28, May 2024
Unveiling The Secrets Of The Sky: A Comprehensive Guide To Weather Radar
Unveiling the Secrets of the Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Radar
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of the Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Radar
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of the Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Radar. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets of the Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Radar
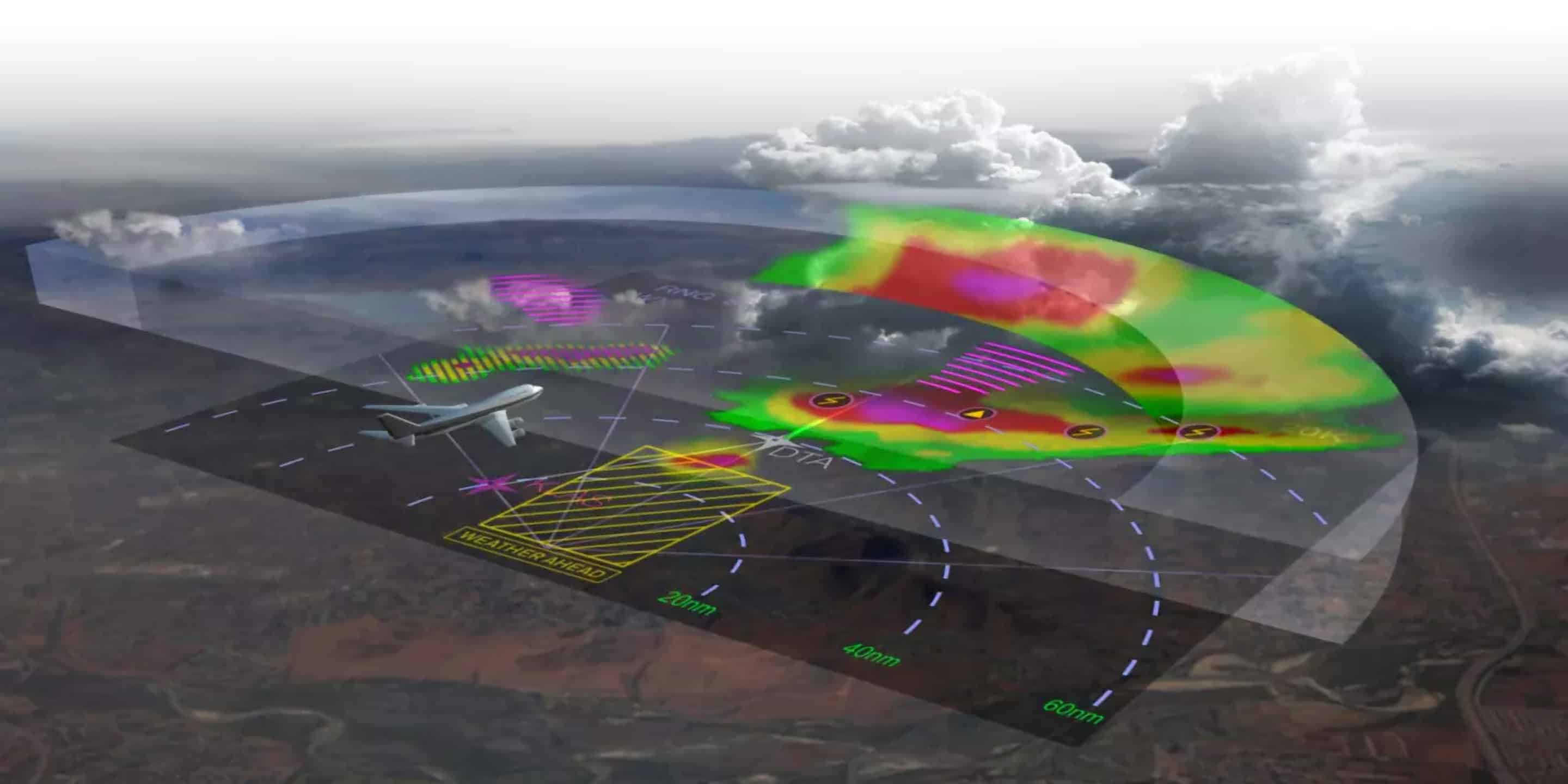
Weather radar, a cornerstone of modern meteorology, plays a crucial role in understanding and predicting the ever-changing dynamics of our atmosphere. It utilizes electromagnetic radiation to detect and analyze precipitation, providing invaluable insights into weather patterns and potential hazards. This article delves into the intricate workings of weather radar, exploring its various applications, benefits, and limitations.
The Science Behind Weather Radar
At its core, weather radar operates on the principle of Doppler effect, a phenomenon where the frequency of a wave changes depending on the relative motion of the source and the observer. In the case of weather radar, a transmitter emits pulses of electromagnetic radiation (typically in the microwave range) towards the atmosphere. These pulses interact with precipitation particles, such as raindrops, snowflakes, or hail, causing them to scatter the radiation back towards the radar antenna.
The scattered signal, known as the radar echo, is received and analyzed by the radar system. By measuring the time it takes for the signal to travel to the target and back, the radar can determine the distance to the precipitation. Furthermore, by analyzing the frequency shift of the scattered signal, the radar can determine the velocity of the precipitation particles, providing information about the movement and intensity of storms.
Types of Weather Radar
Weather radar systems are classified based on their scanning capabilities and the frequency of the electromagnetic radiation they utilize.
1. Conventional Weather Radar:
This type of radar employs a fixed beam that scans the atmosphere in a vertical plane, typically rotating 360 degrees. Conventional radar primarily provides information about precipitation intensity and location.
2. Doppler Weather Radar:
Doppler radar, a significant advancement over conventional radar, utilizes the Doppler effect to measure the velocity of precipitation particles. This additional information allows meteorologists to determine the direction and speed of storm movement, providing crucial insights into potential hazards like strong winds and tornadoes.
3. Dual-Polarization Weather Radar:
Dual-polarization radar transmits and receives electromagnetic radiation in both horizontal and vertical polarizations. This allows for a more detailed analysis of precipitation types, differentiating between rain, snow, hail, and even distinguishing between different types of snow.
4. Phased-Array Weather Radar:
Phased-array radar utilizes an array of antennas that can be electronically steered, allowing for rapid scanning of the atmosphere in multiple directions simultaneously. This technology provides a more comprehensive and real-time view of weather patterns, enhancing the accuracy of weather forecasts.
Applications of Weather Radar
Weather radar has revolutionized our understanding and prediction of weather phenomena, finding applications in various fields:
1. Short-Term Weather Forecasting:
Weather radar provides real-time information on precipitation location, intensity, and movement, enabling meteorologists to issue timely warnings for severe weather events like thunderstorms, tornadoes, and flash floods.
2. Aviation Safety:
Weather radar data is crucial for aviation safety, providing pilots with information on precipitation, turbulence, and wind shear, allowing them to navigate safely through hazardous weather conditions.
3. Hydrology and Water Management:
Radar data helps monitor rainfall patterns, providing crucial information for managing water resources, forecasting floods, and optimizing dam operations.
4. Agriculture and Crop Management:
Weather radar data assists farmers in making informed decisions about irrigation, crop protection, and harvest timing, minimizing potential losses due to adverse weather conditions.
5. Climate Monitoring and Research:
Long-term radar data analysis contributes to understanding climate trends, identifying changes in precipitation patterns, and studying the impact of climate change on weather events.
Benefits of Weather Radar
The widespread use of weather radar has brought numerous benefits:
1. Improved Weather Forecasts:
Radar data provides crucial input for weather models, enhancing the accuracy and reliability of weather forecasts, allowing for better preparedness and mitigation of potential hazards.
2. Enhanced Public Safety:
Timely warnings issued based on radar data enable communities to take appropriate precautions and evacuate areas at risk of severe weather events, saving lives and minimizing damage.
3. Efficient Resource Management:
Radar data helps optimize water resource management, preventing floods and droughts, and ensuring efficient allocation of water for agricultural and industrial needs.
4. Economic Benefits:
Accurate weather information minimizes disruptions to transportation, agriculture, and other industries, contributing to economic growth and stability.
5. Scientific Advancement:
Radar data provides valuable insights into atmospheric processes, contributing to scientific research and a deeper understanding of weather phenomena.
Limitations of Weather Radar
Despite its numerous advantages, weather radar has limitations that should be considered:
1. Ground Clutter:
Radar signals can be reflected by fixed objects on the ground, such as buildings, trees, and mountains, creating false echoes that can interfere with precipitation detection.
2. Attenuation:
Heavy precipitation can absorb radar signals, limiting the radar’s ability to detect precipitation behind heavy rain or hail.
3. Beam Width:
The radar beam has a finite width, which can cause blurring of precipitation features, especially at long distances.
4. Data Gaps:
Radar data is typically collected at discrete intervals, resulting in gaps in the data, which can affect the accuracy of weather forecasts.
5. Technological Limitations:
Weather radar technology is constantly evolving, but limitations in resolution, coverage, and data processing can still impact the accuracy of weather information.
FAQs about Weather Radar
1. How does weather radar work?
Weather radar works by emitting pulses of electromagnetic radiation, which interact with precipitation particles in the atmosphere. The reflected signal, known as the radar echo, provides information about the distance, velocity, and intensity of precipitation.
2. What types of precipitation can weather radar detect?
Weather radar can detect various types of precipitation, including rain, snow, hail, and sleet. It can also distinguish between different types of snow, such as light snow, heavy snow, and graupel.
3. How is weather radar used for forecasting?
Weather radar data is used as input for weather models, providing real-time information on precipitation location, intensity, and movement. This information helps meteorologists predict the development and movement of storms, enabling them to issue timely warnings for severe weather events.
4. What are some of the limitations of weather radar?
Weather radar has limitations such as ground clutter, attenuation, beam width, data gaps, and technological limitations. These limitations can affect the accuracy of weather information and require careful interpretation of radar data.
5. What is the future of weather radar technology?
Weather radar technology is constantly evolving, with advancements in resolution, coverage, and data processing. Future developments may include more accurate precipitation detection, improved storm tracking, and enhanced forecasting capabilities.
Tips for Understanding Weather Radar Data
1. Pay attention to the radar loop:
Observe the movement of precipitation over time to gain insights into storm development and trajectory.
2. Understand the color scale:
Different colors represent different levels of precipitation intensity, allowing you to identify areas of heavy rain or hail.
3. Interpret the Doppler velocity data:
Pay attention to the direction and speed of precipitation movement, as this can indicate the presence of strong winds or tornadoes.
4. Consider the limitations of radar data:
Be aware of the limitations of weather radar, such as ground clutter and attenuation, when interpreting radar information.
5. Consult with a meteorologist:
For a comprehensive understanding of weather radar data, seek guidance from a qualified meteorologist.
Conclusion
Weather radar has revolutionized our understanding and prediction of weather events, providing invaluable insights into the dynamics of our atmosphere. By utilizing the Doppler effect and advanced scanning techniques, weather radar enables meteorologists to monitor and forecast weather patterns with unprecedented accuracy. This information is crucial for public safety, aviation safety, resource management, and scientific advancement. While limitations exist, the continuous development of weather radar technology promises even more accurate and comprehensive weather information in the future, ensuring our safety and well-being in the face of unpredictable weather conditions.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1134692783-6044ad2065db48d696197a6e5531bc83.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of the Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Radar. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin
