17, Aug 2023
The Burning Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis Of New Mexico Wildfires
The Burning Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis of New Mexico Wildfires
Related Articles: The Burning Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis of New Mexico Wildfires
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Burning Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis of New Mexico Wildfires. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Burning Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis of New Mexico Wildfires
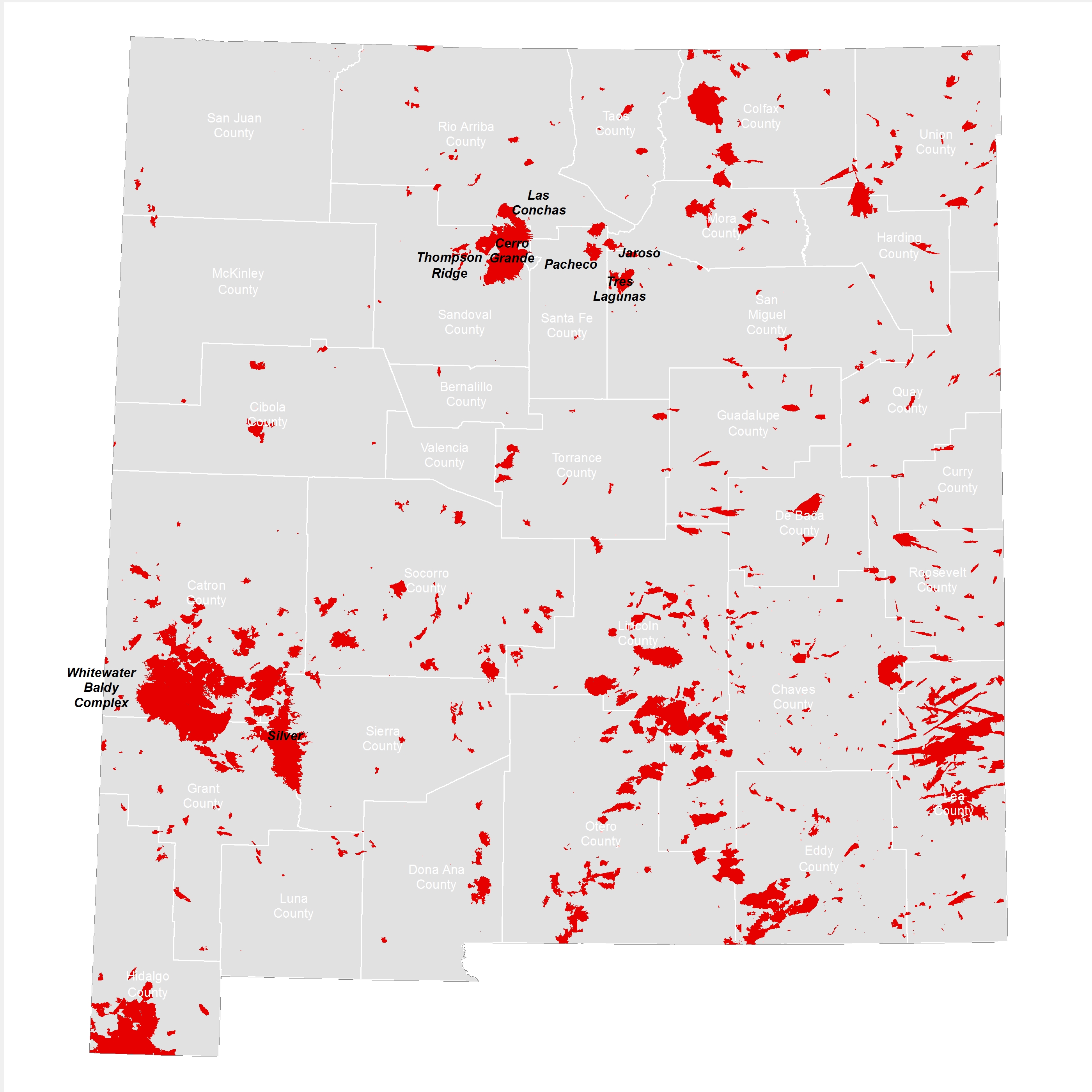
New Mexico, a state renowned for its diverse landscapes, is also grappling with the escalating threat of wildfires. These uncontrolled blazes are a complex phenomenon, driven by a confluence of factors, including climate change, human activity, and the state’s unique ecological makeup. Understanding the dynamics of New Mexico’s wildfires is crucial for mitigating their impact and safeguarding the state’s environment, economy, and communities.
A Historical Perspective: Understanding the Roots of the Problem
New Mexico’s history is intrinsically linked to fire. Indigenous communities have long utilized fire as a tool for land management, promoting biodiversity and controlling fuel loads. However, with the arrival of European settlers, fire suppression became the dominant approach, leading to the accumulation of flammable vegetation and creating conditions conducive to large-scale wildfires.
The Changing Climate: A Catalyst for Increased Wildfire Risk
Climate change is exacerbating the wildfire problem in New Mexico. Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and earlier snowmelt create a drier and more flammable environment. These conditions allow wildfires to ignite more easily, spread rapidly, and burn with greater intensity, posing a significant threat to human life, infrastructure, and natural resources.
The Human Factor: A Crucial Element in Wildfire Dynamics
Human activities play a critical role in igniting wildfires. Accidental and intentional acts, such as campfires, vehicle exhaust, and arson, are major contributors. In addition, human-induced changes to the landscape, such as development and land management practices, can also increase wildfire risk.
Mapping the Threat: Understanding the Geographic Distribution of Wildfires
The spatial distribution of wildfires in New Mexico is not uniform. Certain regions, particularly those with dry vegetation, low humidity, and high wind speeds, are more prone to wildfire activity. Mapping these areas allows for targeted wildfire prevention and response efforts.
The Impact of Wildfires: A Multifaceted Threat
Wildfires have far-reaching consequences for New Mexico, impacting human health, the economy, and the environment.
- Human Health: Smoke from wildfires can cause respiratory problems, cardiovascular issues, and eye irritation. The displacement of residents due to fires can also lead to psychological stress and economic hardship.
- Economic Impact: Wildfires damage infrastructure, disrupt transportation, and impact tourism, leading to economic losses. The costs associated with fire suppression and recovery efforts are also substantial.
- Environmental Damage: Wildfires destroy habitat, release greenhouse gases, and contribute to soil erosion. They can also impact water quality and alter the composition of plant and animal communities.
Navigating the Future: Strategies for Mitigation and Adaptation
Addressing the wildfire problem in New Mexico requires a multi-pronged approach that encompasses prevention, mitigation, and adaptation.
- Prevention: Efforts to reduce the risk of wildfires include public education campaigns, controlled burns, and the creation of fire-resistant landscapes.
- Mitigation: Investing in fire suppression resources, improving early detection systems, and developing strategies for evacuations are crucial for mitigating the impact of wildfires.
- Adaptation: Adapting to the changing wildfire landscape involves building fire-resistant structures, implementing land management practices that reduce fuel loads, and developing strategies for post-fire recovery.
FAQs
- What is the role of climate change in New Mexico wildfires? Climate change is a significant driver of increased wildfire risk in New Mexico due to rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and earlier snowmelt, creating drier and more flammable conditions.
- How do human activities contribute to wildfires? Human activities, such as accidental and intentional fires, development, and land management practices, can increase wildfire risk.
- What are the economic impacts of wildfires in New Mexico? Wildfires damage infrastructure, disrupt transportation, impact tourism, and lead to significant financial losses associated with fire suppression and recovery efforts.
- What are some strategies for preventing wildfires in New Mexico? Prevention strategies include public education campaigns, controlled burns, and the creation of fire-resistant landscapes.
- How are communities adapting to the threat of wildfires? Communities are adapting by building fire-resistant structures, implementing land management practices that reduce fuel loads, and developing strategies for post-fire recovery.
Tips for Staying Safe During Wildfire Season
- Stay informed about current wildfire conditions and evacuation orders.
- Clear vegetation around your home and maintain a defensible space.
- Have a fire escape plan and practice it regularly.
- Be cautious when using fire and dispose of cigarettes properly.
- Avoid activities that could spark a fire, such as driving off-road or operating machinery.
Conclusion
New Mexico’s wildfires are a complex and evolving challenge that requires a comprehensive approach. Understanding the interplay of climate change, human activities, and ecological factors is crucial for developing effective strategies for prevention, mitigation, and adaptation. By investing in research, implementing proactive measures, and fostering community resilience, New Mexico can navigate the challenges of wildfire risk and safeguard its unique natural and cultural heritage for future generations.



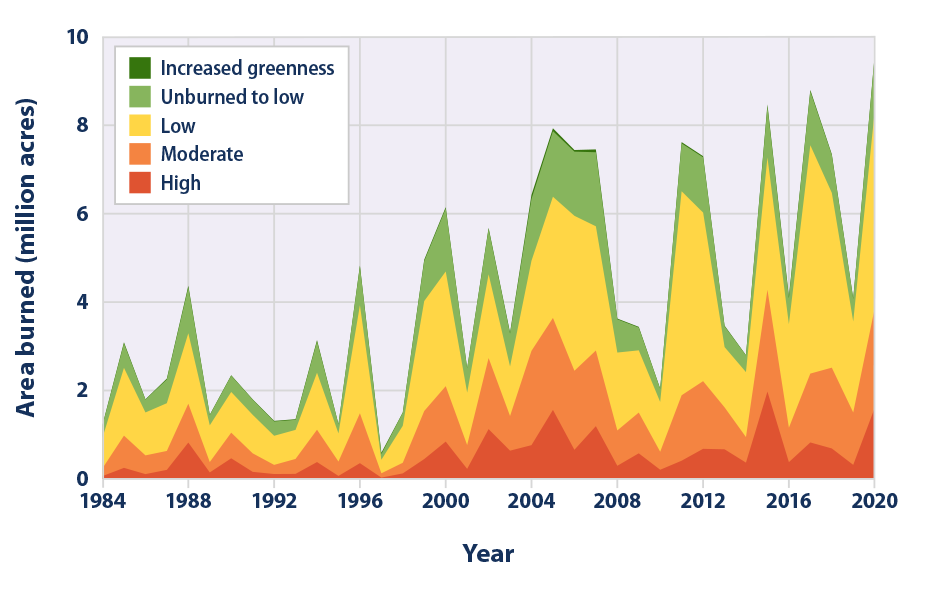
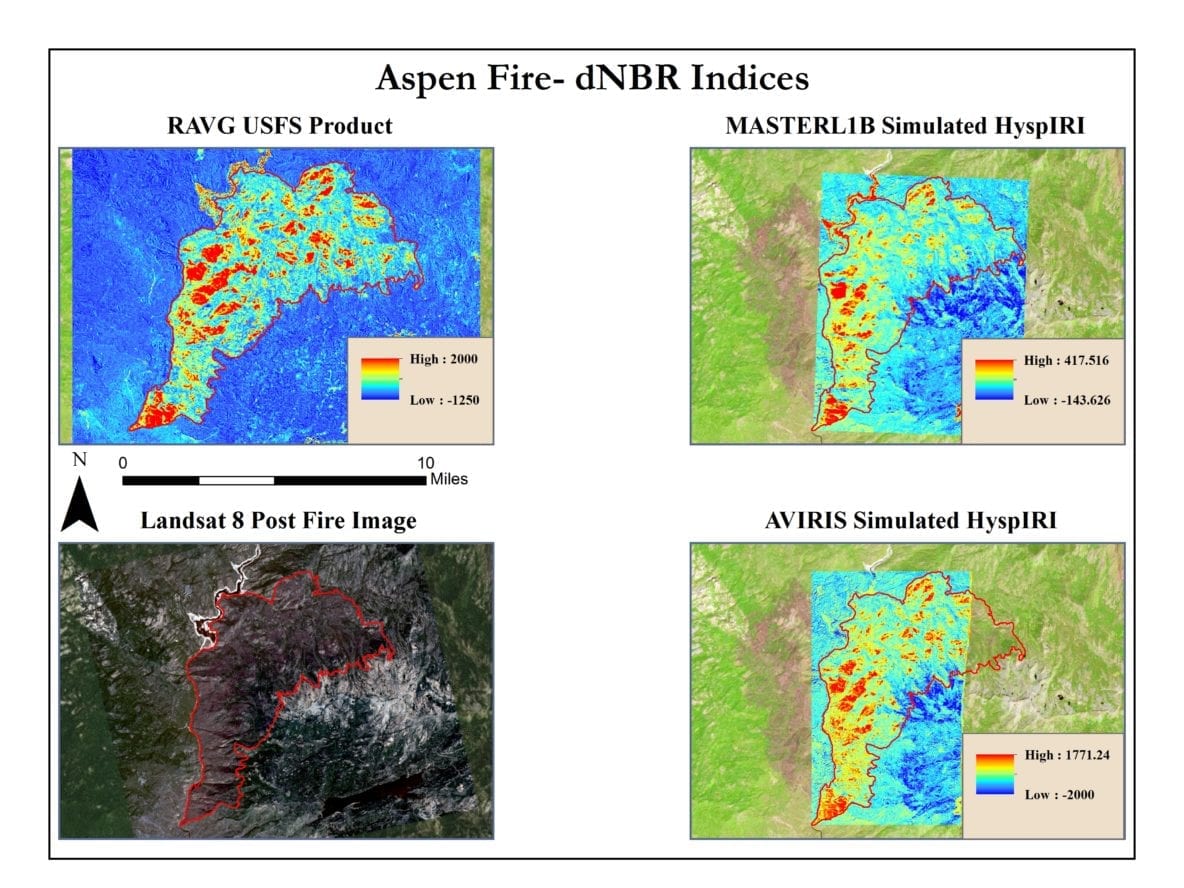



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Burning Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis of New Mexico Wildfires. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
