7, Aug 2023
The Map Of Africa: A Tapestry Of Nations And Cultures
The Map of Africa: A Tapestry of Nations and Cultures
Related Articles: The Map of Africa: A Tapestry of Nations and Cultures
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Map of Africa: A Tapestry of Nations and Cultures. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Map of Africa: A Tapestry of Nations and Cultures

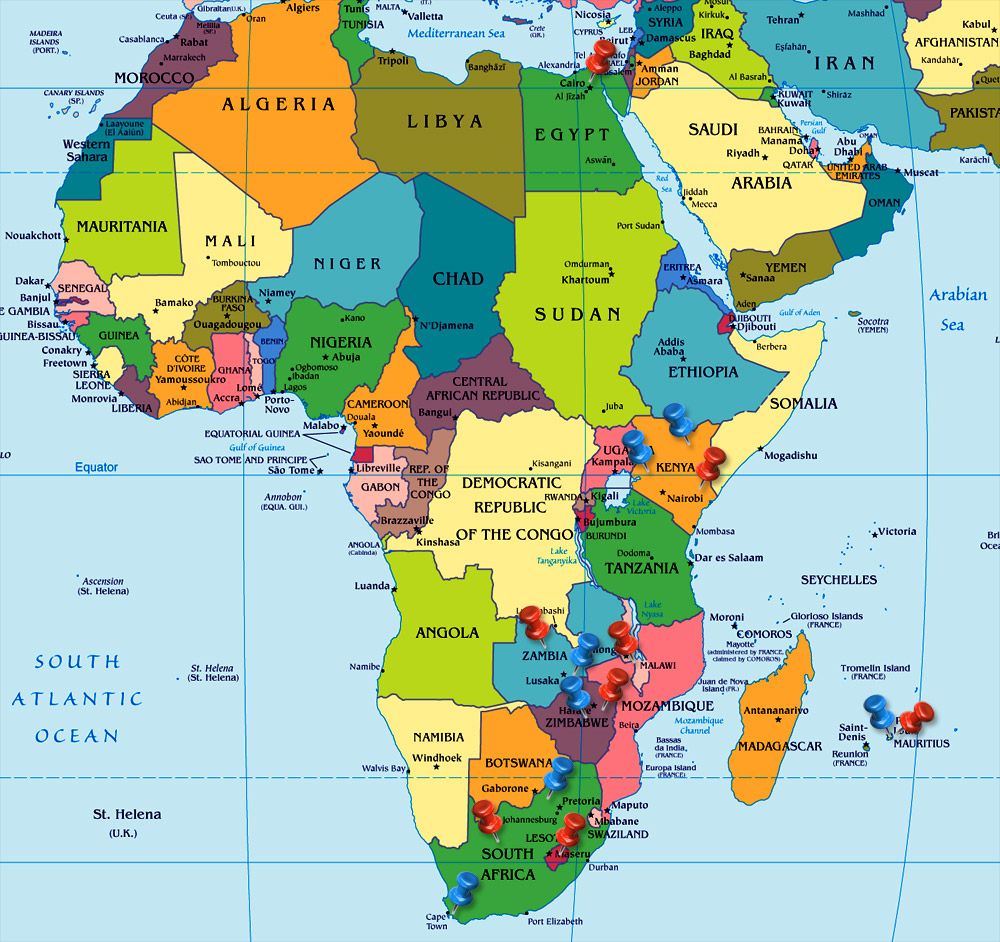
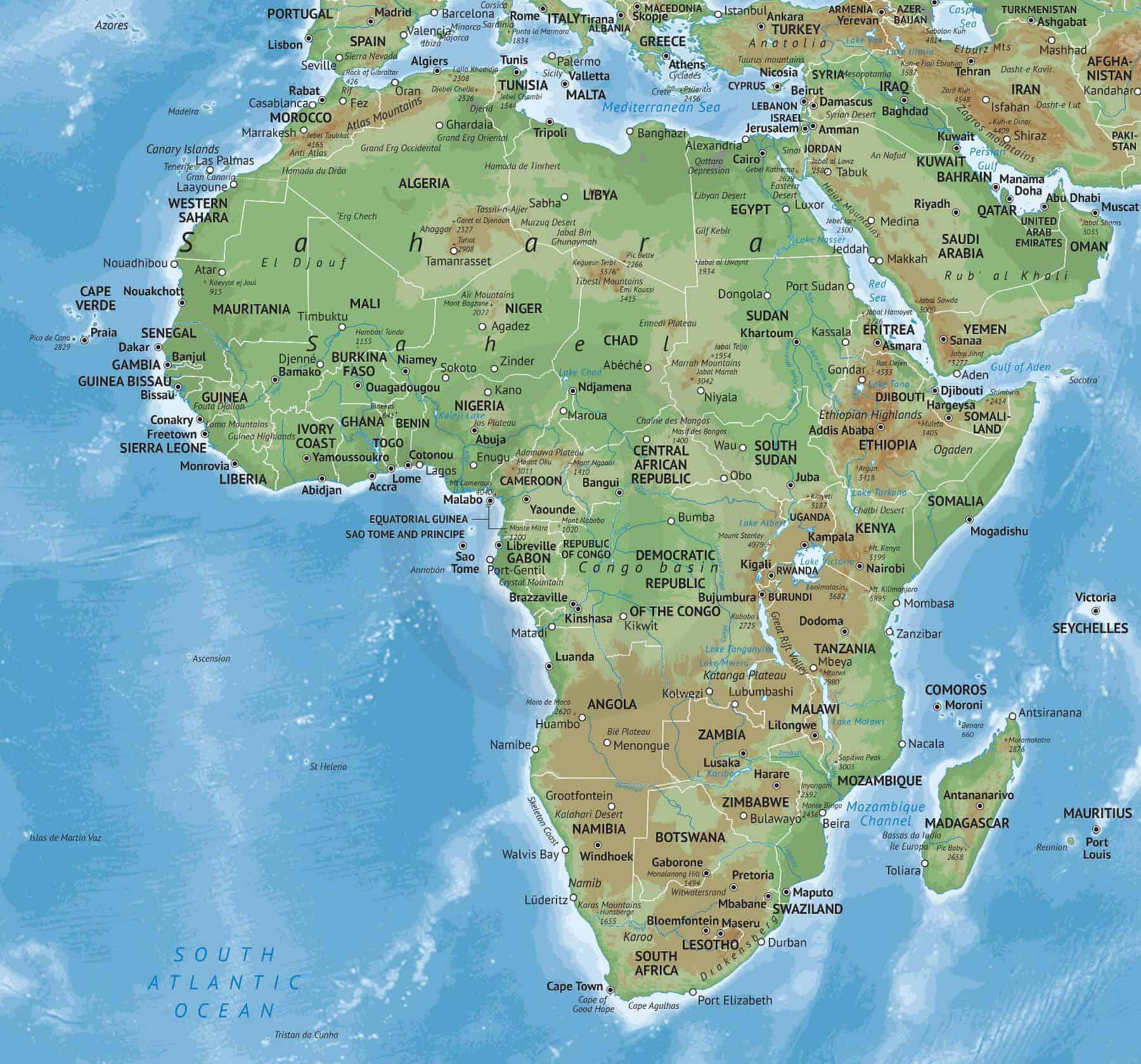
Africa, the second-largest continent on Earth, is a vast and diverse landmass with a rich history, vibrant cultures, and a complex geopolitical landscape. Understanding the intricate tapestry of nations that comprise this continent requires a visual representation – a map. This article delves into the significance of the map of Africa, exploring its historical evolution, its importance in understanding the continent’s geography, politics, and culture, and the insights it provides into the interconnectedness of its people and nations.
The Evolution of the Map of Africa:
The cartographic representation of Africa has undergone a significant transformation over centuries. Early maps, often created by European explorers, were riddled with inaccuracies and biases. The continent was often depicted as a monolithic entity, devoid of the internal diversity and complexity that truly characterizes it. As exploration and scientific understanding advanced, so did the accuracy of these maps.
The development of modern cartography, with its emphasis on precise measurements and detailed information, led to a more nuanced understanding of Africa’s geography. This evolution was further fueled by the rise of nationalism and the decolonization movement in the 20th century. As African nations gained independence, their boundaries were established and formalized, leading to the modern map of Africa we recognize today.
A Visual Representation of Diversity:
The map of Africa is a powerful tool for visualizing the continent’s vast diversity. It reveals the intricate mosaic of nations, each with its unique history, language, culture, and landscape. From the sprawling savannas of the east to the dense rainforests of the west, from the snow-capped peaks of Mount Kilimanjaro to the arid deserts of the Sahara, the map showcases the continent’s remarkable geographical variety.
The map also highlights the geopolitical complexities of Africa. The continent is home to a multitude of political systems, from democracies to autocracies, and a diverse range of economic models. Understanding the spatial distribution of these systems is crucial for comprehending the continent’s political dynamics and its interactions with the global community.
The Importance of Boundaries:
The lines that delineate the borders of African nations on the map are more than just lines on a piece of paper. They represent the culmination of historical processes, often fraught with conflict and tension. These boundaries are the product of colonial legacies, negotiated agreements, and sometimes arbitrary decisions made by external powers.
While these boundaries have provided a framework for governance and stability, they have also contributed to inter-state conflicts, ethnic tensions, and economic disparities. Understanding the historical context and the geopolitical implications of these boundaries is crucial for navigating the complex realities of the African continent.
Beyond Borders: The Interconnectedness of Africa:
Despite the clear delineation of national borders on the map, it is important to remember that Africa is not a collection of isolated entities. The continent’s people, cultures, and economies are deeply interconnected. Trade routes, migration patterns, and shared cultural traditions transcend national boundaries, creating a web of interconnectedness that binds the continent together.
The map of Africa can be a powerful tool for understanding these connections. It can reveal the flow of goods and services across borders, the migration patterns of people seeking economic opportunities or fleeing conflict, and the shared cultural heritage that unites different communities.
The Map of Africa: A Tool for Development and Understanding:
The map of Africa is not merely a static representation of the continent’s geography; it is a dynamic tool for understanding its challenges and opportunities. It can be used to identify areas of vulnerability to climate change, to track the spread of disease, and to plan for sustainable development initiatives.
By visualizing the distribution of resources, infrastructure, and human capital, the map can inform policy decisions and guide development efforts. It can also be used to promote regional integration, fostering collaboration and cooperation between African nations.
Frequently Asked Questions:
- How many countries are in Africa? There are 54 sovereign states recognized by the United Nations in Africa.
- What is the largest country in Africa? Algeria is the largest country in Africa by land area.
- What is the most populous country in Africa? Nigeria is the most populous country in Africa.
- What are the major geographical features of Africa? Africa is home to a diverse range of geographical features, including the Sahara Desert, the Nile River, the Atlas Mountains, and the Great Rift Valley.
- What are the major languages spoken in Africa? Africa is home to a vast number of languages, with Arabic, Swahili, French, English, and Portuguese being some of the most widely spoken.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Africa:
- Pay attention to scale: The map’s scale can significantly impact your understanding of the continent’s size and distances.
- Explore the key geographical features: Identify major rivers, mountains, deserts, and other prominent features to gain a sense of the continent’s landscape.
- Consider the historical context: Understand the colonial legacies and the events that have shaped the political boundaries of African nations.
- Look beyond borders: Recognize the interconnectedness of African nations and the flow of people, goods, and ideas across borders.
- Use the map as a tool for learning: Explore the map to learn about the diverse cultures, languages, and economies of the African continent.
Conclusion:
The map of Africa is more than just a visual representation of the continent’s geography. It is a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s history, culture, politics, and development. By exploring the map, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity and interconnectedness of Africa, its challenges and opportunities, and its unique place in the world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Map of Africa: A Tapestry of Nations and Cultures. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
