7, Dec 2023
Navigating The Tapestry Of Western Europe: A Geographical Overview
Navigating the Tapestry of Western Europe: A Geographical Overview
Related Articles: Navigating the Tapestry of Western Europe: A Geographical Overview
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Tapestry of Western Europe: A Geographical Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Tapestry of Western Europe: A Geographical Overview
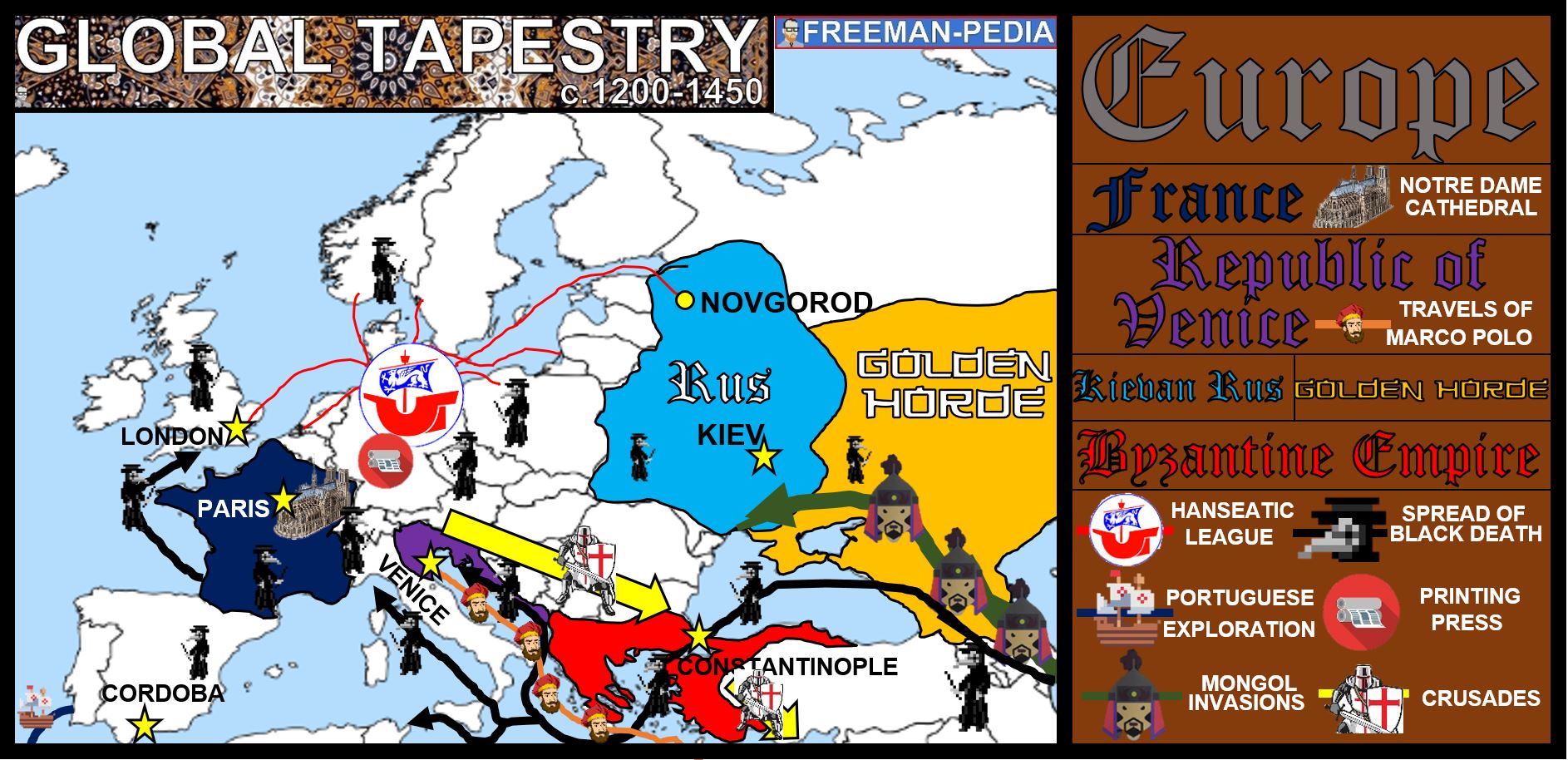
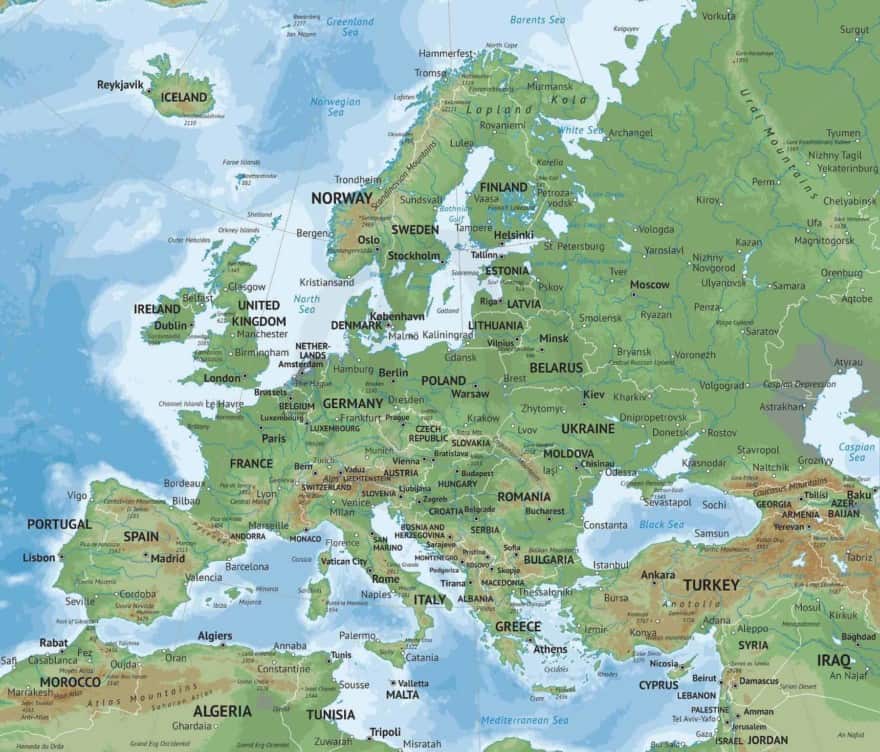
Western Europe, a region teeming with history, culture, and diverse landscapes, is a fascinating study in geographical and political evolution. Understanding the intricate mosaic of nations that comprise this region requires a detailed exploration of its map. This article delves into the geographical characteristics of Western European countries, highlighting their unique features, historical context, and the significance of their spatial relationships.
A Mosaic of Nations:
Western Europe is a tapestry of diverse nations, each with its own distinct identity shaped by historical circumstances, cultural heritage, and geographical features. The region’s boundaries are not static, with ongoing debates and adjustments reflecting evolving political realities. Nonetheless, a general understanding of the major countries and their geographical locations provides a crucial framework for comprehending the region’s complexity.
Key Geographical Features:
- Peninsular Landscapes: Western Europe is characterized by its prominent peninsulas, including the Iberian Peninsula, the Italian Peninsula, and the Balkan Peninsula. These peninsulas have played a significant role in shaping the region’s history and culture, fostering unique identities and influencing trade routes.
- Mountain Ranges: The region is home to imposing mountain ranges, including the Alps, Pyrenees, and Carpathians. These mountain ranges serve as natural barriers, influencing climate, creating distinct ecological zones, and shaping the development of cultural and linguistic boundaries.
- Coastal Zones and Waterways: Western Europe boasts extensive coastlines along the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, and the Mediterranean Sea. These coastlines have been crucial for trade, transportation, and cultural exchange throughout history. Major rivers like the Rhine, Danube, and Thames have also played a vital role in connecting cities and facilitating economic development.
- Climate Diversity: The region experiences a range of climates, from the temperate oceanic climate of the British Isles to the Mediterranean climate of the southern peninsulas. This climatic diversity contributes to the region’s rich biodiversity and agricultural productivity.
Historical Context and Political Evolution:
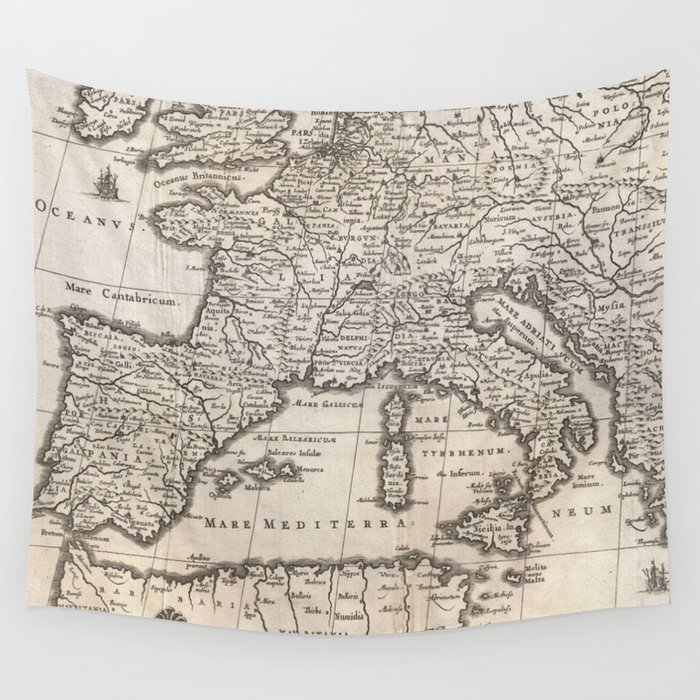
The map of Western Europe is a dynamic entity, reflecting centuries of political and territorial shifts. The region has witnessed the rise and fall of empires, the emergence of nation-states, and the constant reshaping of borders. Understanding these historical processes is crucial for interpreting the current configuration of Western European countries.
- Roman Empire: The Roman Empire’s influence on Western Europe is undeniable. Its legacy is visible in language, legal systems, and infrastructure. The map of the Roman Empire provides valuable insights into the early development of the region’s political organization and cultural exchange.
- Medieval Kingdoms: The Middle Ages saw the rise of numerous kingdoms and principalities, each with its own distinct identity and territorial claims. The map of medieval Europe reflects the fragmentation of power and the emergence of regional identities.
- Nation-State Formation: The rise of nation-states in the 18th and 19th centuries led to significant changes in the map of Western Europe. National identities and territorial claims became increasingly important, leading to conflicts and adjustments in borders.
- Post-World War II Era: The aftermath of World War II witnessed the formation of the European Union, a significant step towards regional integration and cooperation. This process has had a profound impact on the map of Western Europe, fostering economic interdependence and promoting cross-border cooperation.
The Significance of the Map:
Understanding the map of Western Europe offers a multitude of benefits:
- Context for Historical Events: The map provides a visual framework for understanding historical events, such as wars, migrations, and trade routes.
- Understanding Cultural Diversity: The map helps appreciate the region’s cultural diversity, reflecting the distinct languages, traditions, and identities of its constituent nations.
- Economic and Political Interdependence: The map highlights the interconnectedness of Western European countries, emphasizing their economic and political interdependence.
- Environmental Awareness: The map allows for a better understanding of environmental challenges facing the region, such as climate change, pollution, and resource management.
- Strategic Planning: The map is essential for strategic planning, particularly in areas like transportation, trade, and disaster response.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What are the major countries in Western Europe?
A: Western Europe includes countries such as the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Portugal, Belgium, Netherlands, Luxembourg, Austria, Switzerland, Ireland, and others.
Q: What are the geographical boundaries of Western Europe?
A: The boundaries of Western Europe are not definitively fixed, but generally include the countries west of Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, and Hungary, excluding Russia.
Q: What is the significance of the European Union?
A: The European Union is a political and economic union of 27 member states, primarily located in Western Europe. It promotes economic integration, free trade, and cooperation among its members.
Q: What are the major challenges facing Western Europe?
A: Western Europe faces challenges such as economic inequality, immigration, climate change, and terrorism.
Tips for Studying the Map of Western Europe:
- Use online resources: Numerous websites and interactive maps offer detailed information about Western European countries.
- Focus on key geographical features: Pay attention to major mountain ranges, rivers, and coastlines.
- Explore historical maps: Study historical maps to trace the evolution of borders and political entities.
- Connect the map with cultural and historical information: Relate geographical features to cultural traditions, historical events, and political developments.
Conclusion:
The map of Western Europe is a powerful tool for understanding the region’s rich history, diverse cultures, and complex political landscape. By studying its geographical features, historical context, and political evolution, we gain valuable insights into the interconnectedness of nations and the forces shaping the region’s present and future. It serves as a reminder of the dynamic nature of geography and its profound influence on human societies.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Tapestry of Western Europe: A Geographical Overview. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin