19, Oct 2023
The Shifting Sands Of Europe: A Visual History Of World War II
The Shifting Sands of Europe: A Visual History of World War II
Related Articles: The Shifting Sands of Europe: A Visual History of World War II
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Shifting Sands of Europe: A Visual History of World War II. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Shifting Sands of Europe: A Visual History of World War II

World War II, a conflict that engulfed the globe from 1939 to 1945, left an indelible mark on the map of Europe. The war’s tumultuous events, from the rapid rise and fall of empires to the brutal occupation and liberation of territories, dramatically reshaped the political and geographical landscape of the continent. Understanding the map of Europe during World War II is crucial for grasping the complexities of the war, its devastating consequences, and the lasting impact it had on the world.
The Pre-War Landscape:
Before the outbreak of hostilities, Europe was a tapestry of diverse nations, each with its own political system, cultural identity, and territorial ambitions. The map of Europe in the 1930s reflected a fragile balance of power, with major powers like Britain, France, and Germany vying for influence and control. The map also revealed the presence of smaller nations, many of which were caught in the crosshairs of larger powers.
The Axis Threat:
The rise of Nazi Germany, under the leadership of Adolf Hitler, posed a significant challenge to the existing European order. Germany’s aggressive expansionist policies, fueled by ideologies of racial superiority and territorial conquest, led to the annexation of Austria and Czechoslovakia in 1938 and 1939 respectively. These events fundamentally altered the map of Europe, demonstrating Germany’s growing power and its blatant disregard for international agreements.
The Outbreak of War and the Early Years:
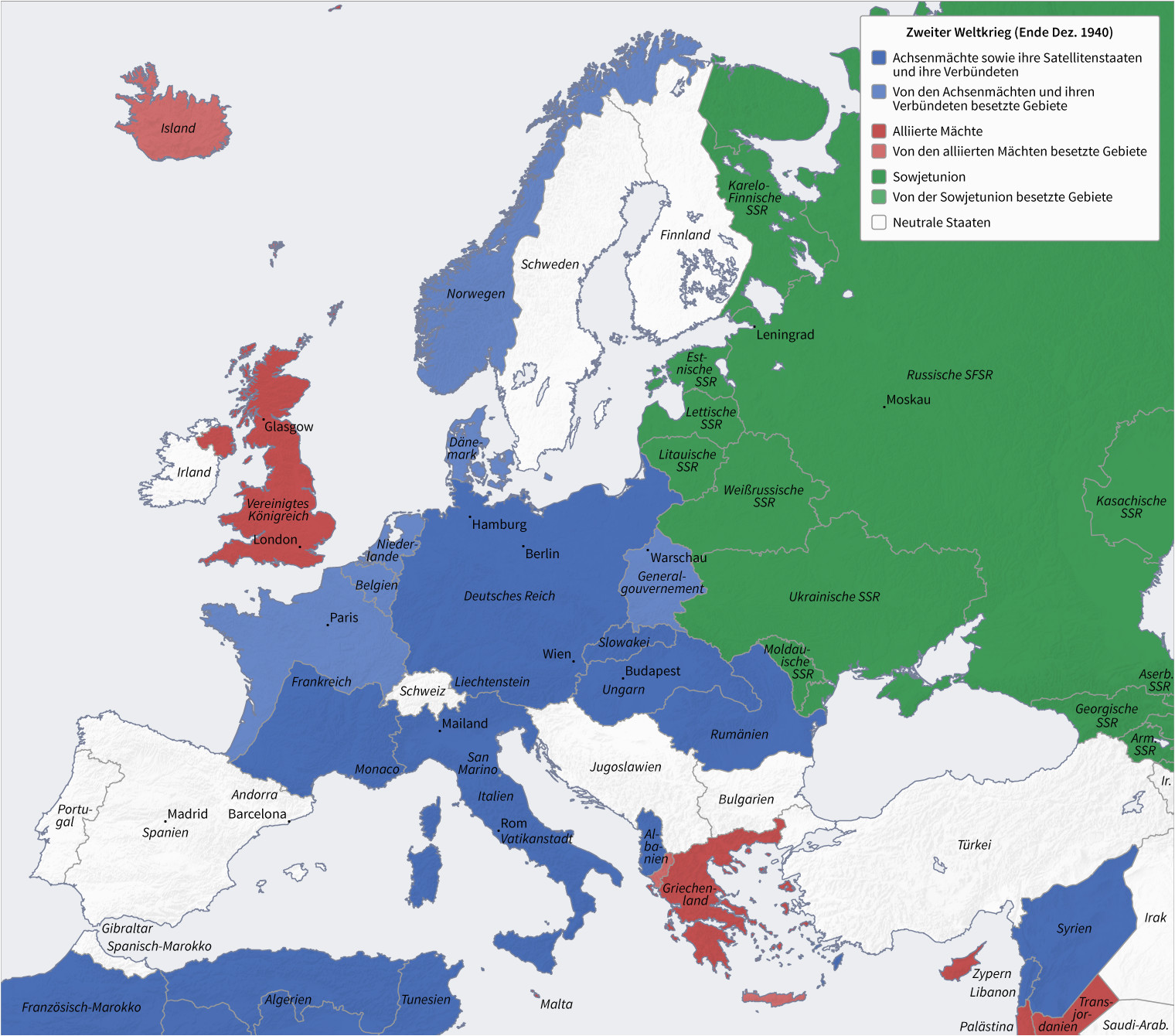
The invasion of Poland by Germany on September 1, 1939, marked the official beginning of World War II. This act triggered a chain reaction, with Britain and France declaring war on Germany. The early years of the war saw Germany’s rapid military successes, leading to the conquest of Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. By 1940, the map of Europe had been dramatically reshaped, with Germany controlling vast swathes of territory in Western and Central Europe.
The Eastern Front and the Soviet Union:
In June 1941, Germany launched Operation Barbarossa, a surprise attack on the Soviet Union. This marked a turning point in the war, as it opened up a vast and brutal front in Eastern Europe. The Eastern Front, characterized by its immense scale and horrific casualties, witnessed fierce battles between the German Wehrmacht and the Red Army. The map of Europe during this period reflects the constant ebb and flow of battles, with territories changing hands numerous times.
The Allied Counteroffensive and Liberation:
Following the initial German successes, the tide of the war began to turn in favor of the Allies. Key victories in North Africa, Italy, and the Eastern Front gradually pushed back German forces. The Allied invasion of Normandy in June 1944, known as D-Day, marked a decisive turning point, opening a second front in Western Europe. The liberation of France, Belgium, and the Netherlands, along with the Allied advance towards Germany, steadily restored the pre-war boundaries on the map of Europe.
The End of the War and its Aftermath:
The war finally ended in Europe in May 1945 with the unconditional surrender of Germany. The map of Europe had been reshaped, with Germany divided into four occupation zones controlled by the Allied powers. The war also led to the creation of new nations, such as Yugoslavia and Czechoslovakia, while others, like Poland, saw their borders significantly altered. The war’s legacy on the map of Europe was profound, leaving behind a continent scarred by conflict and divided by ideological tensions.
The Importance of Studying the Map of Europe during World War II:
The map of Europe during World War II serves as a visual chronicle of the war’s unfolding events. It provides crucial insights into:
- The geographical scope of the war: The map highlights the vast expanse of territory that was engulfed in the conflict, spanning from the Atlantic coast to the Ural Mountains.
- The strategic importance of key locations: The map reveals the significance of strategic locations like the English Channel, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Eastern Front, which played pivotal roles in the war’s course.
- The changing power dynamics: The map reflects the shifting power dynamics throughout the war, showing the rise and fall of empires, the expansion and contraction of territories, and the impact of key battles on the balance of power.
- The human cost of the war: The map helps to visualize the scale of the war’s devastation, highlighting the areas that were most heavily impacted by the conflict and the displacement of populations.
- The impact on the post-war world: The map provides a framework for understanding the geopolitical landscape of Europe after the war, highlighting the emergence of new nations, the redrawing of borders, and the creation of new alliances.
FAQs about the Map of Europe during World War II:
Q: What were the major territorial changes in Europe during World War II?
A: The war led to significant territorial changes in Europe. Germany annexed Austria and Czechoslovakia, expanding its territory eastward. The Soviet Union gained control of territories in Eastern Europe, including Latvia, Lithuania, and Estonia. Poland’s borders were significantly shifted westward, while France lost Alsace-Lorraine to Germany.
Q: How did the map of Europe reflect the changing alliances during the war?
A: The map of Europe reflects the shifting alliances throughout the war. Initially, the Axis powers, Germany, Italy, and Japan, controlled vast territories in Europe. As the war progressed, the Allies, including Britain, the United States, the Soviet Union, and France, gradually gained ground, liberating territories and pushing back the Axis forces.
Q: What were the key strategic locations on the map of Europe during World War II?
A: Key strategic locations on the map of Europe during World War II included the English Channel, the Mediterranean Sea, the Eastern Front, and the North African theater. These locations were crucial for controlling trade routes, launching military operations, and securing access to vital resources.
Q: How did the map of Europe influence the course of the war?
A: The map of Europe played a crucial role in shaping the course of the war. The geographical layout of the continent, the presence of natural barriers like mountains and rivers, and the location of key strategic locations influenced military planning, logistics, and the overall strategy of the war.
Q: What was the impact of the war on the map of Europe after 1945?
A: The war had a profound impact on the map of Europe after 1945. Germany was divided into East and West Germany, with the Soviet Union controlling the eastern half. The Soviet Union also established a sphere of influence in Eastern Europe, leading to the creation of communist states like Poland, Czechoslovakia, and Hungary. The war also led to the creation of new nations like Yugoslavia and the establishment of the United Nations, an international organization aimed at preventing future conflicts.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Europe during World War II:
- Use historical maps: Refer to historical maps of Europe from different periods during the war to visualize the changing boundaries, occupation zones, and military movements.
- Study key battles and campaigns: Understanding the significance of key battles like the Battle of Stalingrad, the Battle of Normandy, and the Battle of the Bulge helps to grasp the strategic importance of specific locations on the map.
- Analyze the impact of geographical features: Consider how mountains, rivers, and coastlines influenced military strategies and the course of the war.
- Explore the human cost of the war: Research the impact of the war on civilian populations, displacement, and the destruction of cities and infrastructure.
Conclusion:
The map of Europe during World War II serves as a powerful visual testament to the destructive nature of war and its profound impact on the continent. It highlights the shifting power dynamics, the strategic importance of key locations, and the immense human cost of the conflict. Studying the map provides invaluable insights into the complexities of the war, its lasting legacy, and the importance of peace and international cooperation in shaping a more peaceful and stable future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Shifting Sands of Europe: A Visual History of World War II. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
