22, May 2024
Navigating The Sierra Nevada: A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding The Region’s Complexities
Navigating the Sierra Nevada: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Region’s Complexities
Related Articles: Navigating the Sierra Nevada: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Region’s Complexities
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Sierra Nevada: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Region’s Complexities. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Sierra Nevada: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Region’s Complexities

The Sierra Nevada mountain range, a majestic and rugged landscape spanning over 400 miles across California, presents a unique challenge for those seeking to explore its beauty and understand its intricacies. From its towering peaks to its diverse ecosystems, the Sierra Nevada is a tapestry of geological, ecological, and human history, requiring a comprehensive approach to fully appreciate its complexity.
This article aims to provide a thorough exploration of the Sierra Nevada, utilizing a multi-faceted approach to understanding its diverse aspects. We will delve into the region’s geological formation, its varied ecosystems, the cultural and historical significance of the Sierra Nevada, and the challenges it faces in the face of climate change and human development.
Geological Foundations: A Story of Uplift and Erosion
The Sierra Nevada’s dramatic landscape is a product of millions of years of geological activity. The range’s foundation lies in the ancient granitic batholith, a massive body of intrusive igneous rock that formed deep beneath the Earth’s surface. This batholith, exposed through uplift and erosion, provides the bedrock for the Sierra Nevada’s towering peaks and rugged terrain.
The Sierra Nevada’s uplift began around 100 million years ago, driven by the collision of the North American and Pacific tectonic plates. This collision, known as subduction, caused the Earth’s crust to buckle and fold, creating the Sierra Nevada’s dramatic elevation. Over millions of years, erosion carved the granite into its present form, shaping the canyons, valleys, and peaks that define the region.
Ecosystem Diversity: A Tapestry of Life
The Sierra Nevada’s varied topography and elevation create a mosaic of ecosystems, each harboring unique plant and animal communities. From the arid foothills to the alpine meadows, the region supports a diverse range of life, including:
- Foothill Woodlands: Characterized by oak, pine, and chaparral, these lower elevations provide habitat for diverse wildlife, including deer, bobcats, and various bird species.
- Mixed Conifer Forests: Dominated by ponderosa pine, sugar pine, and Douglas fir, these forests are home to iconic species like the California condor and the Sierra Nevada red fox.
- Subalpine Forests: Located at higher elevations, these forests are dominated by lodgepole pine and whitebark pine, offering habitat for species adapted to colder temperatures and shorter growing seasons.
- Alpine Meadows: Above the treeline, these meadows are characterized by wildflowers, grasses, and unique alpine species like the pika and the marmot.
These diverse ecosystems are interconnected, with each playing a vital role in the overall health and resilience of the Sierra Nevada. Understanding these connections is crucial for effective conservation and management of the region’s natural resources.
Cultural and Historical Significance: A Tapestry of Stories
The Sierra Nevada has long been a place of cultural and historical significance for indigenous peoples and settlers alike. The region’s rich history is intertwined with the stories of:
- Native American Tribes: For centuries, Native American tribes like the Miwok, Paiute, and Mono have inhabited the Sierra Nevada, relying on its natural resources for survival. Their cultural traditions and knowledge of the land are integral to understanding the region’s history and ecology.
- Gold Rush Era: The discovery of gold in 1848 triggered a mass migration to the Sierra Nevada, transforming the region into a hub of economic activity. Mining towns sprang up, leaving behind a legacy of environmental impact and social change.
- Conservation Movement: The Sierra Nevada has also played a pivotal role in the development of the American conservation movement. Figures like John Muir and Ansel Adams championed the protection of the region’s natural beauty, leading to the establishment of national parks and wilderness areas.
These historical narratives highlight the multifaceted nature of the Sierra Nevada, emphasizing the importance of recognizing and respecting the region’s cultural heritage alongside its natural beauty.
Challenges and Opportunities: A Balancing Act for the Future
The Sierra Nevada faces a number of challenges, including:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and increased wildfire activity are impacting the region’s ecosystems and communities.
- Water Resources: The Sierra Nevada is a critical source of water for California, but climate change and increasing demand are putting pressure on water resources.
- Human Development: Urbanization, tourism, and resource extraction continue to exert pressure on the region’s ecosystems and cultural heritage.
Despite these challenges, the Sierra Nevada also presents opportunities for:
- Climate Adaptation: By understanding the impacts of climate change, communities can develop strategies to adapt and mitigate its effects.
- Sustainable Development: Balancing economic growth with environmental protection is essential for ensuring the long-term health of the Sierra Nevada.
- Cultural Preservation: Preserving and sharing the region’s rich cultural heritage is crucial for maintaining its historical significance and fostering a sense of place.
Navigating the Future: A Path Towards Sustainability
Understanding the Sierra Nevada’s complex history, ecosystems, and challenges is essential for navigating its future. By embracing a holistic approach that incorporates scientific knowledge, cultural understanding, and community engagement, we can work towards a sustainable future for this iconic region.
FAQs
Q: What are the main geological features of the Sierra Nevada?
A: The Sierra Nevada is characterized by its granitic batholith, formed by intrusive igneous rock, and its dramatic uplift caused by tectonic plate movement. Erosion has shaped the region’s canyons, valleys, and peaks over millions of years.
Q: What are the major ecosystems found in the Sierra Nevada?
A: The Sierra Nevada encompasses a diverse range of ecosystems, including foothill woodlands, mixed conifer forests, subalpine forests, and alpine meadows, each supporting unique plant and animal communities.
Q: What are some of the key cultural and historical aspects of the Sierra Nevada?
A: The Sierra Nevada holds significant cultural and historical value, with a long history of Native American inhabitation, the impact of the Gold Rush era, and the development of the American conservation movement.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing the Sierra Nevada?
A: The Sierra Nevada faces challenges like climate change, water resource management, and human development, which require careful consideration and proactive solutions.
Q: What are some opportunities for a sustainable future for the Sierra Nevada?
A: Opportunities for a sustainable future include climate adaptation strategies, sustainable development practices, and cultural preservation initiatives.
Tips
- Embrace the diverse nature of the Sierra Nevada: Explore its various ecosystems, learn about its geological history, and engage with its cultural heritage.
- Respect the environment: Practice responsible outdoor recreation, minimize your impact, and support conservation efforts.
- Support local communities: Patronize businesses, engage with local organizations, and contribute to the region’s economic and social well-being.
- Stay informed about current issues: Keep up-to-date on environmental challenges and opportunities facing the Sierra Nevada, and participate in discussions and initiatives.
Conclusion
The Sierra Nevada is a region of unparalleled beauty, ecological complexity, and cultural significance. Understanding its multifaceted nature is crucial for navigating its future and ensuring its long-term health and resilience. By embracing a holistic approach that recognizes the interconnectedness of its natural, cultural, and human dimensions, we can work towards a sustainable future for this iconic landscape.





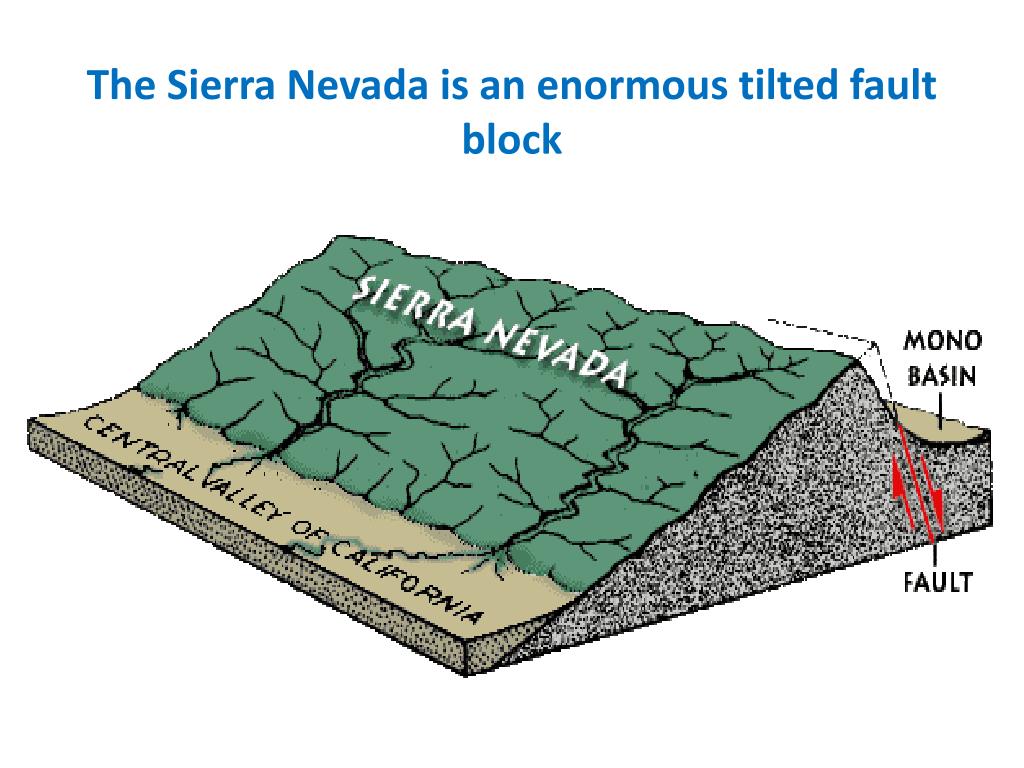

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Sierra Nevada: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Region’s Complexities. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
