10, Mar 2024
Unraveling The Significance Of The MAP NWEA Grade Equivalent Chart: A Comprehensive Guide
Unraveling the Significance of the MAP NWEA Grade Equivalent Chart: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unraveling the Significance of the MAP NWEA Grade Equivalent Chart: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Significance of the MAP NWEA Grade Equivalent Chart: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Significance of the MAP NWEA Grade Equivalent Chart: A Comprehensive Guide
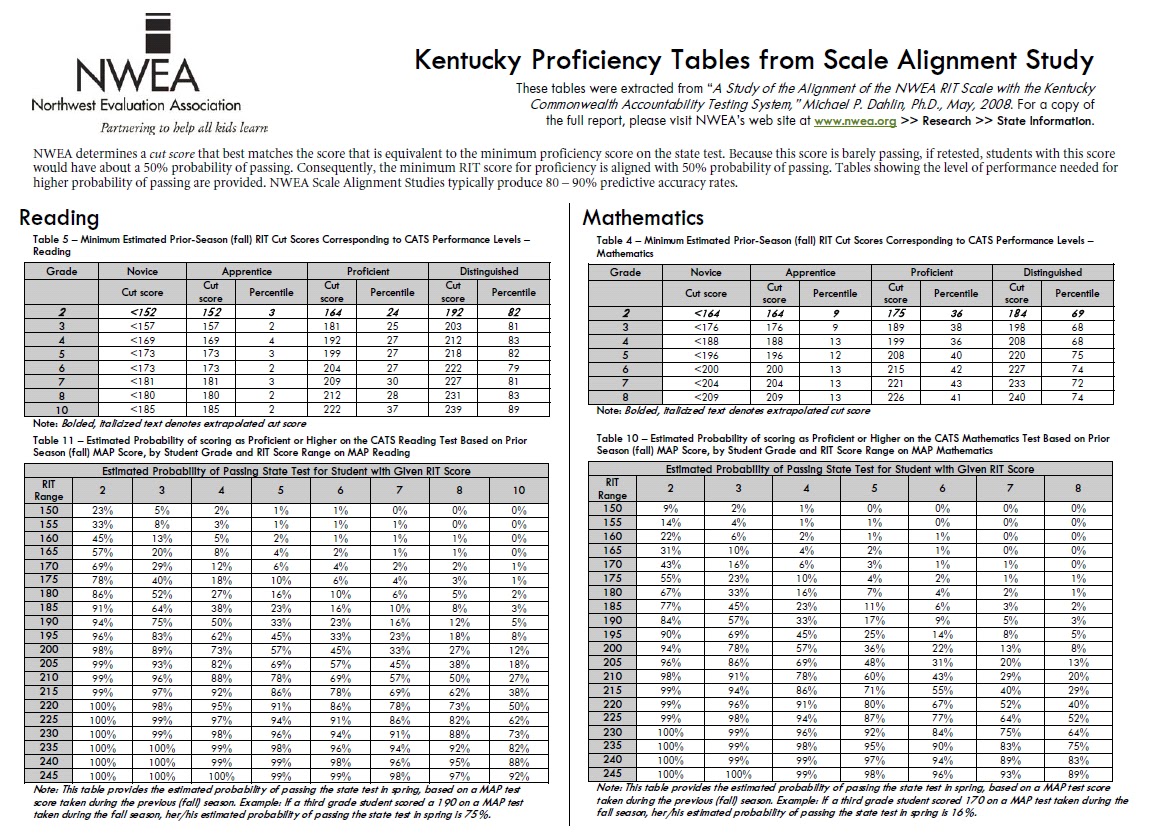
The MAP (Measures of Academic Progress) NWEA (Northwest Evaluation Association) assessment is a widely used standardized test designed to measure student growth in reading, language usage, and mathematics. A key element in interpreting MAP results is the grade equivalent score, which is often displayed on a chart alongside the student’s RIT (Rasch Unit) score. Understanding the grade equivalent chart and its nuances is crucial for educators, parents, and students alike. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to the MAP NWEA grade equivalent chart, highlighting its significance and practical applications.
What is a Grade Equivalent Score?
A grade equivalent score is a numerical representation of a student’s performance on a standardized test, expressed in terms of the grade level at which a typical student would achieve that score. For example, a grade equivalent score of 5.2 indicates that a student is performing at the level of a typical student in the second month of the fifth grade. It is important to note that grade equivalent scores are not a direct measure of a student’s grade level. They do not imply that a student is ready to advance to a higher grade or that they possess the knowledge and skills of a student in that specific grade.
The Importance of Understanding Grade Equivalent Scores
While grade equivalent scores can provide a snapshot of a student’s performance relative to their peers, it is crucial to understand their limitations. They should not be interpreted as a definitive measure of a student’s overall academic ability or potential. Several factors can influence a student’s grade equivalent score, including:
- Test content: The specific content covered in the MAP assessment may not perfectly align with the curriculum a student is currently studying.
- Individual learning pace: Students learn at different rates. A student performing above grade level may be a fast learner, while a student performing below grade level may be a slower learner, not necessarily indicative of academic struggles.
- Test anxiety: Some students may perform poorly on standardized tests due to anxiety or test-taking strategies.
Interpreting the Grade Equivalent Chart
The MAP NWEA grade equivalent chart typically displays a student’s RIT score along with the corresponding grade equivalent score. The RIT score is a scale that reflects a student’s overall academic growth, independent of grade level. The chart allows educators and parents to visualize a student’s progress over time and compare their performance to national norms.
How to Use the Grade Equivalent Chart Effectively
- Focus on growth: The most valuable aspect of the grade equivalent chart is its ability to track a student’s academic growth over time. Compare a student’s current score to their previous scores to assess their progress.
- Consider individual context: Do not solely rely on grade equivalent scores to make judgments about a student’s academic abilities. Take into account their individual learning pace, strengths, and areas for improvement.
- Use it as a tool for communication: The grade equivalent chart can be a valuable tool for communication between educators, parents, and students. It provides a common language for discussing a student’s academic performance and setting goals for future growth.
Frequently Asked Questions about the MAP NWEA Grade Equivalent Chart
Q: Can a student’s grade equivalent score change drastically from one test to the next?
A: While fluctuations in grade equivalent scores can occur, significant changes should be investigated further. Factors like test anxiety, changes in curriculum, or learning gaps can contribute to score variations.
Q: What if a student’s grade equivalent score is significantly lower than their actual grade level?
A: This could indicate a need for additional support or intervention. Educators should assess the student’s specific needs and implement appropriate strategies to address any learning gaps.
Q: Is it possible for a student to have a grade equivalent score above their actual grade level?
A: Yes, it is possible for a student to perform above their grade level. This indicates strong academic abilities and a potential for accelerated learning.
Q: How can I use the grade equivalent chart to set goals for my child’s academic progress?
A: The chart can help identify areas where your child may need additional support or opportunities for enrichment. Discuss your child’s scores with their teacher and work together to set realistic and achievable goals.
Tips for Using the Grade Equivalent Chart Effectively
- Focus on individual progress: Use the chart to track a student’s progress over time, not just their performance relative to others.
- Don’t overemphasize grade equivalents: Remember that these scores are just one piece of the puzzle. Consider other factors like effort, engagement, and classroom performance.
- Collaborate with educators: Communicate with teachers and school staff to get a comprehensive understanding of a student’s academic needs and progress.
- Use the chart as a starting point for discussion: The chart can be a valuable tool for initiating conversations about a student’s academic strengths and areas for growth.
Conclusion
The MAP NWEA grade equivalent chart is a valuable tool for educators, parents, and students. It provides a snapshot of a student’s performance relative to national norms and can be used to track their academic growth over time. However, it is crucial to understand the limitations of grade equivalent scores and to consider them within the context of a student’s individual learning pace, strengths, and needs. By using the chart effectively and engaging in open communication, educators, parents, and students can work together to support each student’s academic success.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Significance of the MAP NWEA Grade Equivalent Chart: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
