24, Feb 2024
The Shifting Sands Of Europe: A Historical Journey Through Maps
The Shifting Sands of Europe: A Historical Journey Through Maps
Related Articles: The Shifting Sands of Europe: A Historical Journey Through Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Shifting Sands of Europe: A Historical Journey Through Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Shifting Sands of Europe: A Historical Journey Through Maps

The map of Europe, a continent rich in history and constantly evolving, is a fascinating tapestry woven from countless narratives of conquest, migration, and cultural exchange. To truly understand the complexities of the modern European landscape, one must delve into the past, tracing the shifting borders and political entities that have shaped the continent’s identity. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the evolving map of Europe, focusing on the period preceding the 21st century, with an emphasis on the historical context and significance of these transformations.
The Ancient Foundations:
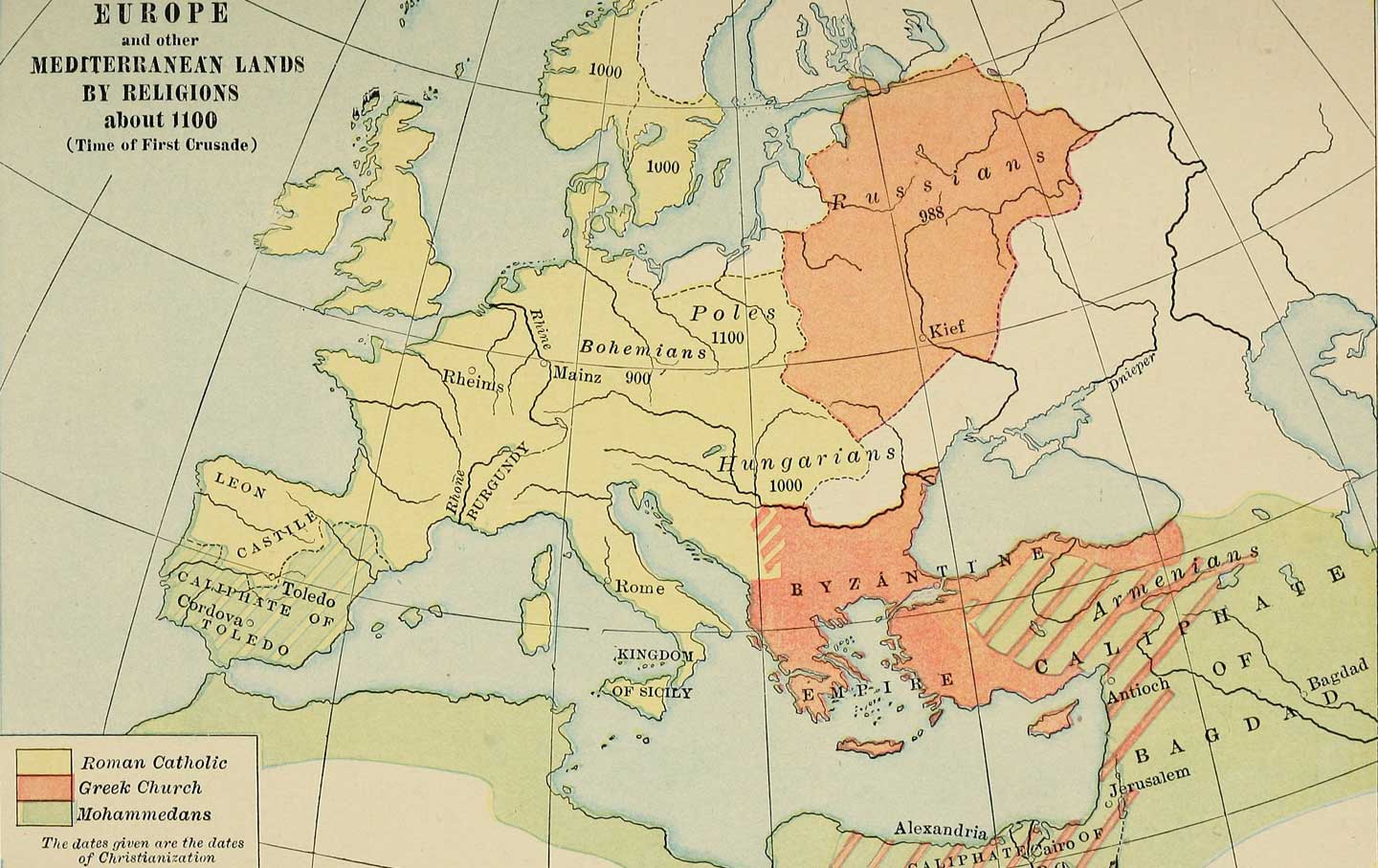
The map of Europe in antiquity was a mosaic of diverse civilizations, each leaving their imprint on the continent’s cultural and political landscape. The Roman Empire, at its zenith, extended its dominion across much of Western and Southern Europe, imposing a unified administration and infrastructure that would shape the region for centuries to come. The legacy of Rome is evident in the languages, legal systems, and architectural marvels that still define many European nations.
However, the Roman Empire was not the only influential force in ancient Europe. The Greeks, with their flourishing intellectual and artistic traditions, left an indelible mark on the Eastern Mediterranean. Beyond these empires, numerous Celtic, Germanic, and Slavic tribes occupied vast territories, contributing to the complex tapestry of European culture.
The Middle Ages: A Period of Fragmentation and Consolidation:
The collapse of the Roman Empire in the 5th century AD marked the beginning of a new era in European history. The continent was fragmented into numerous kingdoms, duchies, and principalities, each vying for power and influence. The emergence of Christianity as a dominant force further shaped the political and social landscape, leading to the establishment of powerful religious institutions that played a pivotal role in medieval Europe.
The map of Europe during this period was characterized by constant flux. Kingdoms rose and fell, alliances shifted, and territories were contested. The Carolingian Empire under Charlemagne briefly united much of Western Europe in the 8th and 9th centuries, but its fragmentation after his death marked the return to a fragmented political landscape.
The Rise of Nation-States: A New Order Emerges:
The late Middle Ages and the Early Modern period witnessed the rise of nation-states, a significant shift in the European political landscape. Centralized monarchies, often aided by burgeoning national identities, began to consolidate power, gradually replacing the fragmented feudal order. The emergence of powerful states like France, England, Spain, and Portugal, each with its own distinct political and cultural identity, profoundly altered the map of Europe.
This period also saw the expansion of European influence beyond the continent’s borders. The Age of Exploration, fueled by a thirst for wealth and power, led to the establishment of vast colonial empires, extending European dominance across the globe. This period of expansion further shaped the map of Europe, influencing trade routes, cultural exchanges, and ultimately, the very fabric of European society.
The 19th Century: Nationalism and the Unification of Italy and Germany:
The 19th century was a period of intense nationalism in Europe. The rise of national consciousness, often fueled by shared language, culture, and history, spurred movements for unification and independence. This trend culminated in the unification of Italy and Germany, two significant events that dramatically altered the map of Europe.
The unification of Italy in 1861, after centuries of division, brought together a diverse range of regional kingdoms and states under a single banner. Similarly, the unification of Germany in 1871, under the leadership of Prussia, marked the emergence of a powerful new nation-state on the European stage. These events had profound implications for the continent’s political balance, leading to increased competition for power and dominance.
The 20th Century: Wars, Revolutions, and Shifting Borders:
The 20th century was a period of immense upheaval and transformation in Europe. Two world wars, fueled by nationalism, imperialism, and ideological conflicts, ravaged the continent, leaving behind a trail of devastation and profound social and political change. These conflicts led to the redrawing of borders, the rise and fall of empires, and the emergence of new political ideologies.
The Treaty of Versailles, signed after World War I, significantly reshaped the map of Europe, dissolving the Austro-Hungarian and Ottoman Empires and creating new nations. However, this peace was short-lived, as the rise of Nazi Germany and the outbreak of World War II further destabilized the continent. The end of World War II witnessed the collapse of the Nazi regime and the division of Europe into two opposing blocs: the communist East and the capitalist West.
The Cold War and the Post-Cold War Era:
The Cold War, a period of geopolitical tension between the Soviet Union and the United States, dominated the latter half of the 20th century. This ideological conflict led to the formation of the Warsaw Pact and NATO, military alliances that further divided Europe into opposing camps. The Iron Curtain, a symbolic barrier separating East and West, became a defining feature of the Cold War era.
The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 marked the beginning of the end of the Cold War. The subsequent collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 ushered in a new era of political and economic transformation in Europe. The map of Europe was once again redrawn, as the former Soviet republics gained independence, and the Eastern European nations transitioned to democracy and market economies.
The European Union: A New Chapter in European History:
The end of the Cold War saw the emergence of the European Union, a supranational organization aimed at fostering economic integration and political cooperation among its member states. The EU’s expansion in recent decades has significantly altered the map of Europe, bringing together a diverse group of nations under a common banner.
The EU’s influence extends beyond its borders, playing a significant role in shaping global trade, diplomacy, and security. The organization’s successes and challenges continue to shape the political and economic landscape of Europe, offering a unique model of regional integration in the 21st century.
The Importance of Understanding the Evolving Map of Europe:
Understanding the evolving map of Europe is crucial for comprehending the continent’s rich history, cultural diversity, and political complexities. By tracing the shifting borders and political entities that have shaped the European landscape, we gain insights into the forces that have driven its development, the challenges it has faced, and the opportunities that lie ahead.
The study of historical maps provides valuable context for understanding contemporary events. It helps us to appreciate the long-term trends that have shaped the continent’s trajectory, the interplay of power and influence that has determined its political landscape, and the cultural exchanges that have enriched its heritage.
FAQs:
Q: What are some of the key historical events that have significantly altered the map of Europe?
A: Key events include the fall of the Roman Empire, the rise of nation-states, the unification of Italy and Germany, the two world wars, the Cold War, and the emergence of the European Union.
Q: What is the significance of the European Union in shaping the map of Europe?
A: The EU represents a significant shift towards regional integration, bringing together diverse nations under a common banner, fostering economic cooperation, and promoting political stability.
Q: How has the map of Europe influenced its cultural and linguistic diversity?
A: The shifting borders and political entities have contributed to the development of distinct languages, cultures, and traditions across Europe. The continent’s rich tapestry of cultures is a testament to its diverse history and the interplay of various influences.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing the map of Europe in the 21st century?
A: Challenges include managing migration flows, addressing economic inequality, maintaining political stability amidst rising nationalism, and navigating the complexities of global power dynamics.
Tips:
- Utilize historical maps as a tool for learning about the evolution of European borders and political entities.
- Explore the historical context surrounding key events that have shaped the map of Europe.
- Analyze the interplay of power and influence that has shaped the continent’s political landscape.
- Examine the cultural exchanges and interactions that have contributed to Europe’s diverse heritage.
- Consider the challenges and opportunities facing the map of Europe in the 21st century.
Conclusion:
The map of Europe is a dynamic and ever-evolving entity, reflecting the continent’s rich history, cultural diversity, and political complexities. By tracing the shifting borders and political entities that have shaped the European landscape, we gain a deeper understanding of the forces that have driven its development, the challenges it has faced, and the opportunities that lie ahead. Understanding the historical evolution of the map of Europe provides valuable insights into the continent’s present and future, offering a framework for navigating the complexities of the modern world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Shifting Sands of Europe: A Historical Journey Through Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
