9, Oct 2023
The European Landscape Bordering Russia: A Geopolitical Overview
The European Landscape Bordering Russia: A Geopolitical Overview
Related Articles: The European Landscape Bordering Russia: A Geopolitical Overview
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The European Landscape Bordering Russia: A Geopolitical Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The European Landscape Bordering Russia: A Geopolitical Overview
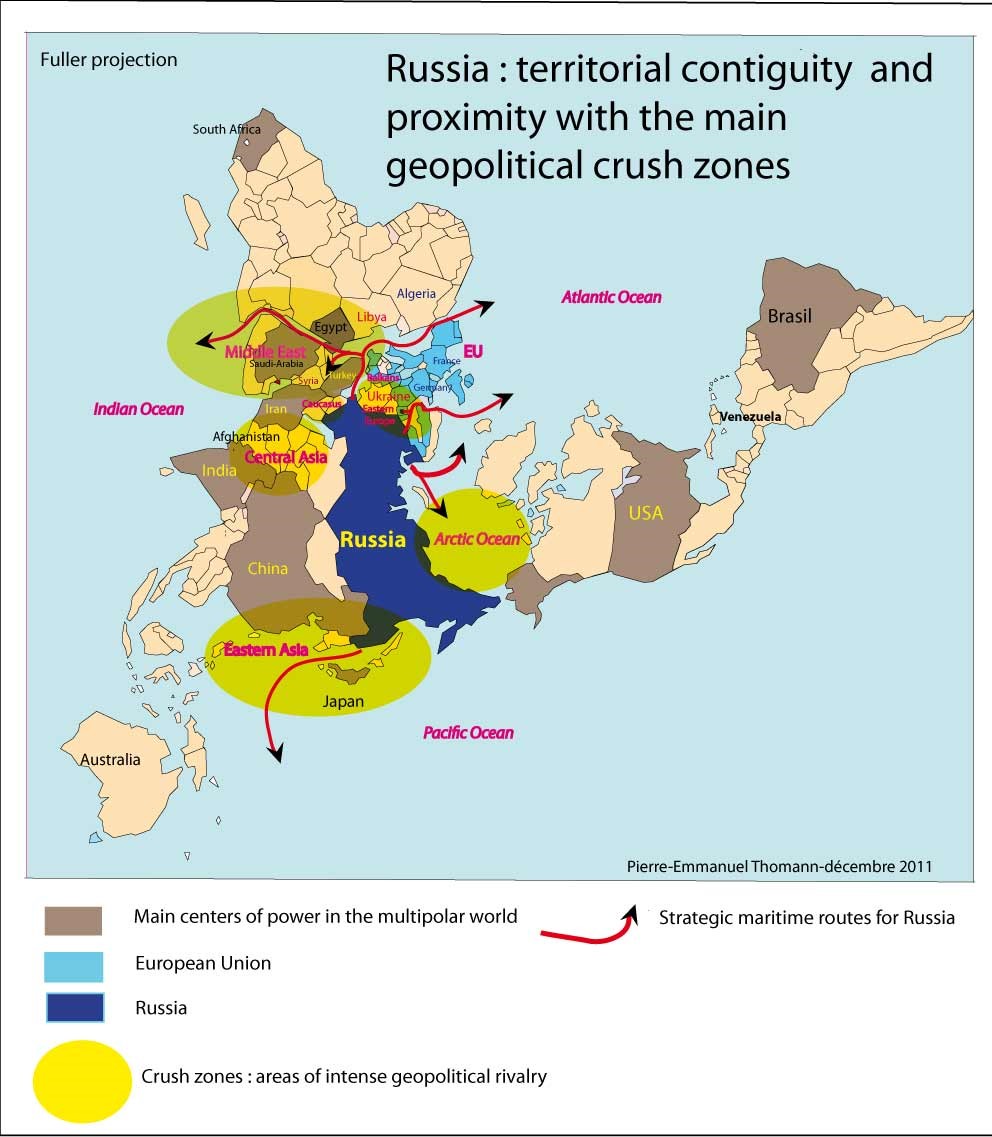
The European landscape bordering Russia presents a complex tapestry of nations, each with its own history, culture, and geopolitical interests. Understanding this region’s geography and its intricate relationship with Russia is crucial for comprehending contemporary European affairs, global security, and international relations.
A Geographical Perspective:
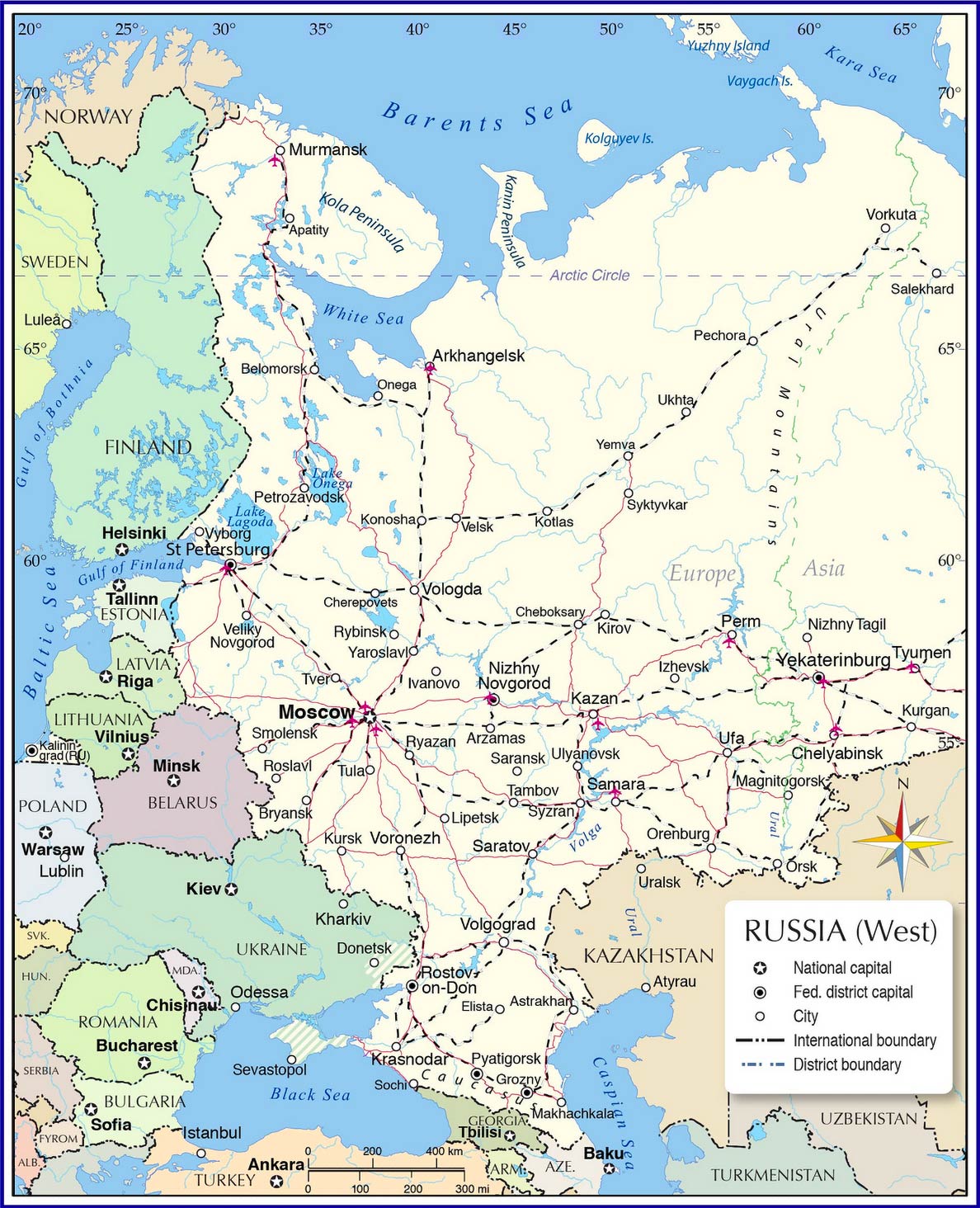
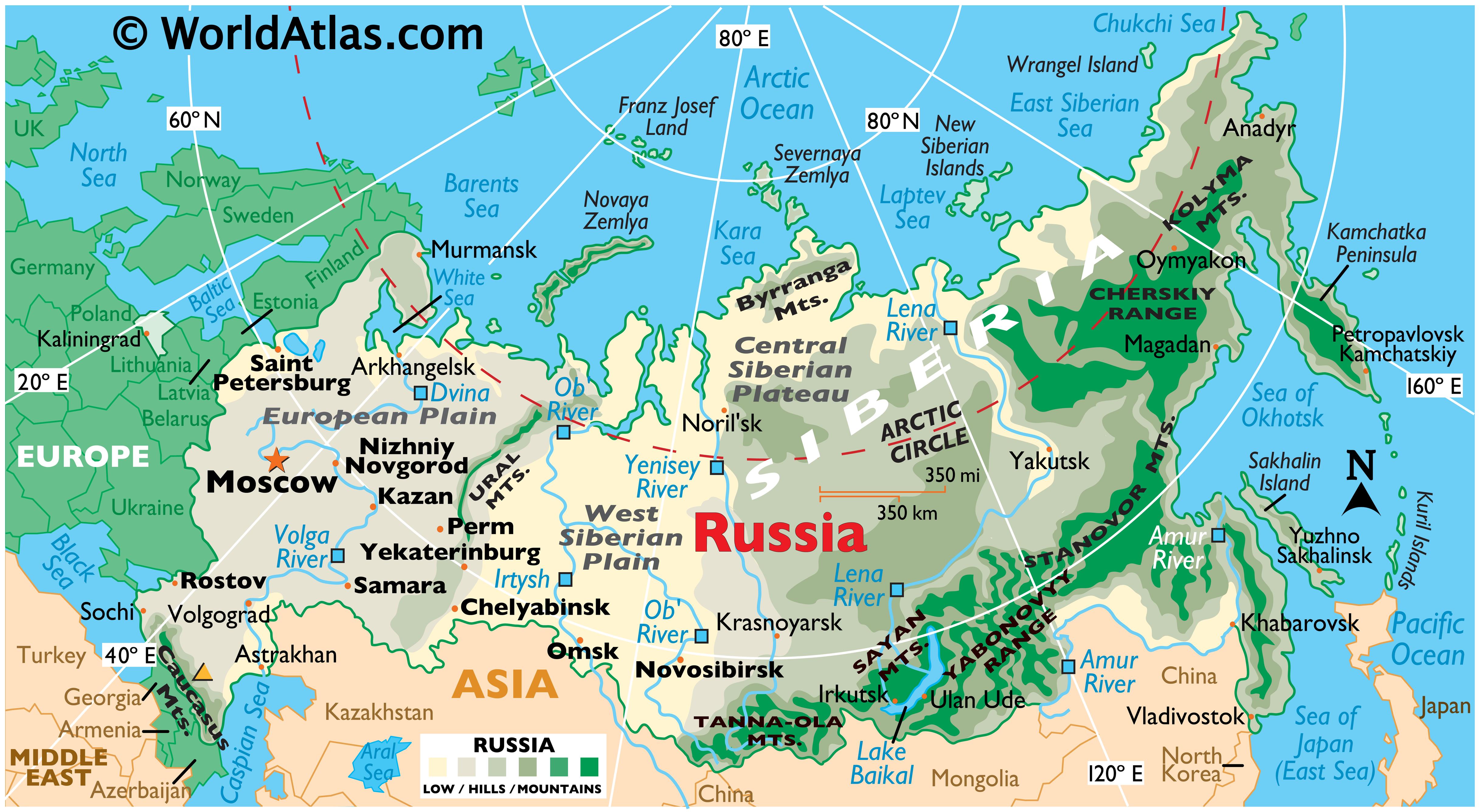
The European countries bordering Russia stretch across a vast expanse, encompassing a diverse range of landscapes and climates. From the Baltic Sea in the north to the Black Sea in the south, these nations share a significant portion of their borders with Russia.
- The Baltic States: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, situated on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea, were once part of the Soviet Union. They gained independence in 1991 and have since sought closer ties with the West, joining NATO and the European Union.
- Finland: Sharing a long land border with Russia, Finland maintains a unique position, balancing its close historical ties with Russia with its strong alignment with the West.
- Poland: A significant player in Central Europe, Poland has a long and complex history with Russia, marked by periods of both conflict and cooperation. It plays a key role in NATO’s eastern flank and is a staunch supporter of Ukrainian sovereignty.
- Belarus: Often referred to as Russia’s closest ally, Belarus maintains a close political and economic relationship with its larger neighbor. This close association has raised concerns about Belarus’s potential role in Russia’s foreign policy objectives.
- Ukraine: Sharing a lengthy border with Russia, Ukraine has been at the center of geopolitical tensions in recent years. Its struggle for independence and territorial integrity has become a key factor in shaping European security.
- Moldova: Located between Ukraine and Romania, Moldova maintains a fragile relationship with Russia, facing challenges stemming from the breakaway region of Transnistria, which has close ties with Moscow.
- Georgia: Located in the Caucasus region, Georgia has a history of conflict with Russia, particularly over the breakaway regions of Abkhazia and South Ossetia.
Historical Context:
The historical relationship between Russia and its European neighbors has been marked by both cooperation and conflict. The expansion of the Russian Empire throughout the 19th century brought numerous European territories under its control, leading to significant cultural and political influence. The 20th century saw the rise of the Soviet Union, which further shaped the geopolitical landscape of the region.
The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 ushered in a new era, with many former Soviet republics gaining independence. However, the legacy of the Soviet era continues to influence the region’s dynamics, particularly in terms of economic ties, cultural exchange, and security concerns.
Geopolitical Significance:
The European countries bordering Russia hold immense geopolitical significance for a number of reasons:
- Security Concerns: The presence of a powerful and assertive Russia on their doorstep has led these nations to prioritize their security. Many have sought membership in NATO, a military alliance designed to deter Russian aggression.
- Economic Interdependence: Despite political tensions, Russia and its European neighbors remain economically intertwined. Trade and energy flows continue to connect them, creating both opportunities and challenges.
- Energy Security: Russia is a major energy exporter, providing significant amounts of oil and natural gas to European countries. This dependence creates vulnerabilities for European nations, making them susceptible to Russian political pressure.
- Cultural and Historical Ties: Centuries of interaction have fostered cultural and historical ties between Russia and its European neighbors. This shared heritage creates opportunities for dialogue and cooperation but also raises concerns about Russian influence.
Current Challenges and Future Prospects:
The relationship between Russia and its European neighbors remains complex and dynamic. Recent events, such as the annexation of Crimea, the ongoing conflict in eastern Ukraine, and the military buildup along Russia’s borders, have heightened tensions and fueled concerns about Russian aggression.
- The Ukraine Crisis: The conflict in Ukraine has become a major flashpoint in European security. Russia’s annexation of Crimea and its support for separatists in eastern Ukraine have raised serious concerns about Russian intentions and have led to significant sanctions against Russia.
- NATO Expansion: The expansion of NATO eastward, encompassing many of the former Soviet republics, has been a source of tension with Russia. Moscow views this expansion as a threat to its security interests, while NATO argues that it is a defensive measure to ensure the security of its members.
- Energy Dependence: European dependence on Russian energy supplies continues to be a significant geopolitical challenge. The European Union has sought to diversify its energy sources and reduce its reliance on Russia, but this process has been slow and complex.
The future relationship between Russia and its European neighbors will depend on a number of factors, including:
- The outcome of the conflict in Ukraine: The resolution of the conflict in Ukraine will be a key factor in shaping the future of the region.
- Russia’s foreign policy objectives: Russia’s long-term foreign policy objectives will determine its approach towards its European neighbors.
- European unity and resolve: The ability of European nations to maintain unity and resolve in the face of Russian pressure will be crucial in shaping the region’s future.
Conclusion:
The European landscape bordering Russia presents a complex and dynamic geopolitical landscape. Understanding this region’s history, geography, and current challenges is essential for comprehending contemporary European affairs and global security. The future relationship between Russia and its European neighbors will be shaped by a range of factors, including the resolution of the conflict in Ukraine, Russia’s foreign policy objectives, and European unity and resolve. The ability of these nations to navigate these challenges and build a stable and prosperous future will require careful diplomacy, strategic cooperation, and a commitment to shared values.
FAQs:
Q: What are the main geopolitical concerns of the European countries bordering Russia?
A: The main geopolitical concerns include Russian aggression, the potential for conflict, energy dependence, and Russian influence.
Q: How has the Ukraine crisis impacted the relationship between Russia and its European neighbors?
A: The Ukraine crisis has significantly strained relations, leading to increased tensions, sanctions, and a heightened sense of insecurity.
Q: What are the main challenges facing the European Union in its relationship with Russia?
A: The main challenges include energy dependence, Russian disinformation campaigns, and maintaining unity in the face of Russian pressure.
Q: What are the potential future scenarios for the relationship between Russia and its European neighbors?
A: Potential scenarios include continued tension and conflict, a gradual rapprochement, or a more cooperative relationship based on shared interests.
Tips:
- Stay informed about current events: Monitor news and analysis related to Russia and its European neighbors.
- Understand the historical context: Gain a deeper understanding of the historical relationship between Russia and the region.
- Consider different perspectives: Explore diverse viewpoints on the geopolitical challenges facing the region.
- Engage in constructive dialogue: Participate in discussions and debates about the future of the relationship between Russia and its European neighbors.
Conclusion:
The European landscape bordering Russia is a region of immense geopolitical significance. Understanding its complexities and challenges is crucial for navigating the complexities of the 21st century. By fostering dialogue, cooperation, and a commitment to shared values, European nations can work towards a future of peace, stability, and prosperity in the region.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The European Landscape Bordering Russia: A Geopolitical Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
