24, Sep 2023
Navigating The Tapestry Of Western Europe: A Geographical Exploration
Navigating the Tapestry of Western Europe: A Geographical Exploration
Related Articles: Navigating the Tapestry of Western Europe: A Geographical Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Tapestry of Western Europe: A Geographical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Tapestry of Western Europe: A Geographical Exploration

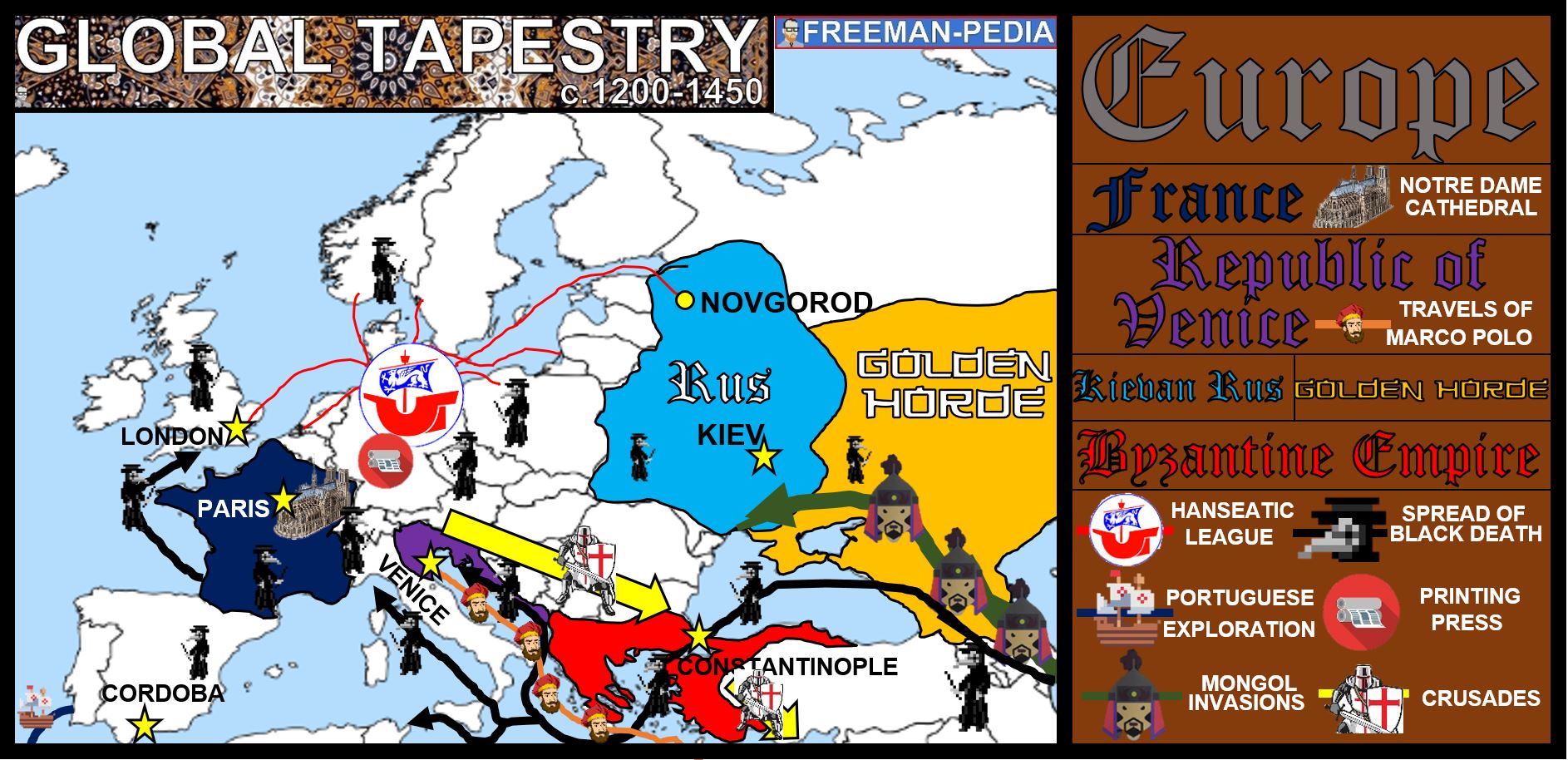
Western Europe, a region of immense historical, cultural, and economic significance, is a mosaic of nations intricately woven together by shared heritage, geographical proximity, and a complex web of political and social interactions. Understanding the geographical composition of this region, its countries, and their unique characteristics is crucial for comprehending its past, present, and future.
A Visual Guide to Western Europe’s Nations:
Visualizing the countries of Western Europe is fundamental to appreciating the region’s diversity. A map serves as a powerful tool, providing a clear and concise representation of the geographical boundaries and relative positions of each nation.
The Western European Landscape:
1. The Core of Western Europe:
- France: Situated in the heart of Western Europe, France boasts a diverse landscape, encompassing rolling hills, fertile plains, the majestic Alps, and the rugged Pyrenees. Its coastline stretches along the Atlantic Ocean, the English Channel, and the Mediterranean Sea.
- Germany: Germany, a nation of central importance, is characterized by its central location, vast plains, and the sprawling Rhine River. Its varied terrain includes the Alps in the south and the North German Plain in the north.
- United Kingdom: The United Kingdom, an island nation, comprises England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. Its diverse landscape encompasses rolling hills, rugged mountains, and picturesque coastlines.
- Italy: Italy, a peninsula nation, is known for its dramatic coastline, rolling hills, and towering Alps. Its geographical position, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, has shaped its history and culture.
- Spain: Spain, located on the Iberian Peninsula, boasts a diverse landscape, including the towering Pyrenees Mountains, the arid plains of Castile, and the fertile valleys of Andalusia.
2. The Northern Fringe:
- Belgium: Belgium, a small country nestled between France, Germany, and the Netherlands, is known for its flat landscape and its strategic position at the crossroads of Europe.
- Netherlands: The Netherlands, renowned for its flat landscape, extensive canals, and its position at the mouth of the Rhine River, is a nation deeply connected to the sea.
- Luxembourg: Luxembourg, a small but strategically important nation, is located in the heart of Western Europe, bordering Belgium, France, and Germany.
- Ireland: Ireland, an island nation located off the western coast of Great Britain, is known for its rolling hills, rugged coastlines, and lush green landscapes.
3. The Southern Frontier:
- Portugal: Portugal, located on the Iberian Peninsula, shares a border with Spain and boasts a diverse landscape, including the Serra da Estrela mountain range, the fertile Douro Valley, and the dramatic coastline of the Algarve.
- Andorra: Andorra, a microstate nestled in the Pyrenees Mountains, is known for its stunning scenery and its tax haven status.
- Monaco: Monaco, a microstate located on the French Riviera, is famous for its casinos, luxury resorts, and its Formula One Grand Prix.
Understanding the Importance of a Western European Map:
- Geographical Awareness: A map provides a visual representation of the location, size, and shape of each country, fostering a greater understanding of the region’s geography.
- Historical Context: The map reveals the historical relationships between countries, highlighting border changes, past conflicts, and shared cultural influences.
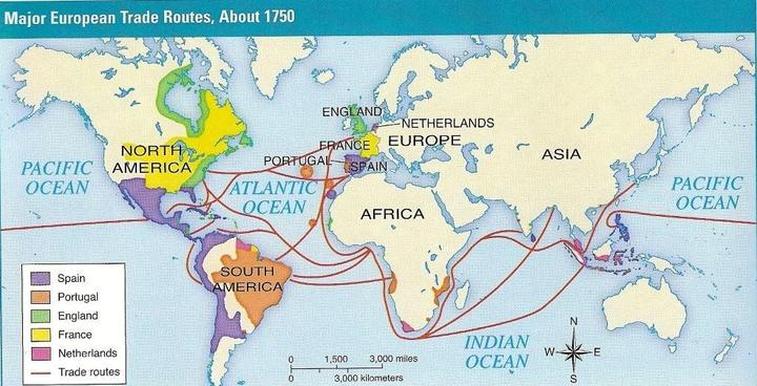
- Economic Connections: The map illuminates the economic interdependence of Western European nations, demonstrating trade routes, industrial centers, and key infrastructure networks.
- Political Dynamics: The map provides a visual framework for understanding political alliances, regional organizations, and the complex web of political relationships within the region.
- Cultural Diversity: The map underscores the rich cultural diversity of Western Europe, highlighting the unique traditions, languages, and artistic expressions of each nation.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What are the key geographical features of Western Europe?
Western Europe is characterized by a diverse landscape, encompassing rolling hills, fertile plains, rugged mountains, and extensive coastlines. The region is bisected by the Rhine River, a major waterway connecting the North Sea to the Swiss Alps.
2. How does the geography of Western Europe influence its history and culture?
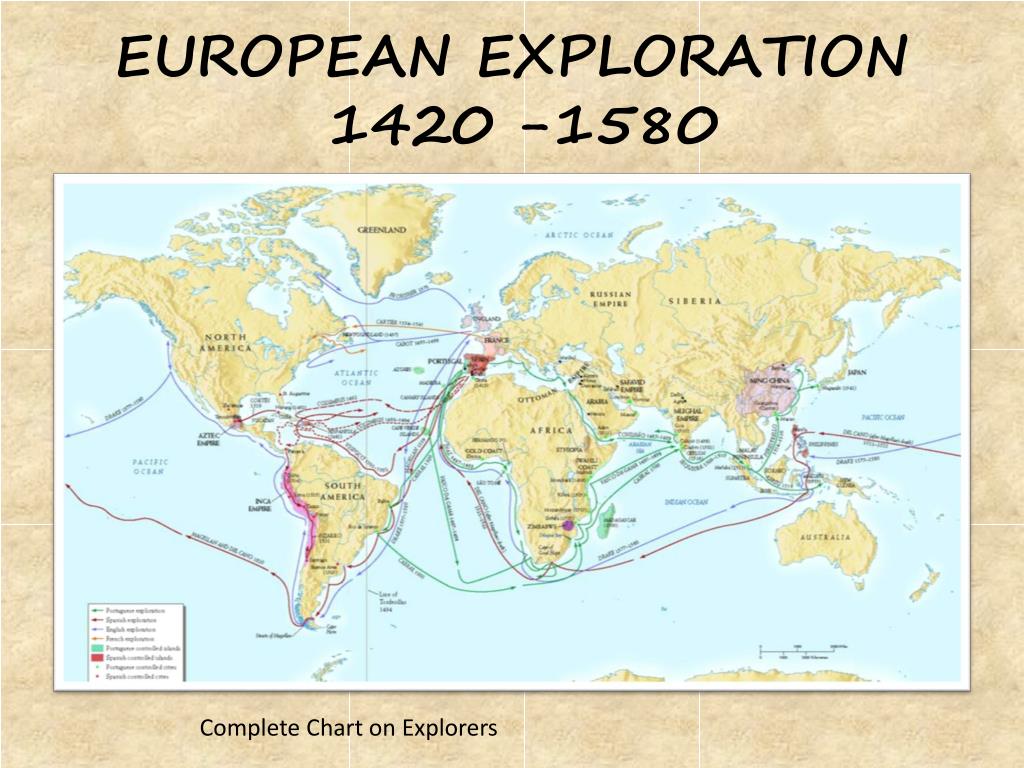
The geography of Western Europe has played a crucial role in shaping its history and culture. Its proximity to the sea facilitated trade and exploration, while its diverse landscape fostered a variety of agricultural practices and cultural traditions.
3. What are the major economic activities in Western Europe?
Western Europe is a hub of economic activity, with a focus on manufacturing, finance, tourism, and technology. The region boasts a highly developed infrastructure, including extensive transportation networks and advanced communication systems.
4. What are some of the key political organizations in Western Europe?
Western European nations are members of the European Union (EU), a political and economic union that promotes cooperation and integration among its member states. Other key organizations include the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) and the Council of Europe.
5. How has Western Europe evolved over time?
Western Europe has undergone significant political, economic, and social transformations throughout its history. From the rise of powerful empires to the development of modern nation-states, the region has witnessed periods of conflict and cooperation, innovation and change.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Western Europe:
- Focus on Key Features: Pay attention to major rivers, mountains, and coastlines, as these features have shaped the region’s history and culture.
- Examine Borders: Study the borders between countries, noting any historical changes or disputes.
- Consider Scale: Recognize the relative size and location of each country within the region.
- Explore Cultural Markers: Identify key cultural landmarks, cities, and regions that represent the diversity of Western Europe.
- Research Connections: Investigate the economic, political, and social connections between countries, understanding the complex web of relationships that binds them together.
Conclusion:
The map of Western Europe is not merely a static representation of geographical boundaries. It serves as a dynamic tool for understanding the region’s intricate history, cultural tapestry, and complex political landscape. By navigating the map, we gain insights into the shared heritage, diverse traditions, and interconnected destinies of Western European nations, appreciating the rich and multifaceted character of this vibrant region.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Tapestry of Western Europe: A Geographical Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin