28, Nov 2023
The Economic Landscape Of Europe: A Mosaic Of Prosperity And Challenges
The Economic Landscape of Europe: A Mosaic of Prosperity and Challenges
Related Articles: The Economic Landscape of Europe: A Mosaic of Prosperity and Challenges
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Economic Landscape of Europe: A Mosaic of Prosperity and Challenges. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Economic Landscape of Europe: A Mosaic of Prosperity and Challenges

Europe, a continent rich in history, culture, and diversity, also boasts a complex and dynamic economic landscape. Understanding this intricate mosaic of economic strengths and weaknesses is crucial for navigating the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. This article delves into the economic map of Europe, examining key trends, disparities, and the factors shaping its future.
A Tale of Two Europes: Core and Periphery
The European Union, with its single market and shared currency, has fostered economic integration, but significant disparities remain. A clear divide exists between the "core" and "periphery" regions.
Core Economies:
- Germany: The economic powerhouse of Europe, boasting a robust manufacturing sector, technological innovation, and a skilled workforce.
- France: A major player in the global economy, with a diversified industrial base, a strong agricultural sector, and a significant role in the service industry.
- United Kingdom: A financial hub with a large service sector, though its departure from the EU has introduced uncertainty and economic challenges.
- Netherlands: A leader in logistics, agriculture, and high-tech industries, with a highly competitive business environment.
- Nordic Countries (Denmark, Finland, Sweden, Norway): Known for their high levels of social welfare, innovative industries, and strong environmental policies.
These core economies enjoy higher levels of per capita GDP, lower unemployment rates, and greater access to capital and technology. They play a dominant role in shaping European economic policies and driving regional growth.
Peripheral Economies:
- Southern Europe (Greece, Italy, Portugal, Spain): Facing significant economic challenges, including high unemployment, government debt, and sluggish growth.
- Eastern Europe (Bulgaria, Romania, Hungary, Poland): Exhibiting a mix of economic performance, with some countries experiencing rapid growth while others struggle with structural issues.
- Baltic States (Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania): Making significant progress in catching up to the EU average, but facing challenges related to income inequality and a lack of skilled labor.
Peripheral economies often experience lower levels of investment, limited access to financial markets, and a reliance on less diversified industries. These factors contribute to economic vulnerabilities and slower growth rates compared to their core counterparts.
Key Economic Drivers and Challenges:
1. Globalization and Trade:
- EU Single Market: The EU’s single market has facilitated free trade and movement of goods, services, and people, promoting economic growth and integration.
- Global Trade Wars: The rise of protectionist policies and trade tensions pose a significant threat to European economies, particularly those heavily reliant on exports.
- Brexit: The UK’s departure from the EU has created uncertainty and disrupted trade flows, impacting both the UK and the EU economies.
2. Technological Innovation:
- Digitalization: The rapid adoption of digital technologies offers significant opportunities for economic growth and innovation, particularly in areas like e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and data analytics.
- Skills Gap: The transition to a digital economy requires a highly skilled workforce, creating a gap between the demand for skilled workers and the supply, particularly in peripheral economies.
- Green Transition: Europe is committed to a green transition, investing in renewable energy, sustainable transportation, and circular economy models, creating new economic opportunities while posing challenges for traditional industries.
3. Demographic Trends:
- Aging Population: Europe faces a growing aging population, leading to rising healthcare costs, a shrinking workforce, and a potential strain on social security systems.
- Immigration: Immigration is essential for maintaining a growing workforce and contributing to economic growth, but it also raises social and political challenges.
- Brain Drain: The migration of skilled workers from peripheral to core economies can hinder economic development in the former, exacerbating existing inequalities.
4. Political and Social Factors:
- EU Integration: The EU’s future direction and its ability to address shared challenges, such as migration, climate change, and security, will influence economic stability and growth.
- Political Polarization: Growing political polarization and populism can undermine economic policymaking and create uncertainty for businesses and investors.
- Social Inequality: Persistent income inequality and social exclusion can lead to social unrest and hinder economic progress, particularly in peripheral economies.
The Importance of a Balanced and Sustainable Economic Model:
Addressing the economic challenges facing Europe requires a holistic approach that focuses on:
- Promoting Investment and Innovation: Investing in research and development, infrastructure, and human capital is essential for fostering economic growth and competitiveness.
- Enhancing Competitiveness: Supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), fostering entrepreneurship, and promoting a flexible labor market can boost economic dynamism.
- Reducing Inequality: Addressing income inequality, promoting social mobility, and investing in education and healthcare are crucial for creating a more inclusive and resilient society.
- Strengthening the EU: A strong and united EU is essential for tackling shared challenges, promoting economic integration, and ensuring stability in the region.
- Promoting Sustainable Development: Transitioning to a green economy, investing in renewable energy, and protecting the environment are crucial for long-term economic prosperity and environmental sustainability.
FAQs on the Economic Map of Europe:
1. What is the biggest economic challenge facing Europe?
The biggest challenge is likely the combination of demographic changes (aging population, brain drain), global trade uncertainties, and the need for a green transition. These factors interact in complex ways, requiring a multifaceted approach to address them.
2. Is the EU a success story in economic terms?
The EU has undoubtedly fostered economic integration and growth, but it faces significant challenges in ensuring fair distribution of prosperity and addressing disparities among member states. The EU’s future success will depend on its ability to adapt to global changes and address these challenges effectively.
3. What are the key factors driving economic growth in Europe?
Key factors include technological innovation, investment in human capital, a strong focus on research and development, and a commitment to sustainable development.
4. How does Brexit impact the European economy?
Brexit has created uncertainty and disrupted trade flows, impacting both the UK and the EU economies. The long-term economic consequences of Brexit are still unfolding, but it is clear that it has had a negative impact on overall economic growth and stability.
5. What are the main differences between core and peripheral economies in Europe?
Core economies generally enjoy higher levels of investment, a more diversified industrial base, and greater access to financial markets, leading to higher per capita GDP and lower unemployment rates. Peripheral economies often face challenges related to lower levels of investment, limited access to capital, and a reliance on less diversified industries, resulting in slower economic growth and higher unemployment.
Tips for Understanding the Economic Map of Europe:
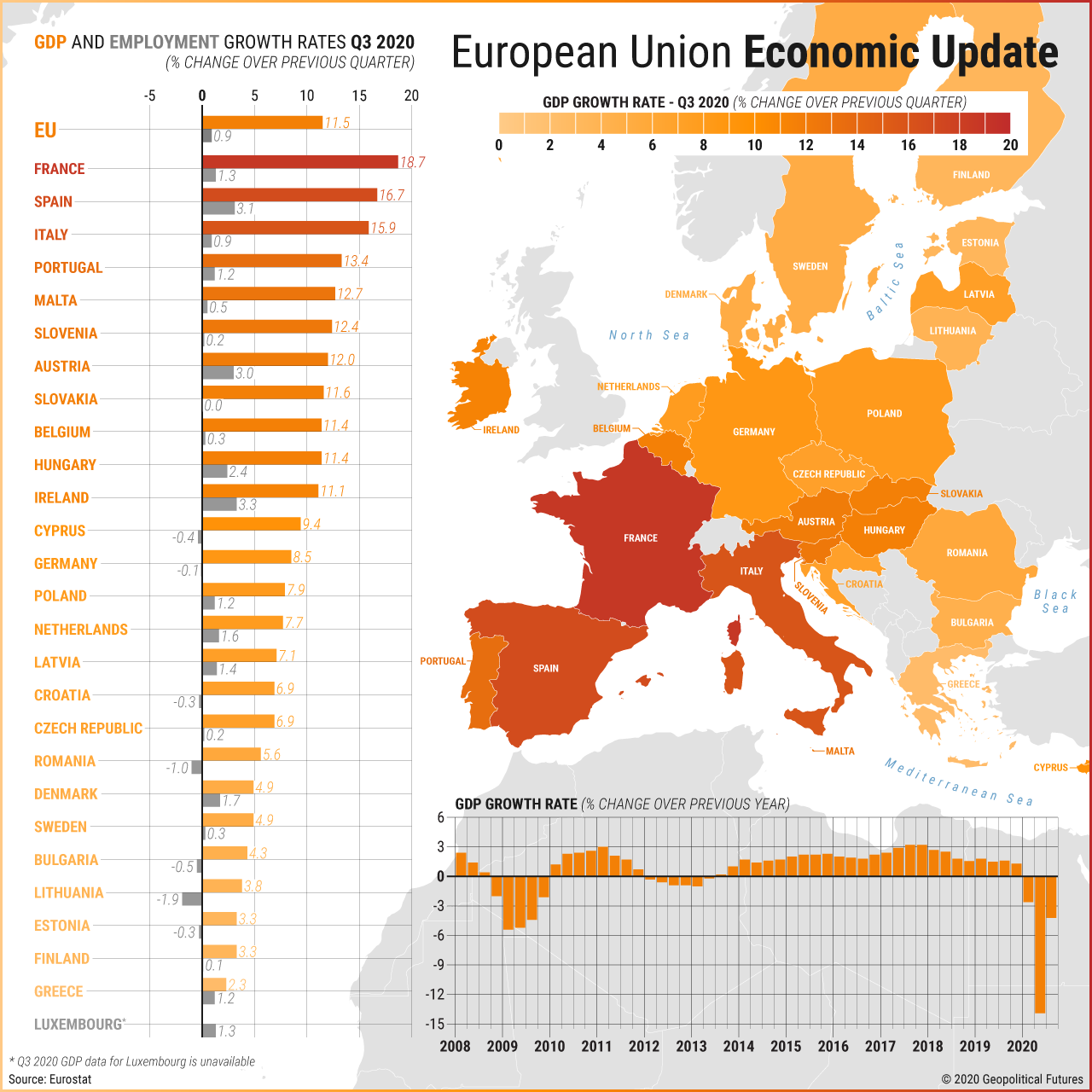
- Focus on data and trends: Use economic indicators like GDP growth, unemployment rates, and investment levels to compare and contrast different countries and regions.
- Consider the interconnectedness of economies: Remember that economic developments in one country can have ripple effects on others, particularly within the EU.
- Pay attention to policy changes: Government policies, including trade agreements, fiscal measures, and regulatory frameworks, significantly influence economic performance.
- Explore diverse perspectives: Consider the views of economists, policymakers, and business leaders from different countries and sectors to gain a comprehensive understanding of the economic landscape.
Conclusion:
The economic map of Europe is a complex and dynamic landscape, characterized by both opportunities and challenges. Understanding the key economic drivers, disparities, and trends is crucial for navigating the future. By promoting investment, innovation, and sustainable development, while addressing inequality and fostering a strong and united EU, Europe can create a more balanced, prosperous, and resilient future for all its citizens.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Economic Landscape of Europe: A Mosaic of Prosperity and Challenges. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
