1, Apr 2024
The Shifting Sands Of Power: Europe After World War I
The Shifting Sands of Power: Europe After World War I
Related Articles: The Shifting Sands of Power: Europe After World War I
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Shifting Sands of Power: Europe After World War I. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Shifting Sands of Power: Europe After World War I
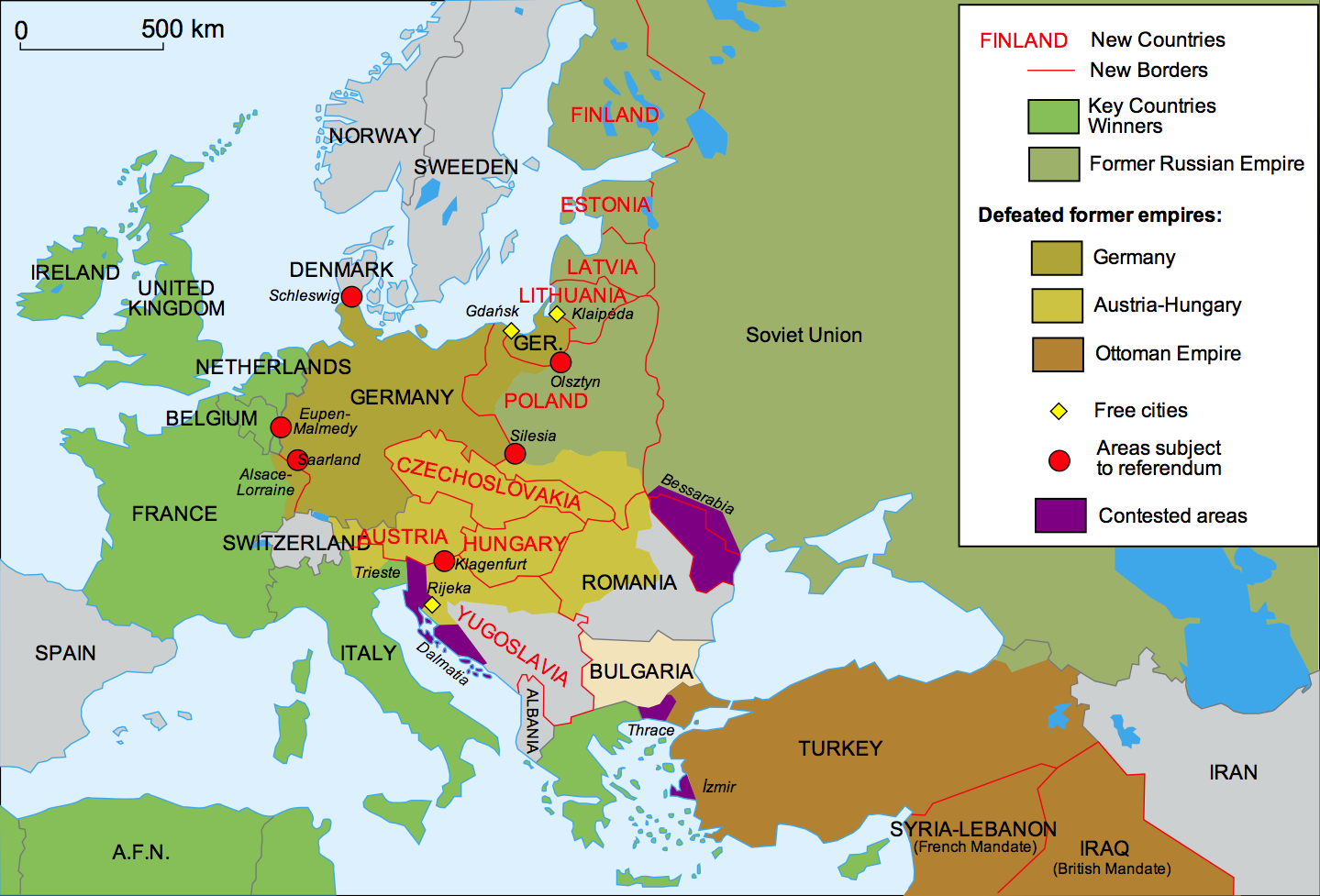
The conclusion of World War I in 1918 marked a pivotal moment in European history. The conflict, which had ravaged the continent for four long years, left in its wake a landscape of shattered empires, fractured borders, and a profound sense of uncertainty. The map of Europe, once a patchwork of established powers, was dramatically redrawn, reflecting the profound political and social transformations that had occurred.
The Collapse of Empires:
The war’s aftermath witnessed the demise of several long-standing empires. The Austro-Hungarian Empire, a multinational entity encompassing diverse ethnicities and cultures, crumbled under the weight of internal tensions and the pressures of wartime defeat. Its disintegration gave birth to new nation-states, including Austria, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, and Yugoslavia. Similarly, the Ottoman Empire, weakened by decades of internal strife and external pressures, was forced to cede vast territories in the Middle East and the Balkans, paving the way for the creation of modern Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Iraq, and Palestine.
The Rise of New Nations:
The disintegration of empires led to the emergence of numerous new nation-states on the European map. Poland, which had been partitioned for over a century, was re-established as an independent nation, regaining its long-lost sovereignty. Finland, Latvia, Estonia, and Lithuania, previously under Russian rule, gained independence, solidifying their status as independent entities. These newly formed nations, fueled by a strong sense of national identity and a desire for self-determination, embarked on a journey to establish their own political and economic systems.
The Treaty of Versailles and its Aftermath:
The Treaty of Versailles, signed in 1919, aimed to establish a lasting peace in Europe by addressing the grievances of the victorious Allied powers. However, its harsh terms, particularly those imposed on Germany, sowed the seeds of future conflict. Germany was forced to cede territories, accept responsibility for the war, and pay substantial reparations, leaving its economy and national pride deeply wounded. The treaty’s punitive nature, coupled with the rise of nationalist sentiment in Germany, contributed to the volatile political climate that would eventually lead to the rise of Adolf Hitler and the outbreak of World War II.
The League of Nations and International Cooperation:
The establishment of the League of Nations, an intergovernmental organization aimed at promoting international cooperation and preventing future conflicts, represented a significant attempt to build a new world order. However, the League’s effectiveness was hampered by its inability to enforce its decisions, the lack of support from major powers like the United States, and the growing tensions between nations. Despite its limitations, the League of Nations served as a precursor to the United Nations, laying the foundation for future efforts to foster international cooperation and address global challenges.
The Changing Political Landscape:
The political landscape of Europe after World War I was characterized by a complex interplay of forces. The rise of communism in Russia, the spread of socialist ideas in various European countries, and the growing popularity of nationalist movements contributed to a period of instability and social upheaval. The redrawing of borders, the emergence of new nations, and the economic and social consequences of the war created a fertile ground for political and ideological clashes, shaping the course of European history for decades to come.
The Map of Europe: A Visual Representation of Transformation:
The map of Europe after World War I vividly illustrates the profound changes that had swept across the continent. The old empires had vanished, replaced by a mosaic of new nation-states. The borders, once firmly established, were redrawn, reflecting the shifting power dynamics and the aspirations of newly independent nations. The map served as a visual testament to the tumultuous period of upheaval and transformation that Europe had undergone, leaving a lasting imprint on the continent’s political and social landscape.
FAQs on the Map of Europe After World War I:
1. What were the major changes to the map of Europe after World War I?
The map of Europe after World War I saw the dissolution of major empires like the Austro-Hungarian and Ottoman Empires, leading to the creation of numerous new nation-states. The borders of existing countries were also significantly altered, with Germany losing territories and Poland regaining its independence.
2. How did the Treaty of Versailles impact the map of Europe?
The Treaty of Versailles, which imposed harsh terms on Germany, led to the loss of territory and the payment of reparations, contributing to the rise of nationalist sentiment in Germany and the subsequent outbreak of World War II.
3. What were the key challenges faced by newly formed nations in Europe after World War I?
Newly formed nations faced numerous challenges, including establishing stable political institutions, rebuilding war-torn economies, and managing ethnic and cultural tensions within their newly defined borders.
4. How did the rise of communism in Russia influence the map of Europe?
The rise of communism in Russia led to the creation of the Soviet Union, a vast and powerful state that would become a major player in the Cold War and have a significant impact on the political landscape of Europe.
5. What was the significance of the League of Nations in the post-World War I era?
The League of Nations, although ultimately unsuccessful, represented a significant attempt to establish a system of international cooperation and prevent future conflicts, laying the groundwork for the United Nations.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Europe After World War I:
- Focus on the major empires that collapsed: Pay attention to the disintegration of the Austro-Hungarian and Ottoman Empires and the emergence of new nation-states from their former territories.
- Identify the newly formed nations: Explore the emergence of Poland, Finland, Latvia, Estonia, Lithuania, Czechoslovakia, and Yugoslavia, and their significance in the changing political landscape of Europe.
- Analyze the impact of the Treaty of Versailles: Understand how the treaty’s harsh terms on Germany contributed to the rise of nationalism and the subsequent outbreak of World War II.
- Consider the role of the League of Nations: Evaluate the League’s successes and failures in promoting international cooperation and preventing conflicts.
- Reflect on the political and social changes: Explore the rise of communism, the spread of socialist ideas, and the growing influence of nationalist movements in shaping the political and social landscape of post-war Europe.
Conclusion:
The map of Europe after World War I serves as a powerful reminder of the profound transformations that can reshape the political and social fabric of a continent. The collapse of empires, the emergence of new nations, and the redrawing of borders created a new geopolitical landscape, rife with both opportunities and challenges. The legacy of World War I, reflected in the map’s altered configuration, continues to influence the political and social dynamics of Europe today, underscoring the importance of understanding the past to navigate the complexities of the present.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Shifting Sands of Power: Europe After World War I. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
