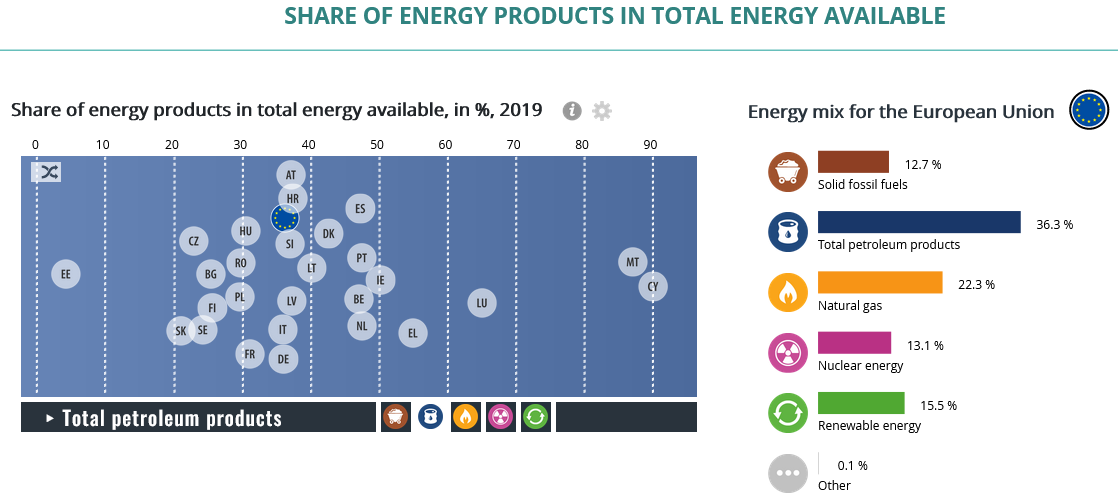
2. European Supply and Demand:
- European Production: Europe’s own natural gas production capacity is limited, making it heavily reliant on imports. The availability and price of imported gas significantly influence prices within the European market.
- European Demand: Factors such as weather patterns, industrial activity, and household energy consumption impact demand within Europe. Cold winters or increased industrial activity can lead to higher prices.
3. Infrastructure and Transportation:
- Pipeline Infrastructure: The availability and capacity of pipelines for transporting natural gas across Europe are crucial for ensuring supply and influencing prices. Bottlenecks or disruptions in pipeline networks can lead to price spikes.
- Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG): The growing importance of LNG imports, particularly from countries like Qatar and the United States, has added another layer of complexity to the European gas market. LNG imports offer flexibility but are often more expensive than pipeline gas.
4. Geopolitical Factors:
- Political Tensions: Geopolitical tensions, such as those between Russia and the West, can significantly impact gas prices. Disputes over gas supply contracts or sanctions can lead to price volatility.
- Energy Security Concerns: European countries are increasingly concerned about their energy security, particularly in light of their dependence on Russian gas. This concern drives efforts to diversify supply sources and reduce reliance on a single supplier, potentially influencing prices.
5. Government Policies:
- Energy Policies: National policies aimed at promoting renewable energy sources or reducing reliance on fossil fuels can influence gas prices. For example, subsidies for renewable energy could decrease demand for natural gas, potentially leading to lower prices.
- Taxation and Regulation: Government taxes and regulations on gas production, transportation, and consumption can also impact prices.
The Importance of Understanding Gas Prices in Europe
A comprehensive understanding of the gas price map of Europe is crucial for a variety of reasons:
- Energy Security: By analyzing price trends and understanding the factors influencing them, policymakers can develop strategies to enhance energy security and reduce dependence on single suppliers.
- Economic Stability: Fluctuating gas prices can have significant economic implications, impacting businesses, consumers, and national economies. Understanding price dynamics can help businesses mitigate risks and make informed decisions.
- Environmental Sustainability: The transition to a low-carbon economy requires a careful analysis of the role of natural gas and its price. Understanding price trends can guide policymakers in designing effective policies for promoting renewable energy sources while ensuring energy affordability.
FAQs: Demystifying the Gas Price Map
Q: What are the main factors driving gas price fluctuations in Europe?
A: The most significant factors are global supply and demand dynamics, European production and consumption patterns, pipeline infrastructure, geopolitical tensions, and government policies.
Q: How can I access the latest gas price data for Europe?
A: Several reputable sources provide real-time and historical gas price data, including the European Commission’s Energy Platform, the International Energy Agency (IEA), and various industry publications.
Q: How do gas prices in Europe compare to those in other regions?
A: European gas prices are generally higher than in regions with abundant natural gas resources, such as North America. However, prices can fluctuate significantly depending on specific factors in each region.
Q: How are gas prices impacting the European economy?
A: High gas prices can lead to increased energy costs for businesses and consumers, potentially impacting economic growth, inflation, and household budgets.
Q: What measures can be taken to mitigate the impact of high gas prices?
A: Possible measures include diversifying energy sources, promoting energy efficiency, developing alternative energy technologies, and implementing targeted support measures for vulnerable households.
Tips for Navigating the Gas Price Landscape:
- Stay informed: Regularly consult reliable sources for updates on gas prices, market trends, and relevant policy developments.
- Consider energy efficiency: Implement measures to reduce energy consumption, such as insulating homes, using energy-efficient appliances, and optimizing heating systems.
- Explore alternative energy sources: Investigate renewable energy options, such as solar panels or heat pumps, to reduce reliance on natural gas.
- Support government policies: Advocate for policies that promote energy security, diversify energy sources, and encourage the development of sustainable energy technologies.
Conclusion: A Dynamic and Complex Landscape
The gas price map of Europe is a dynamic and complex landscape, shaped by a multitude of factors. Understanding this landscape is essential for navigating the challenges of energy security, economic stability, and environmental sustainability. By staying informed, making informed choices, and supporting policies that promote a sustainable energy future, we can navigate this evolving terrain and ensure a brighter future for Europe.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Shifting Sands: Understanding Europe’s Gas Price Landscape. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
