20, Mar 2024
Navigating The Tapestry Of Europe: An Exploration Of European Maps With Countries
Navigating the Tapestry of Europe: An Exploration of European Maps with Countries
Related Articles: Navigating the Tapestry of Europe: An Exploration of European Maps with Countries
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Tapestry of Europe: An Exploration of European Maps with Countries. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Tapestry of Europe: An Exploration of European Maps with Countries

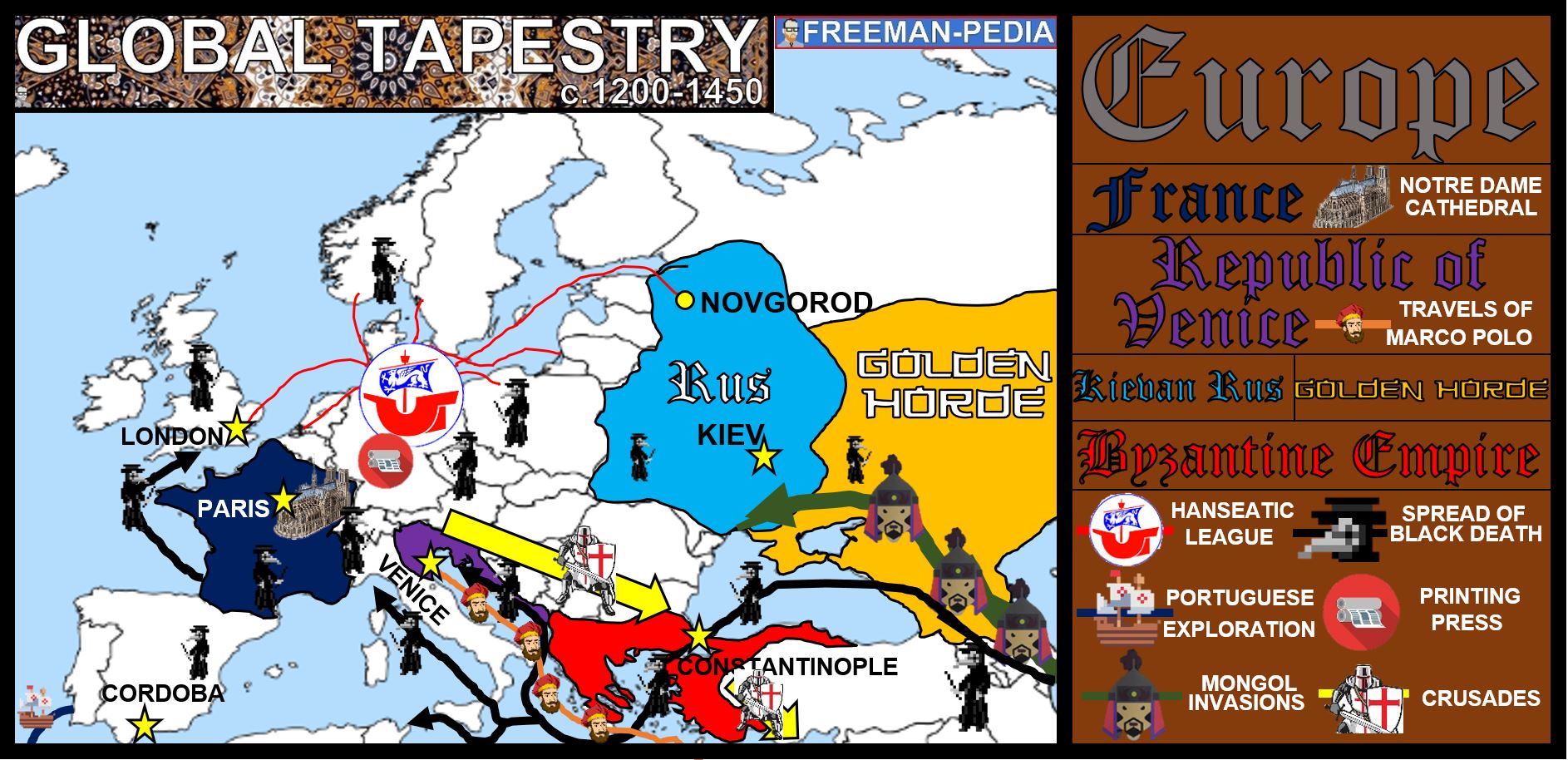
Europe, a continent steeped in history, culture, and diverse landscapes, is a captivating tapestry woven from the threads of numerous nations. Understanding the intricate relationships between these nations requires a clear and comprehensive visual representation – a European map with countries. This article delves into the significance of these maps, exploring their evolution, functionalities, and the vital role they play in comprehending Europe’s complex geopolitical landscape.
The Evolution of European Maps: From Antiquity to the Modern Era
The desire to map Europe dates back to antiquity. Ancient Greek geographers like Ptolemy produced maps based on limited exploration and hearsay, resulting in representations that were often inaccurate and incomplete. The Middle Ages saw a shift towards more detailed maps, particularly those created by Arab cartographers, who incorporated valuable navigational knowledge from their voyages.
The Renaissance marked a turning point in mapmaking. With the advent of printing and renewed interest in exploration, Europe witnessed a surge in the production of maps. The pioneering work of Gerardus Mercator, who developed the Mercator projection, revolutionized mapmaking by offering a more accurate representation of the Earth’s surface.
The 18th and 19th centuries saw the rise of scientific cartography. Advances in surveying techniques, coupled with the increasing availability of data, led to more precise and detailed maps. The development of national atlases, which provided comprehensive maps of individual countries, further enhanced the understanding of Europe’s geopolitical structure.
Beyond Borders: The Importance of European Maps with Countries
European maps with countries serve as invaluable tools for understanding the continent’s complex political, economic, and cultural landscape. They provide a visual framework for:
- Political Geography: Maps highlight the boundaries of individual countries, revealing their territorial extent and relationships with neighboring states. This information is crucial for comprehending international agreements, historical conflicts, and contemporary political dynamics.
- Economic Geography: Maps can illustrate the distribution of resources, major industries, trade routes, and economic hubs across Europe. This data is essential for understanding the continent’s economic performance, identifying areas of potential growth, and strategizing trade policies.
- Cultural Geography: Maps can depict the distribution of languages, religions, and ethnicities across Europe, providing insights into the diverse cultural tapestry of the continent. This information is crucial for fostering cultural understanding and promoting intercultural dialogue.
- Historical Geography: Maps can visualize historical events, such as migrations, conquests, and empires, providing a visual context for understanding the evolution of Europe’s political landscape. This historical perspective is essential for interpreting current geopolitical trends and predicting future developments.
- Environmental Geography: Maps can illustrate the distribution of natural resources, climate zones, and environmental hazards, providing a framework for understanding the continent’s ecological challenges and formulating sustainable development strategies.
Navigating the Map: Key Features and Considerations
European maps with countries are not just static representations but dynamic tools for analysis and interpretation. Several key features and considerations enhance their utility:
- Projection: The choice of projection, such as the Mercator projection or the Lambert conformal conic projection, influences the shape and size of countries on the map. Understanding the limitations of each projection is crucial for accurate interpretation.
- Scale: The scale of the map determines the level of detail it can provide. Large-scale maps focus on specific regions, while small-scale maps offer a broader overview of the continent. Choosing the appropriate scale depends on the intended use of the map.
- Data Representation: Maps can incorporate various types of data, including political boundaries, population density, economic indicators, and environmental data. The choice of data representation, such as symbols, colors, or shading, influences the map’s message and clarity.
- Accessibility: The availability of maps in digital formats, such as online platforms and interactive atlases, has significantly enhanced their accessibility and usability. Users can now zoom in and out, explore specific regions, and overlay different datasets to create customized maps.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Specialized Maps
Beyond the standard political maps, specialized maps offer deeper insights into specific aspects of European geography:
- Historical Maps: These maps depict the evolution of political boundaries, the rise and fall of empires, and the movement of populations throughout history. They provide a valuable historical context for understanding the current geopolitical landscape.
- Economic Maps: These maps illustrate the distribution of industries, trade routes, and economic activity across Europe. They are essential for understanding the continent’s economic performance and identifying areas of potential growth.
- Environmental Maps: These maps depict the distribution of natural resources, climate zones, and environmental hazards. They are crucial for understanding the continent’s ecological challenges and formulating sustainable development strategies.
- Cultural Maps: These maps illustrate the distribution of languages, religions, and ethnicities across Europe. They provide insights into the diverse cultural tapestry of the continent and foster cultural understanding.
FAQs about European Maps with Countries
Q: What is the most accurate map of Europe?
A: There is no single "most accurate" map of Europe, as accuracy depends on the chosen projection and the purpose of the map. Different projections distort the shape and size of countries in different ways, making each projection suitable for specific applications.
Q: What is the difference between a political map and a physical map of Europe?
A: A political map focuses on the boundaries of countries and administrative divisions, while a physical map emphasizes the continent’s natural features, such as mountains, rivers, and lakes.
Q: How can I find reliable maps of Europe?
A: Reputable sources for maps include national geographic societies, government agencies, academic institutions, and online mapping platforms. It is essential to verify the source and the date of publication to ensure the map’s accuracy and relevance.
Q: Are there any online tools for creating custom maps of Europe?
A: Yes, several online tools allow users to create custom maps by overlaying different datasets, choosing specific projections, and adjusting the scale. These tools provide a flexible and interactive approach to mapmaking.
Tips for Using European Maps with Countries Effectively
- Consider the purpose of the map: What information are you trying to convey or understand? This will help you choose the appropriate type of map and data representation.
- Understand the limitations of the map: Every map is a simplification of reality. Be aware of the projection used, the scale of the map, and the data it represents.
- Use multiple maps: Combining different types of maps, such as political, physical, and economic maps, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of Europe’s complex landscape.
- Be critical of the information: Always verify the source of the map and the date of publication to ensure its accuracy and relevance.
Conclusion
European maps with countries are not simply static representations of borders; they are powerful tools for understanding the continent’s history, culture, politics, and economics. By exploring these maps, we gain insights into the intricate relationships between European nations, the challenges they face, and the opportunities they share. As the continent continues to evolve, the importance of these maps will only grow, providing a visual framework for navigating the complex tapestry of Europe.
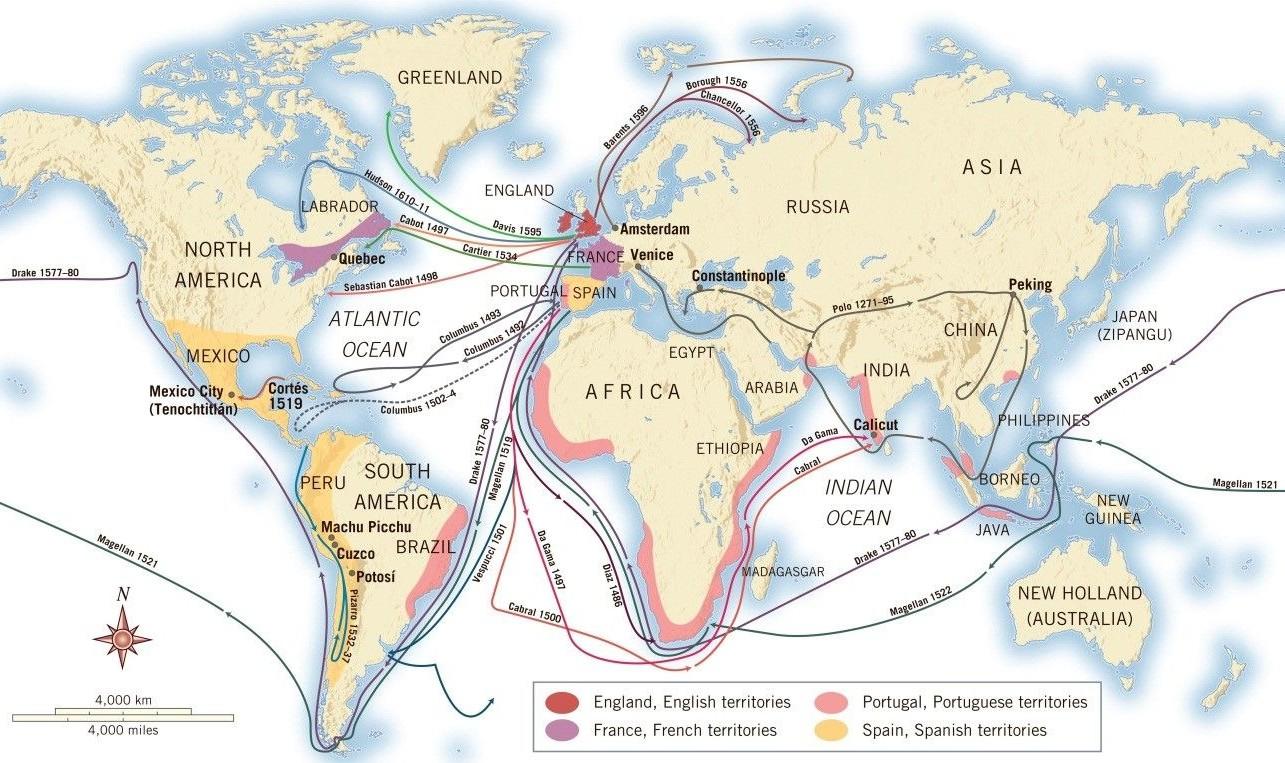
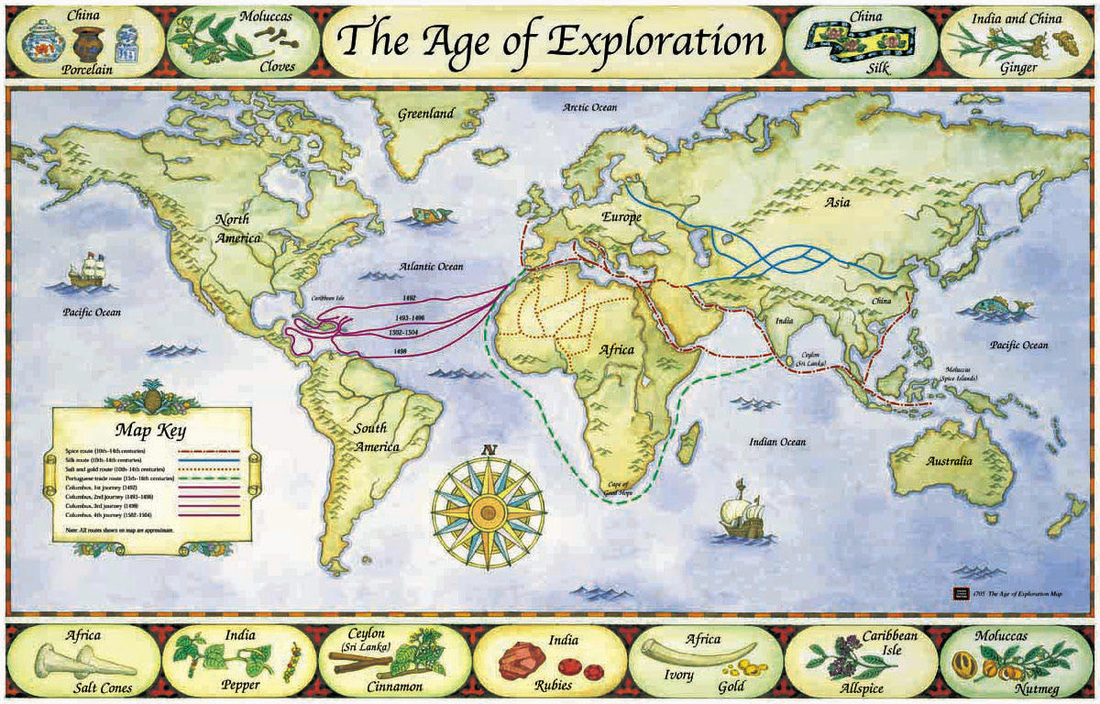
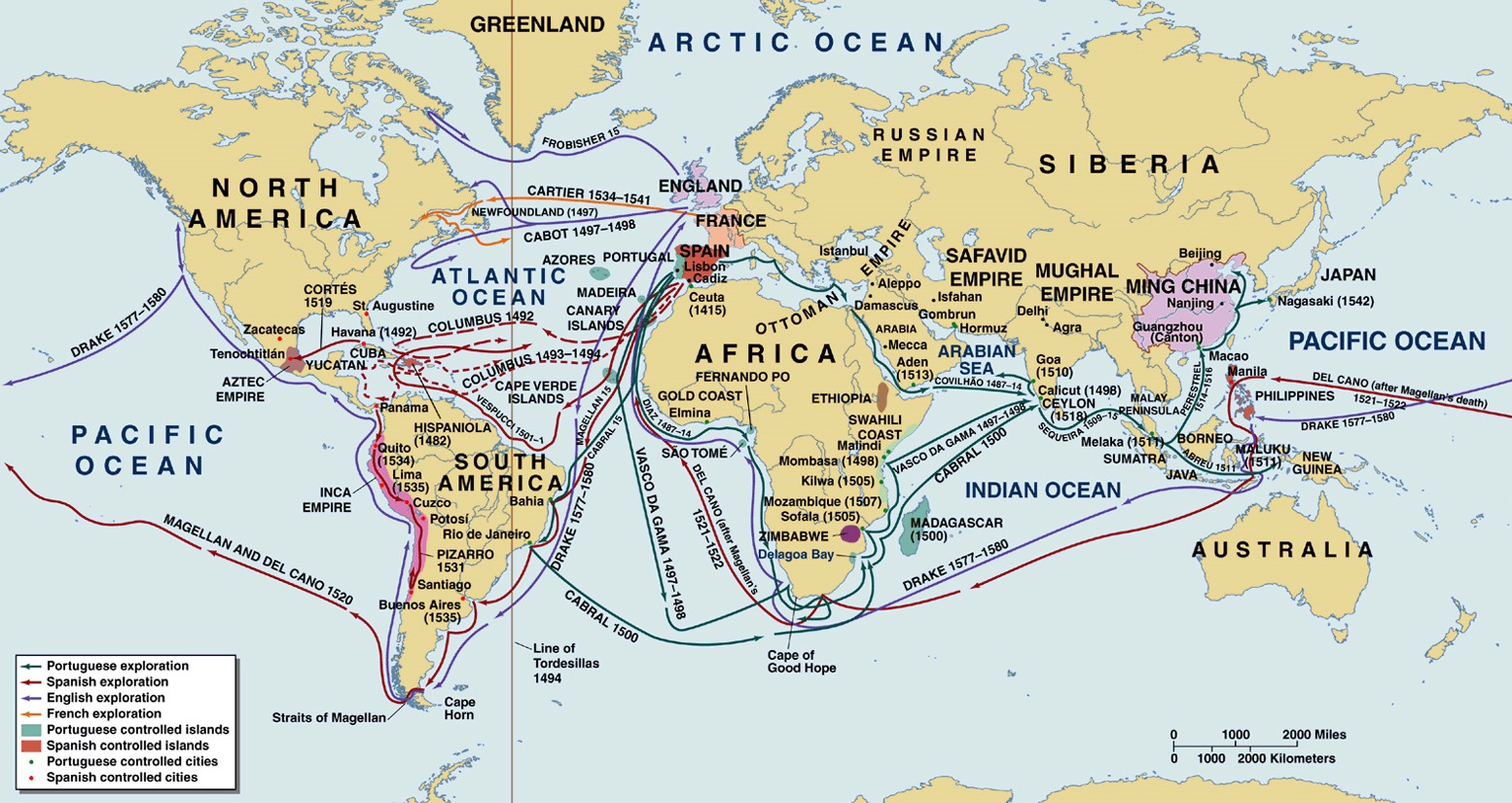

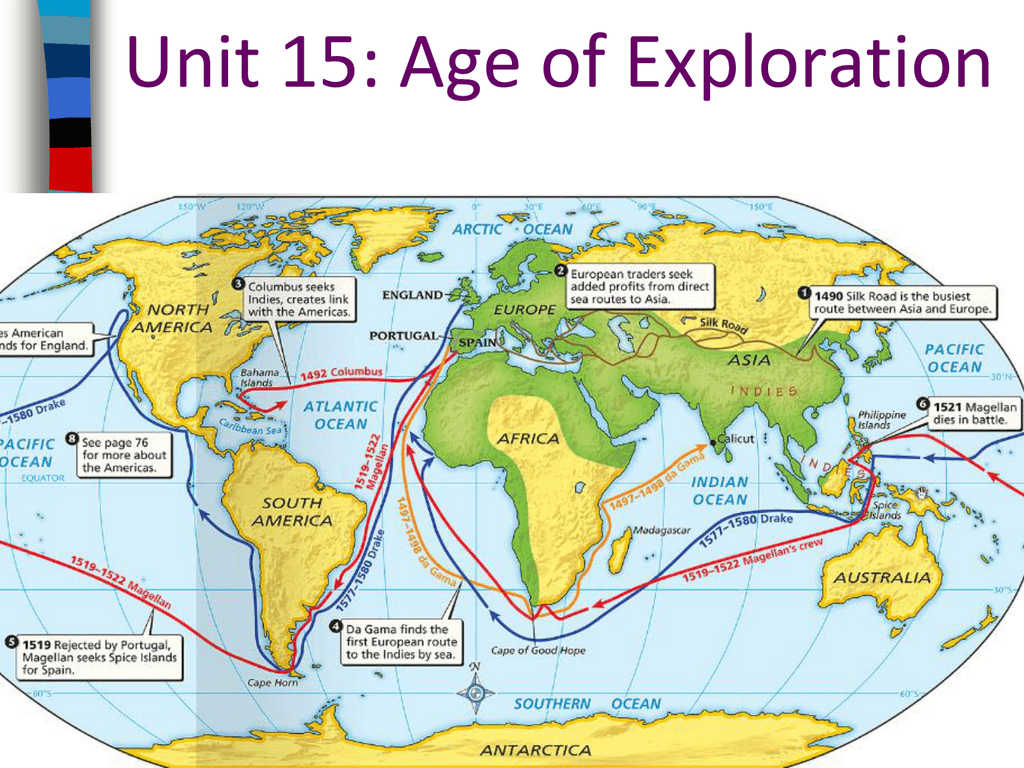
![Exploration and colonization of European Empires 1400-1600 [2500 × 2014] : r/MapPorn](https://i.redd.it/ozx5kp4sc54z.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Tapestry of Europe: An Exploration of European Maps with Countries. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
