9, Nov 2023
Unraveling The Seismic Tapestry Of California And Nevada: A Deep Dive Into The USGS Earthquake Index Map
Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of California and Nevada: A Deep Dive into the USGS Earthquake Index Map
Related Articles: Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of California and Nevada: A Deep Dive into the USGS Earthquake Index Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of California and Nevada: A Deep Dive into the USGS Earthquake Index Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of California and Nevada: A Deep Dive into the USGS Earthquake Index Map
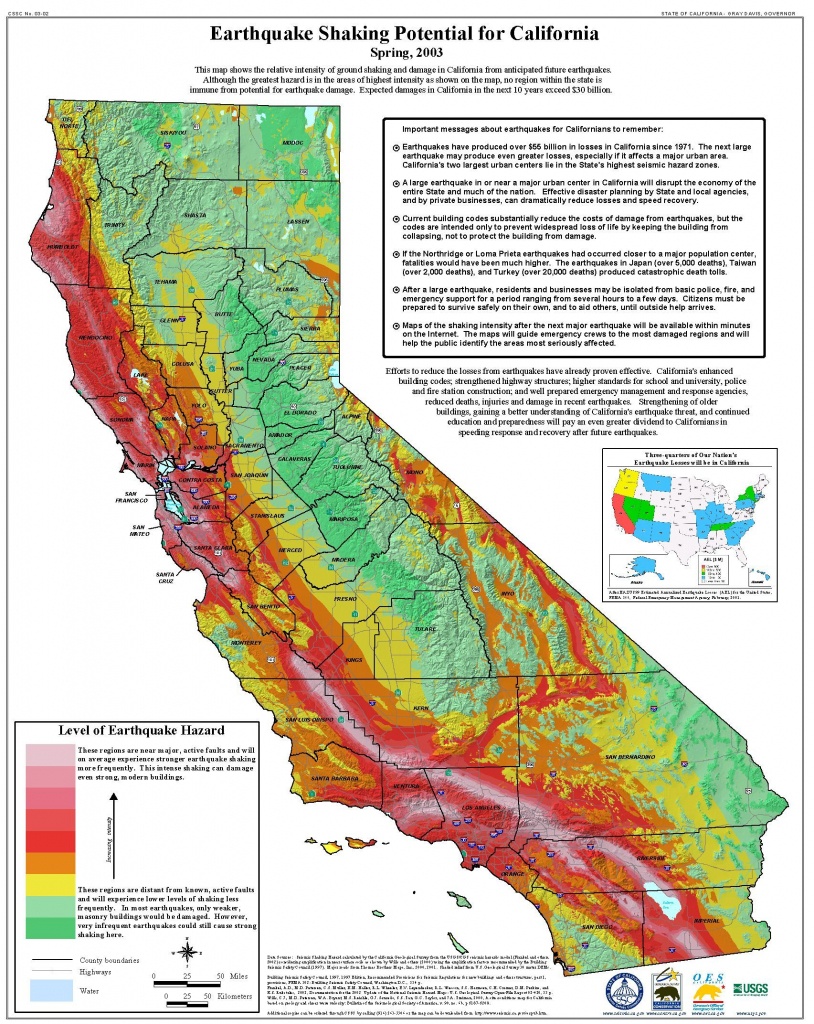
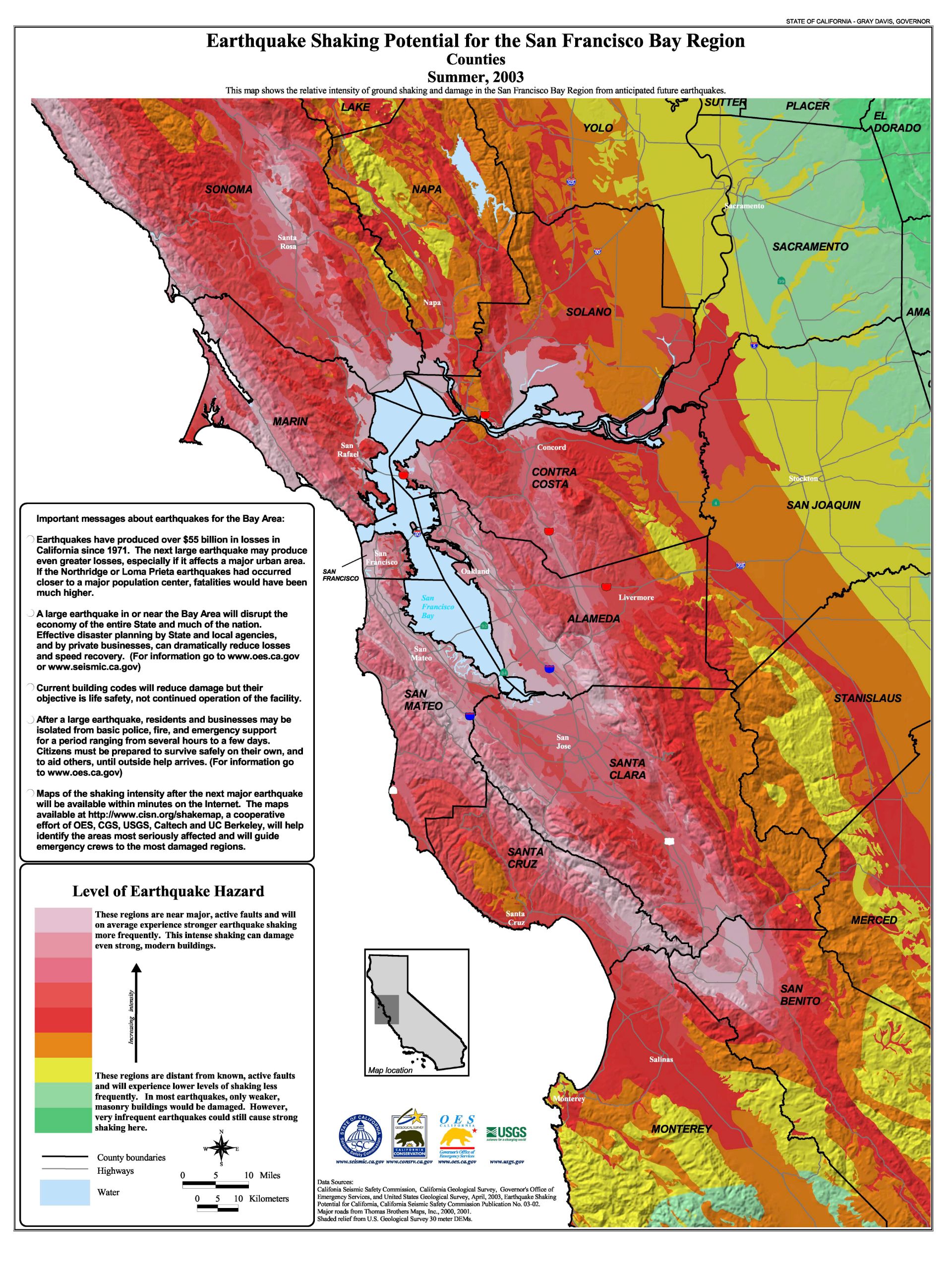
The United States Geological Survey (USGS) California-Nevada Earthquake Index Map is a powerful visualization tool that unveils the intricate seismic landscape of two of the most earthquake-prone regions in the United States. This map, a product of decades of meticulous scientific research and data collection, serves as a crucial resource for understanding past earthquake activity, assessing future seismic hazards, and informing crucial decisions related to earthquake preparedness and mitigation.
A Window into the Past: Unveiling the Seismic History
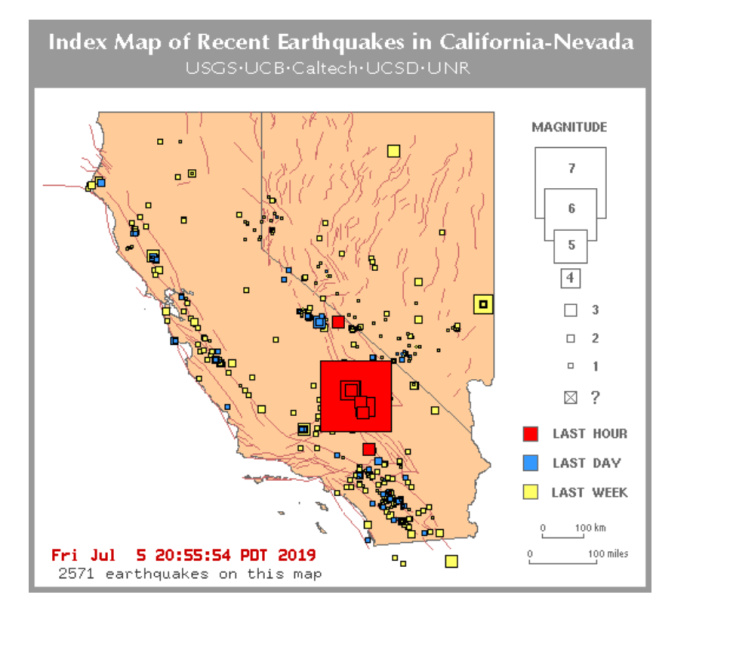
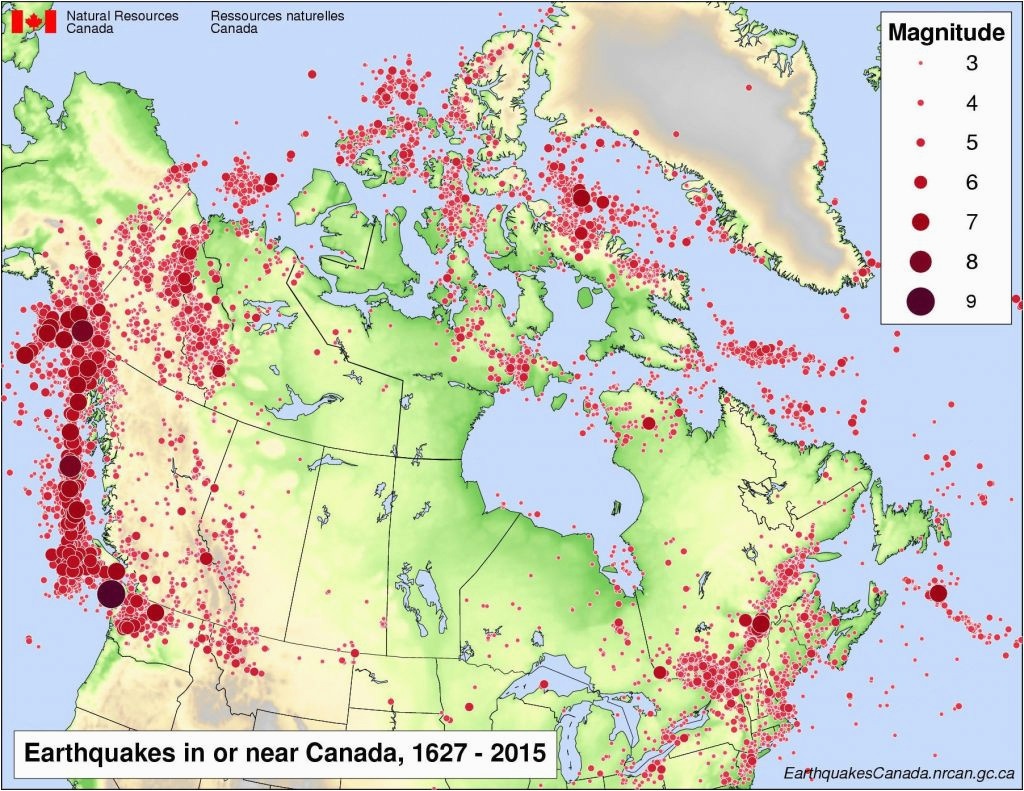
The USGS map is not merely a static representation of earthquake locations. It is a dynamic chronicle of seismic activity, capturing the frequency, magnitude, and distribution of earthquakes that have shaken California and Nevada over centuries. Each point on the map represents a recorded earthquake, with its size and color reflecting its magnitude. This visual tapestry reveals patterns of earthquake clustering, highlighting regions with a higher concentration of seismic activity.
For instance, the map clearly illustrates the presence of major fault systems like the San Andreas Fault, the Cascadia Subduction Zone, and the Sierra Nevada Fault, which have historically generated some of the most powerful earthquakes in the region. This historical perspective provides vital insights into the long-term seismic behavior of these fault zones, allowing scientists to predict potential future earthquake activity with greater accuracy.
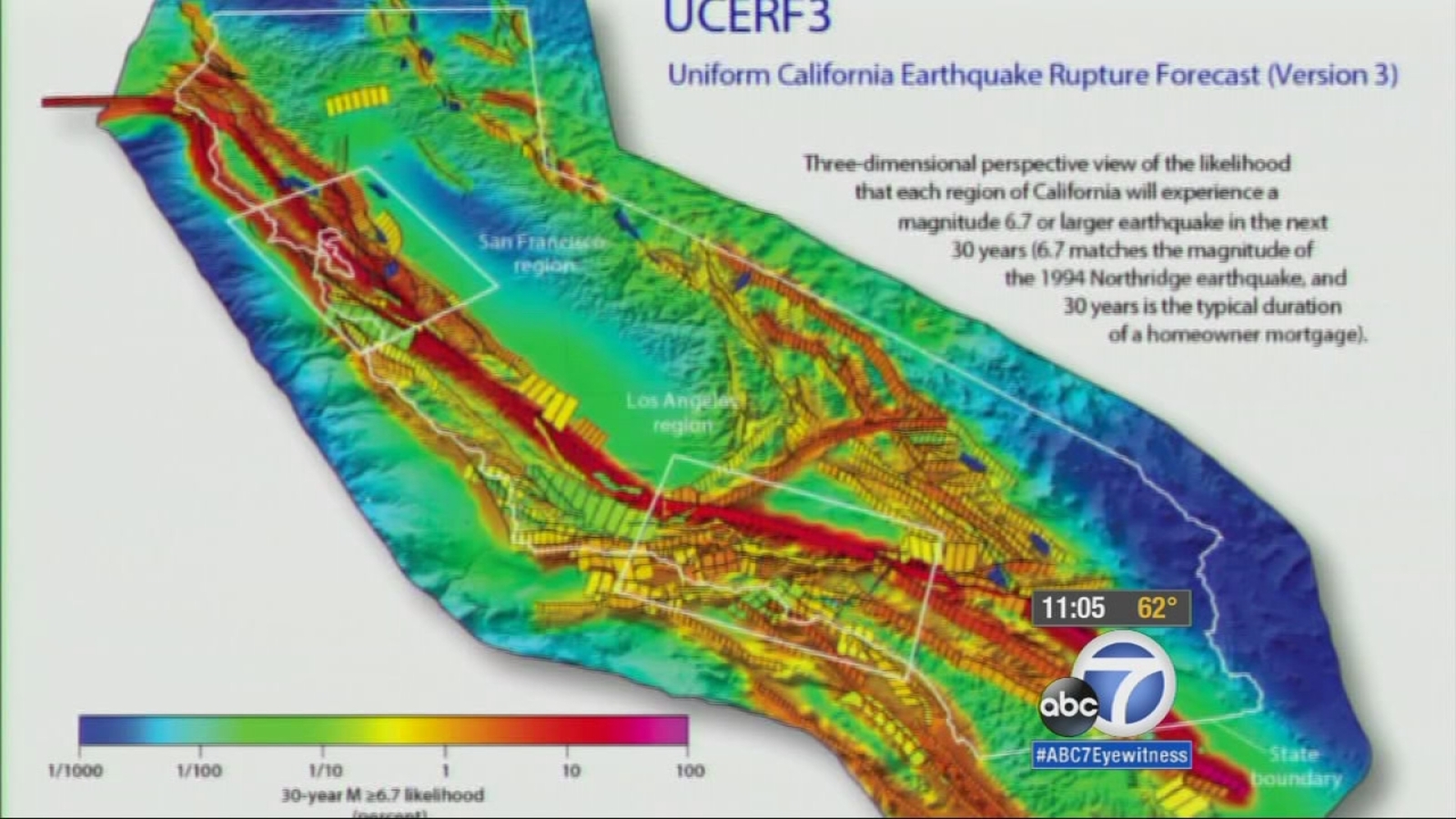
Beyond the Past: Forecasting Future Seismic Hazards
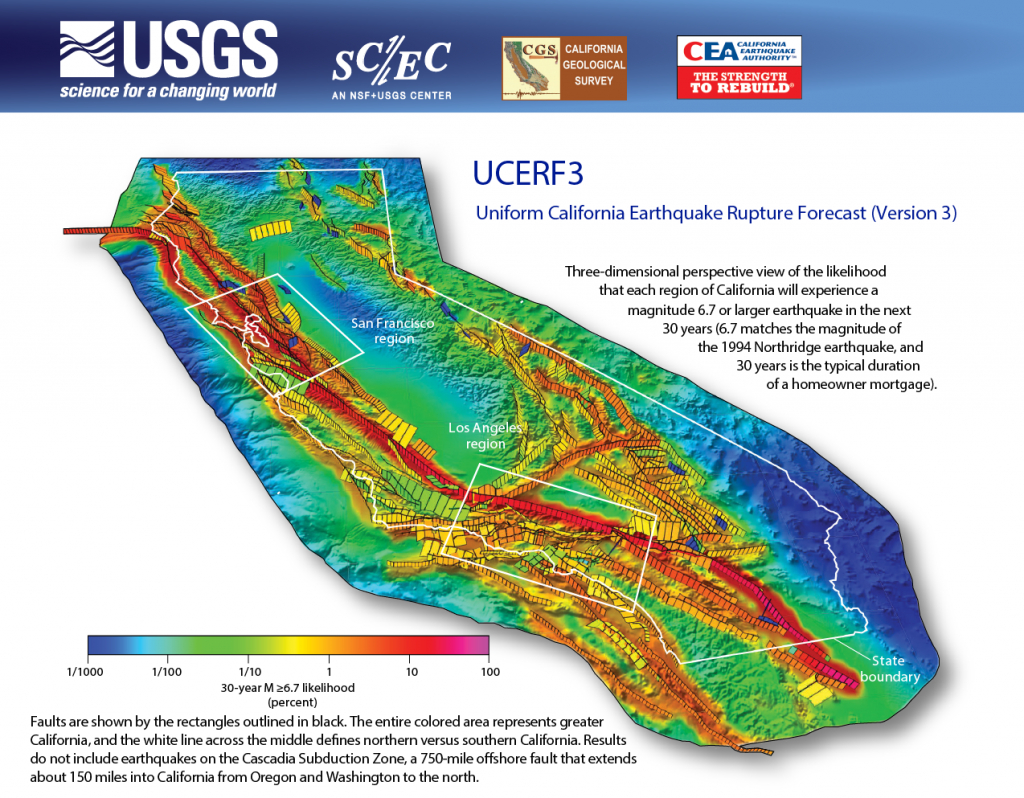
The USGS map extends beyond merely documenting past earthquakes. It serves as a critical tool for assessing future earthquake hazards. By analyzing the historical earthquake data, scientists can identify regions with a higher probability of experiencing significant earthquakes in the future. This information is crucial for informing decisions related to earthquake-resistant building codes, infrastructure design, and emergency preparedness planning.
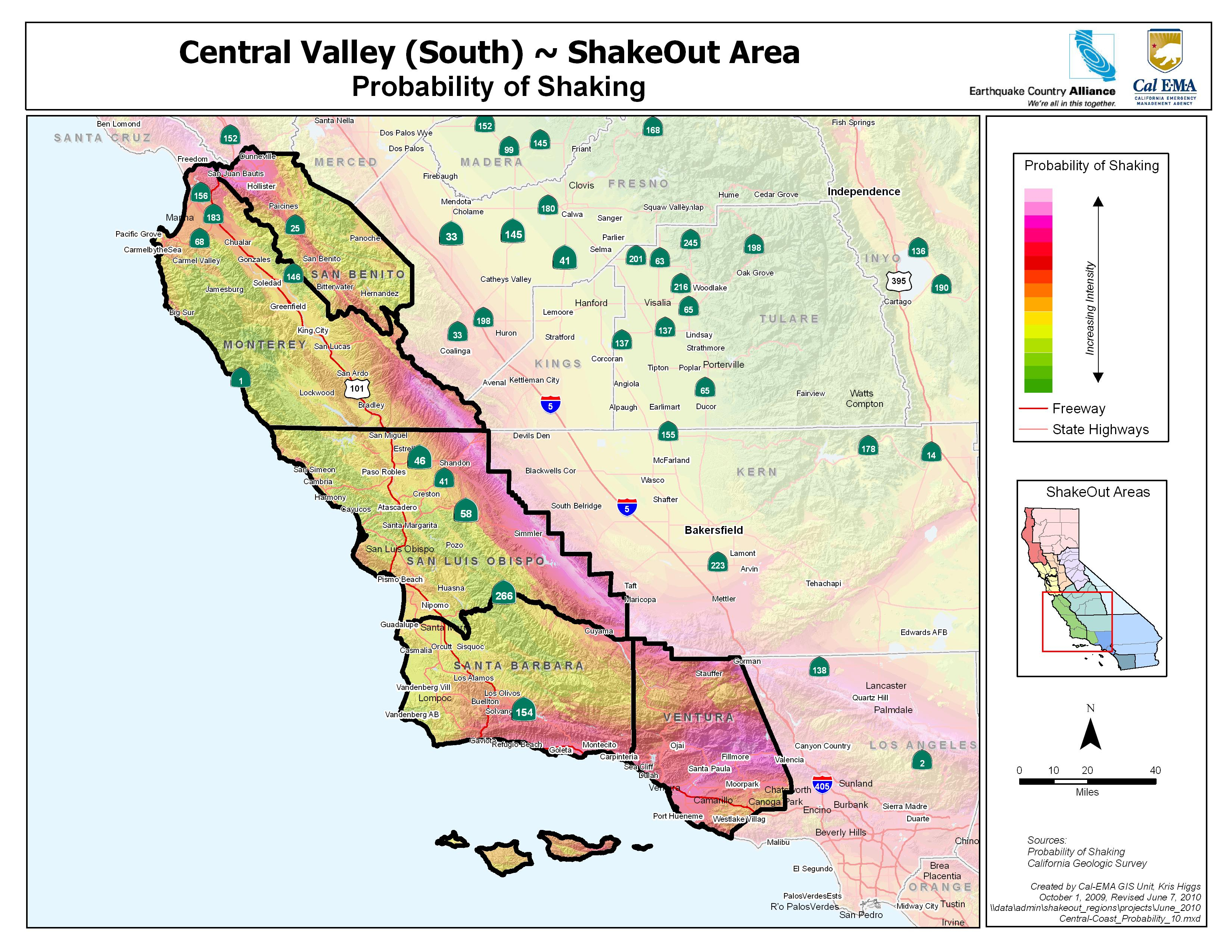
The map utilizes a color-coded system to denote different levels of seismic hazard. Regions with a higher concentration of past earthquakes and active fault systems are marked with darker colors, indicating a higher risk of future earthquakes. This visual representation allows policymakers, planners, and the public to quickly grasp the relative seismic hazard levels across California and Nevada.
Navigating the Map: Understanding the Data and Its Implications
The USGS map provides a wealth of information, but interpreting its data requires a basic understanding of seismic terminology and concepts. The following definitions will help in navigating the map effectively:
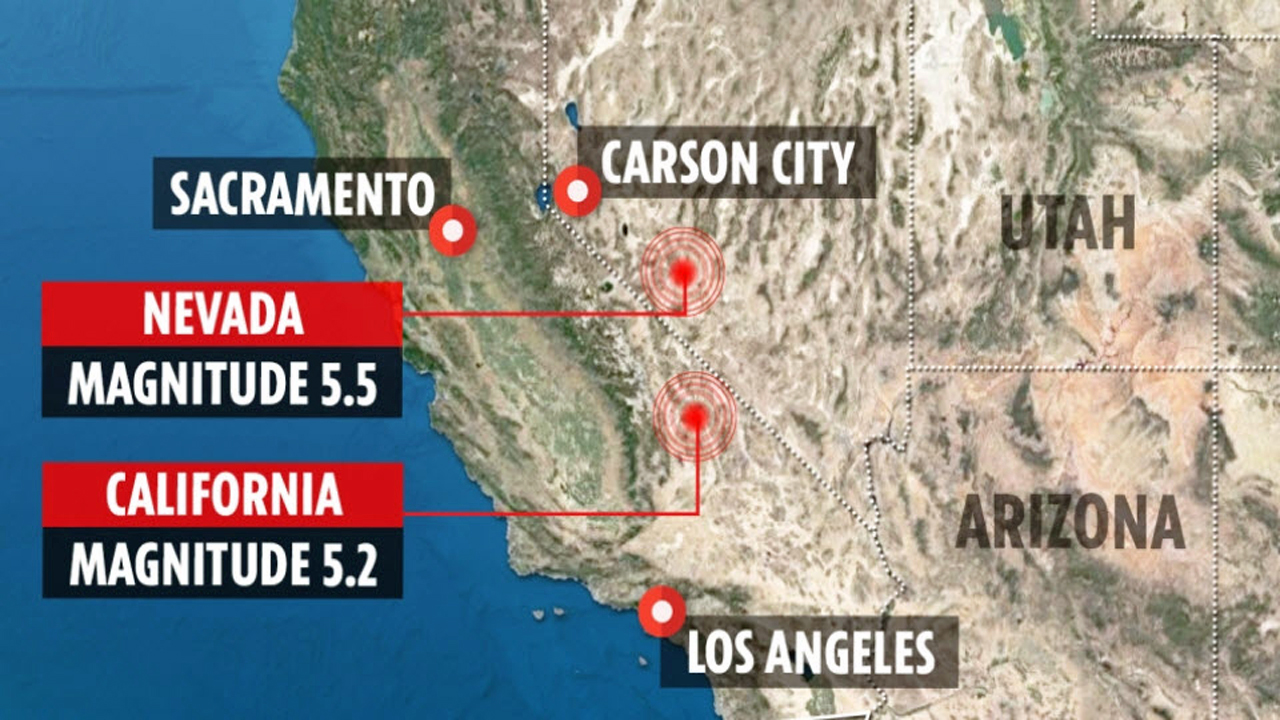
- Magnitude: This refers to the amount of energy released by an earthquake, measured on the Richter scale. Higher magnitude earthquakes release more energy and are typically more destructive.
- Epicenter: This is the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the focus, the point where the earthquake originates.
- Fault: A fracture in the Earth’s crust along which rocks on either side have moved past each other.
- Seismic Hazard: The probability of an earthquake occurring in a specific area within a given timeframe.
- Seismic Risk: The potential for damage and losses caused by an earthquake, taking into account factors like population density, infrastructure, and building codes.
Beyond the Map: The Importance of Continuous Research and Data Collection
The USGS California-Nevada Earthquake Index Map is a powerful tool, but it is only as accurate as the data it is based upon. The USGS, along with other research institutions, is constantly collecting new seismic data, improving earthquake detection and location techniques, and refining models for predicting future seismic activity. This ongoing research is essential for keeping the map updated and ensuring its continued relevance in understanding and mitigating earthquake hazards.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What is the purpose of the USGS California-Nevada Earthquake Index Map?
A: The map serves as a comprehensive resource for visualizing past earthquake activity, assessing future seismic hazards, and informing decisions related to earthquake preparedness and mitigation.
Q: How is the map updated?
A: The map is continuously updated with new earthquake data collected by the USGS and other research institutions.
Q: What is the difference between seismic hazard and seismic risk?
A: Seismic hazard refers to the probability of an earthquake occurring in a specific area, while seismic risk considers the potential for damage and losses caused by an earthquake, taking into account factors like population density, infrastructure, and building codes.
Q: Can the map predict when an earthquake will occur?
A: While the map can identify regions with a higher probability of experiencing earthquakes, it cannot predict the exact timing of an earthquake.
Q: What are some of the benefits of using the map?
A: The map provides valuable information for:
- Earthquake preparedness: Identifying areas at risk and developing effective emergency plans.
- Infrastructure design: Incorporating earthquake-resistant features in buildings and other structures.
- Land-use planning: Avoiding construction in areas with high seismic hazard.
- Public awareness: Educating the public about earthquake risks and preparedness.
Tips for Utilizing the USGS Map Effectively
- Explore the map’s features: Familiarize yourself with the map’s legend, color-coding system, and interactive features.
- Focus on specific areas: Zoom in on areas of interest to examine past earthquakes and assess seismic hazard levels.
- Consider multiple sources of information: Combine the map data with other resources, such as geological maps and fault zone information.
- Stay informed about updates: The USGS regularly updates the map with new data, so check for the latest version.
- Share the information: Spread awareness about earthquake risks and the importance of preparedness.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Understanding and Mitigating Seismic Risks
The USGS California-Nevada Earthquake Index Map is an invaluable tool for understanding the seismic landscape of these earthquake-prone regions. It provides a visual representation of past earthquakes, allowing scientists to identify patterns and assess future seismic hazards. By utilizing this map, policymakers, planners, and the public can make informed decisions related to earthquake preparedness, infrastructure design, and land-use planning. As research and data collection continue, the map will evolve, providing an even more accurate and comprehensive picture of the seismic risks facing California and Nevada. Ultimately, this map serves as a reminder of the importance of understanding and mitigating earthquake hazards for the safety and well-being of communities across these regions.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of California and Nevada: A Deep Dive into the USGS Earthquake Index Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
