17, May 2024
Understanding Seismic Risk: A Deep Dive Into California And Nevada’s Earthquake Index Map
Understanding Seismic Risk: A Deep Dive into California and Nevada’s Earthquake Index Map
Related Articles: Understanding Seismic Risk: A Deep Dive into California and Nevada’s Earthquake Index Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Seismic Risk: A Deep Dive into California and Nevada’s Earthquake Index Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Seismic Risk: A Deep Dive into California and Nevada’s Earthquake Index Map
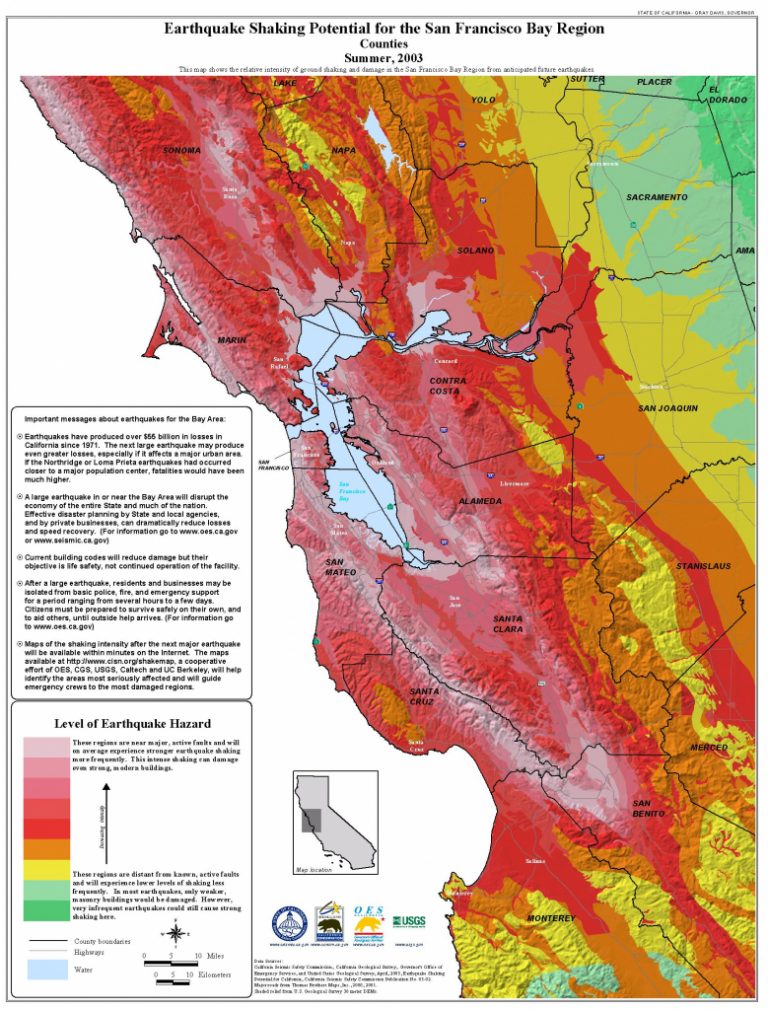
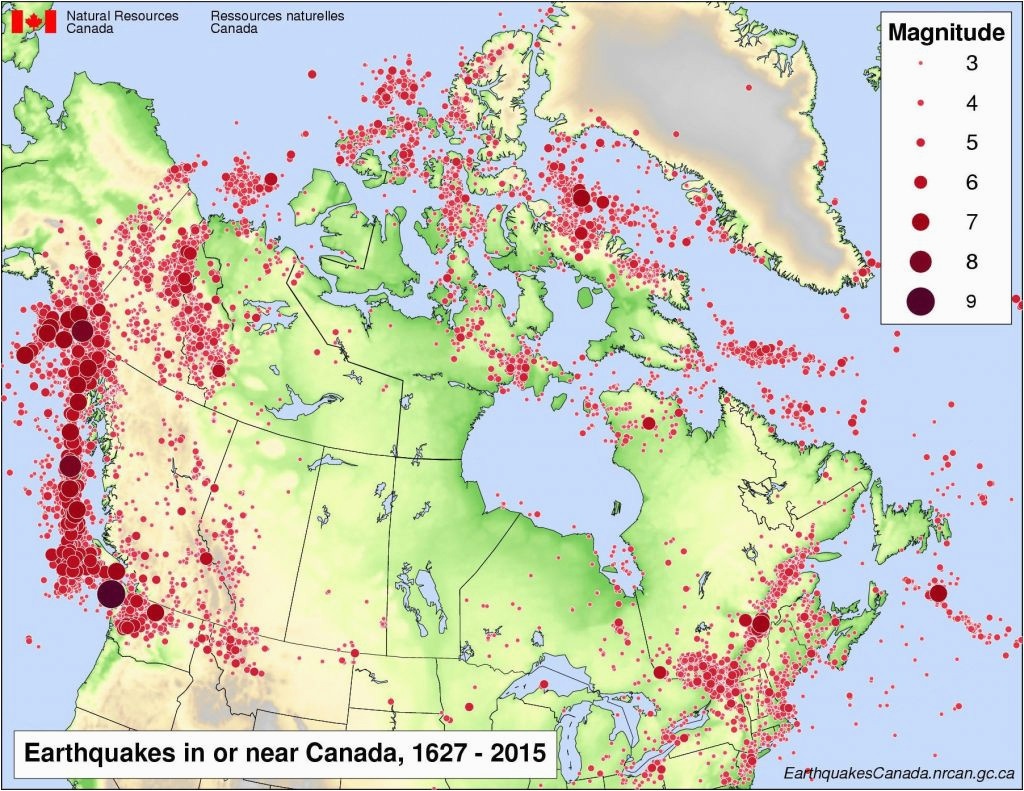
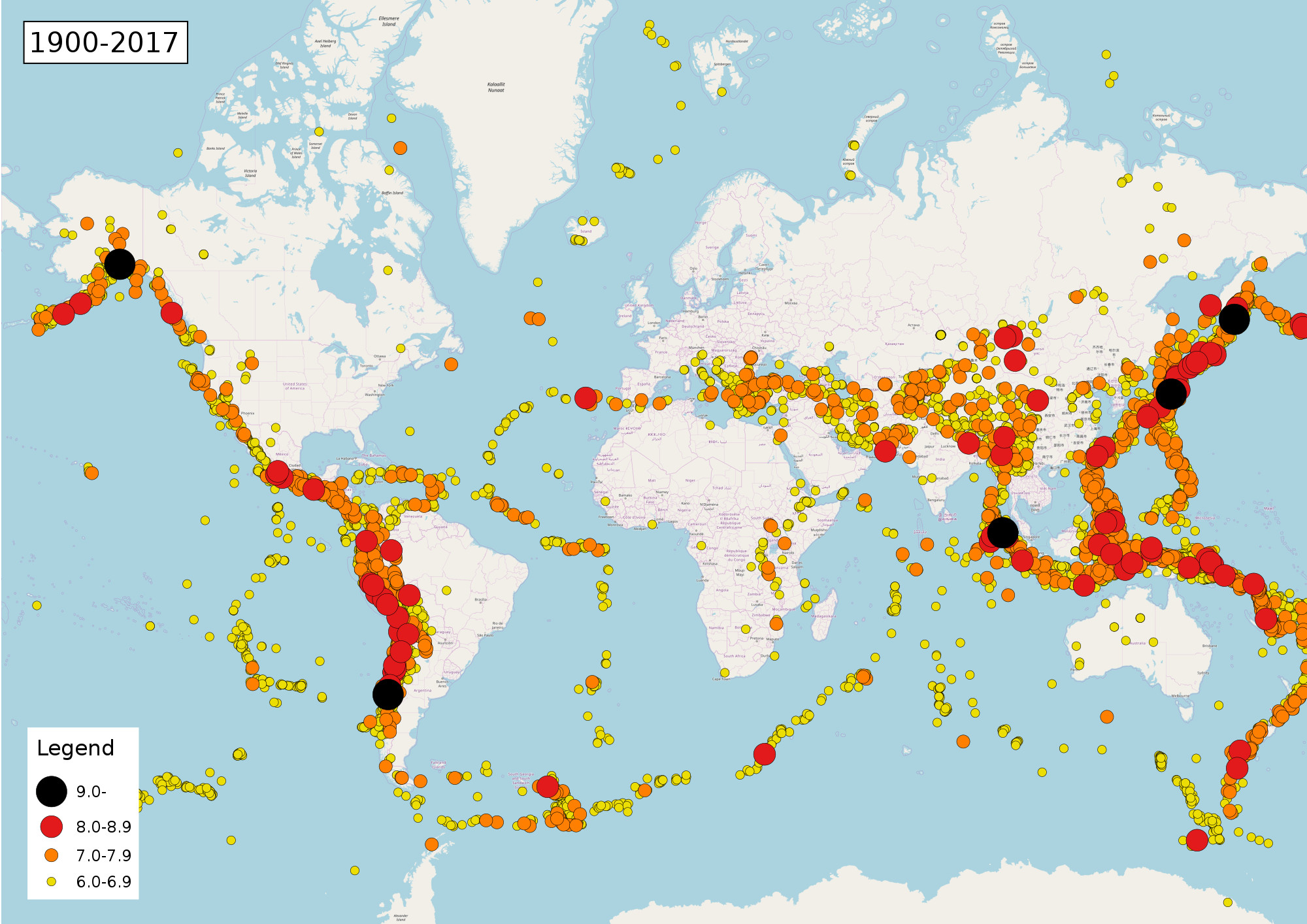
The Earth’s crust is in constant motion, a dynamic system characterized by the slow but relentless movement of tectonic plates. This movement, while imperceptible in our daily lives, manifests in dramatic ways, most notably through earthquakes. California and Nevada, situated along the volatile San Andreas Fault system, are particularly susceptible to these seismic events, making it imperative to understand and mitigate the associated risks. This is where the California and Nevada earthquake index map plays a crucial role.
The Significance of the Earthquake Index Map
The California and Nevada earthquake index map is a powerful tool for visualizing and understanding the seismic hazard across these states. This map, developed and maintained by various geological and seismological organizations, utilizes a combination of data sources, including:
- Historical earthquake records: These records provide a historical perspective on the frequency, magnitude, and location of past earthquakes.
- Fault mapping: Detailed maps of active fault lines, including their length, orientation, and slip rate, are crucial for identifying areas prone to future seismic activity.
- Geophysical data: Analysis of seismic waves, ground deformation, and other geophysical parameters helps refine the understanding of fault behavior and potential earthquake hazards.
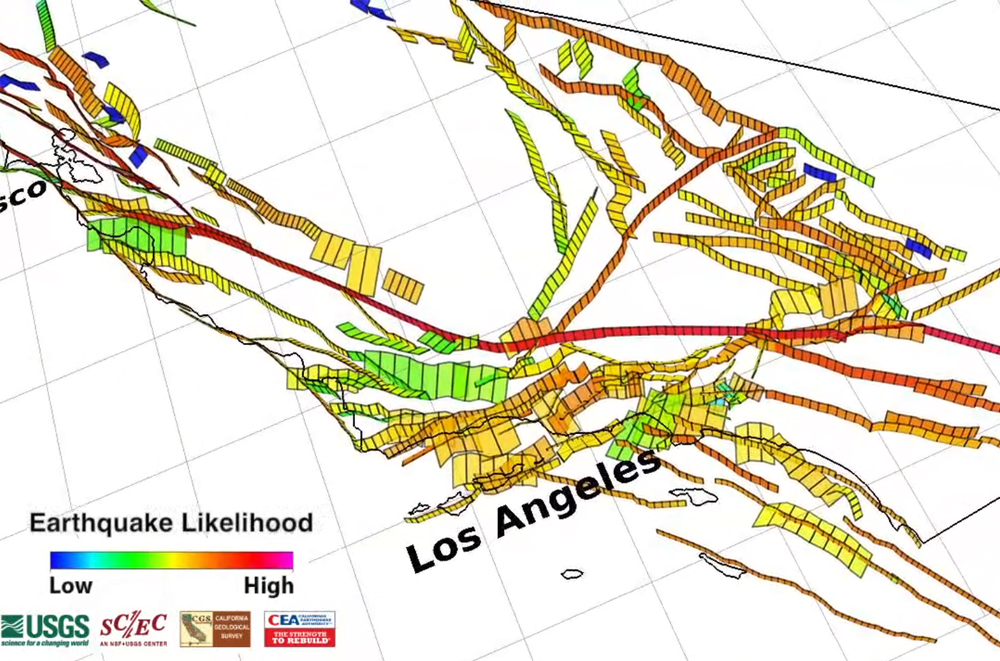
By integrating this diverse dataset, the earthquake index map assigns a seismic risk rating to various regions across California and Nevada. This rating, often represented by color-coded zones, indicates the likelihood and severity of future earthquakes.
Deciphering the Map’s Key Components
The earthquake index map is not a static representation of seismic hazard; it is a dynamic tool that evolves as new data emerges and our understanding of earthquake processes deepens. The map typically incorporates the following key elements:
- Earthquake Zones: These zones are defined based on the historical earthquake activity and the presence of known active faults. Areas with frequent and powerful earthquakes are designated as high-risk zones, while regions with limited seismic history are classified as low-risk zones.
- Fault Lines: Major and minor fault lines are prominently displayed on the map, providing a visual representation of the tectonic framework of the region. This information helps identify areas most susceptible to ground shaking and rupture during an earthquake.
- Seismic Hazard Levels: The map often assigns numerical or color-coded hazard levels to different zones, reflecting the estimated probability and intensity of future earthquakes. These levels are crucial for planning and implementing earthquake-resistant infrastructure and disaster preparedness measures.
- Ground Motion Intensity: This component of the map indicates the potential severity of ground shaking during an earthquake. It is represented by contour lines, with higher values signifying areas expected to experience stronger ground motion. This information is critical for designing buildings and infrastructure to withstand seismic forces.
Applications and Benefits of the Earthquake Index Map
The earthquake index map serves as a valuable resource for a wide range of stakeholders, including:
- Government Agencies: Local, state, and federal agencies utilize the map to inform land-use planning, building codes, and disaster preparedness strategies. The map helps them prioritize resources and allocate funding for earthquake mitigation projects.
- Engineers and Architects: The map is an essential tool for designing earthquake-resistant structures, particularly in high-risk zones. Engineers use the information on ground motion intensity and fault locations to ensure buildings can withstand seismic forces.
- Insurance Companies: The map assists insurance companies in assessing seismic risk and setting appropriate premiums for property and casualty insurance. This information helps them better understand the potential financial impact of earthquakes and develop effective risk management strategies.
- Public Awareness: The earthquake index map is an effective tool for raising public awareness about seismic hazards and promoting earthquake preparedness. The map helps people understand the potential risks in their area and encourages them to take proactive steps to protect themselves and their families.
Understanding Earthquake Risk: FAQs
Q: What does it mean if my area is in a high-risk earthquake zone?
A: A high-risk zone indicates that the area has a higher likelihood of experiencing a significant earthquake. This means that the region has a history of strong earthquakes, active faults, or other geological features that increase the risk of future seismic events. It is crucial to be prepared for the possibility of an earthquake in such areas.
Q: How often are earthquakes expected in California and Nevada?
A: The frequency of earthquakes varies significantly across different regions. California and Nevada experience a wide range of seismic activity, from frequent, minor tremors to infrequent, powerful earthquakes. While predicting the exact timing and location of earthquakes remains challenging, the earthquake index map helps understand the relative likelihood of earthquakes in different areas.
Q: How can I find out the earthquake risk in my specific location?
A: You can access detailed earthquake index maps and information from various sources, including:
- The United States Geological Survey (USGS): The USGS provides comprehensive earthquake data, including maps, hazard assessments, and educational resources.
- The California Geological Survey (CGS): The CGS offers detailed information on California’s earthquake hazards, fault lines, and seismic risk zones.
- The Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology (NBMG): The NBMG provides geological and seismic information for Nevada, including earthquake risk maps and hazard assessments.
Q: What are some tips for preparing for an earthquake?
A: Being prepared for an earthquake is crucial for ensuring safety and minimizing potential damage. Here are some essential tips:
- Secure Heavy Objects: Secure heavy objects like bookshelves, mirrors, and pictures to prevent them from falling during an earthquake.
- Develop an Emergency Plan: Create a family emergency plan that outlines evacuation routes, communication strategies, and meeting points.
- Prepare an Emergency Kit: Assemble an emergency kit containing essential supplies such as food, water, first aid, and a flashlight.
- Learn First Aid and CPR: Basic first aid and CPR training can be invaluable in the event of an earthquake.
- Participate in Earthquake Drills: Practice earthquake drills regularly to familiarize yourself with safety procedures and ensure everyone in your household knows what to do in case of an earthquake.
Conclusion
The California and Nevada earthquake index map is a vital tool for understanding and managing seismic risk in these earthquake-prone states. By providing a visual representation of earthquake hazard levels, fault lines, and potential ground motion intensity, the map empowers individuals, communities, and institutions to make informed decisions regarding disaster preparedness, infrastructure design, and land-use planning. It serves as a constant reminder of the dynamic nature of the Earth’s crust and the importance of being prepared for the inevitable occurrence of earthquakes. Utilizing the map’s information and implementing appropriate mitigation measures can significantly reduce the impact of earthquakes and enhance the resilience of communities in these seismically active regions.
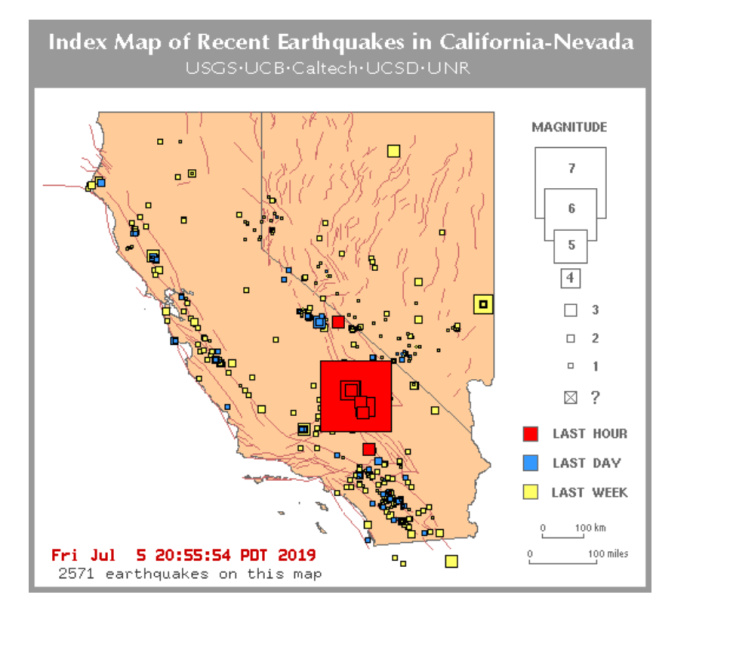
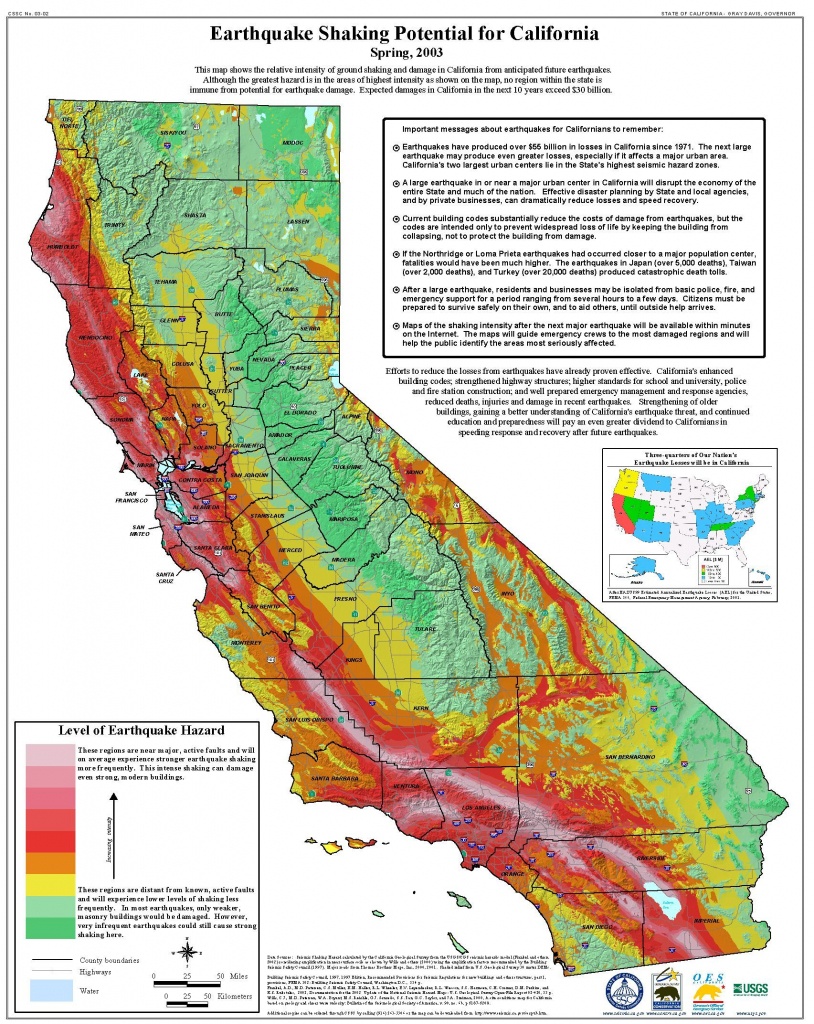
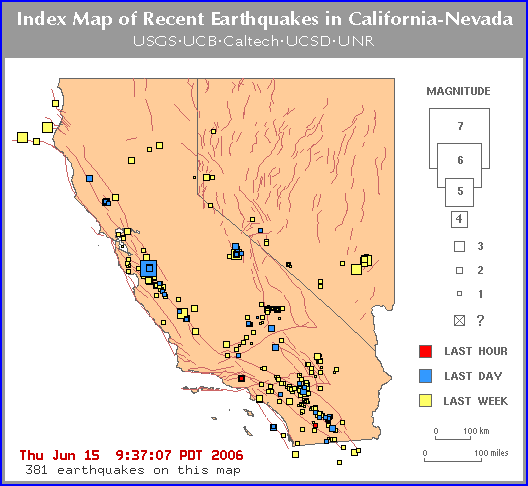


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Seismic Risk: A Deep Dive into California and Nevada’s Earthquake Index Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
